Winsock2 Intro - select mode
http://www.winsocketdotnetworkprogramming.com/winsock2programming/winsock2advancediomethod5a.html
Winsock 2 I/O Methods 5 Part 2
What do we have in this chapter 5 part 2?
-
The select() Program Example
-
The Client Test Program Example
The select() Program Example
The following program example demonstrates the use of select() for server/receiver program.
Add the following source code. |
// Description:
//
// This sample illustrates how to develop a simple echo server Winsock
// application using the select() API I/O model. This sample is
// implemented as a console-style application and simply prints
// messages when connections are established and removed from the server.
// The application listens for TCP connections on port 5150 and accepts
// them as they arrive. When this application receives data from a client,
// it simply echos (this is why we call it an echo server) the data back in
// it's original form until the client closes the connection.
//
// Note: There are no command line options for this sample.
//
// Link to ws2_32.lib
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define PORT 5150
#define DATA_BUFSIZE 8192
typedef struct _SOCKET_INFORMATION {
CHAR Buffer[DATA_BUFSIZE];
WSABUF DataBuf;
SOCKET Socket;
OVERLAPPED Overlapped;
DWORD BytesSEND;
DWORD BytesRECV;
} SOCKET_INFORMATION, * LPSOCKET_INFORMATION;
// Prototypes
BOOL CreateSocketInformation(SOCKET s);
void FreeSocketInformation(DWORD Index);
// Global var
DWORD TotalSockets = 0;
LPSOCKET_INFORMATION SocketArray[FD_SETSIZE];
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
SOCKET ListenSocket;
SOCKET AcceptSocket;
SOCKADDR_IN InternetAddr;
WSADATA wsaData;
INT Ret;
FD_SET WriteSet;
FD_SET ReadSet;
DWORD i;
DWORD Total;
ULONG NonBlock;
DWORD Flags;
DWORD SendBytes;
DWORD RecvBytes;
if ((Ret = WSAStartup(0x0202,&wsaData)) != 0)
{
printf("WSAStartup() failed with error %d\n", Ret);
WSACleanup();
return 1;
}
else
printf("WSAStartup() is fine!\n");
// Prepare a socket to listen for connections
if ((ListenSocket = WSASocket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0, NULL, 0, WSA_FLAG_OVERLAPPED)) == INVALID_SOCKET)
{
printf("WSASocket() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("WSASocket() is OK!\n");
InternetAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
InternetAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
InternetAddr.sin_port = htons(PORT);
if (bind(ListenSocket, (PSOCKADDR) &InternetAddr, sizeof(InternetAddr)) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("bind() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("bind() is OK!\n");
if (listen(ListenSocket, 5))
{
printf("listen() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("listen() is OK!\n");
// Change the socket mode on the listening socket from blocking to
// non-block so the application will not block waiting for requests
NonBlock = 1;
if (ioctlsocket(ListenSocket, FIONBIO, &NonBlock) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("ioctlsocket() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("ioctlsocket() is OK!\n");
while(TRUE)
{
// Prepare the Read and Write socket sets for network I/O notification
FD_ZERO(&ReadSet);
FD_ZERO(&WriteSet);
// Always look for connection attempts
FD_SET(ListenSocket, &ReadSet);
// Set Read and Write notification for each socket based on the
// current state the buffer. If there is data remaining in the
// buffer then set the Write set otherwise the Read set
for (i = 0; i < TotalSockets; i++)
if (SocketArray[i]->BytesRECV > SocketArray[i]->BytesSEND)
FD_SET(SocketArray[i]->Socket, &WriteSet);
else
FD_SET(SocketArray[i]->Socket, &ReadSet);
if ((Total = select(0, & ReadSet, &WriteSet, NULL, NULL)) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("select() returned with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("select() is OK!\n");
// Check for arriving connections on the listening socket.
if (FD_ISSET(ListenSocket, & ReadSet))
{
Total--;
if ((AcceptSocket = accept(ListenSocket, NULL, NULL)) != INVALID_SOCKET)
{
// Set the accepted socket to non-blocking mode so the server will
// not get caught in a blocked condition on WSASends
NonBlock = 1;
if (ioctlsocket(AcceptSocket, FIONBIO, &NonBlock) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("ioctlsocket(FIONBIO) failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("ioctlsocket(FIONBIO) is OK!\n");
if (CreateSocketInformation(AcceptSocket) == FALSE)
{
printf("CreateSocketInformation(AcceptSocket) failed!\n");
return 1;
}
else
printf("CreateSocketInformation() is OK!\n");
}
else
{
if (WSAGetLastError() != WSAEWOULDBLOCK)
{
printf("accept() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("accept() is fine!\n");
}
}
// Check each socket for Read and Write notification until the number
// of sockets in Total is satisfied
for (i = 0; Total > 0 && i < TotalSockets; i++)
{
LPSOCKET_INFORMATION SocketInfo = SocketArray[i];
// If the ReadSet is marked for this socket then this means data
// is available to be read on the socket
if (FD_ISSET(SocketInfo->Socket, & ReadSet))
{
Total--;
SocketInfo->DataBuf.buf = SocketInfo->Buffer;
SocketInfo->DataBuf.len = DATA_BUFSIZE;
Flags = 0;
if (WSARecv(SocketInfo->Socket, & (SocketInfo->DataBuf), 1, &RecvBytes, &Flags, NULL, NULL) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
if (WSAGetLastError() != WSAEWOULDBLOCK)
{
printf("WSARecv() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
FreeSocketInformation(i);
}
else
printf("WSARecv() is OK!\n");
continue;
}
else
{
SocketInfo->BytesRECV = RecvBytes;
// If zero bytes are received, this indicates the peer closed the connection.
if (RecvBytes == 0)
{
FreeSocketInformation(i);
continue;
}
}
}
// If the WriteSet is marked on this socket then this means the internal
// data buffers are available for more data
if (FD_ISSET(SocketInfo->Socket, & WriteSet))
{
Total--;
SocketInfo->DataBuf.buf = SocketInfo->Buffer + SocketInfo->BytesSEND;
SocketInfo->DataBuf.len = SocketInfo->BytesRECV - SocketInfo->BytesSEND;
if (WSASend(SocketInfo->Socket, & (SocketInfo->DataBuf), 1, &SendBytes, 0, NULL, NULL) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
if (WSAGetLastError() != WSAEWOULDBLOCK)
{
printf("WSASend() failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
FreeSocketInformation(i);
}
else
printf("WSASend() is OK!\n");
continue;
}
else
{
SocketInfo->BytesSEND += SendBytes;
if (SocketInfo->BytesSEND == SocketInfo->BytesRECV)
{
SocketInfo->BytesSEND = 0;
SocketInfo->BytesRECV = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
BOOL CreateSocketInformation(SOCKET s)
{
LPSOCKET_INFORMATION SI;
printf("Accepted socket number %d\n", s);
if ((SI = (LPSOCKET_INFORMATION) GlobalAlloc(GPTR, sizeof(SOCKET_INFORMATION))) == NULL)
{
printf("GlobalAlloc() failed with error %d\n", GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
else
printf("GlobalAlloc() for SOCKET_INFORMATION is OK!\n");
// Prepare SocketInfo structure for use
SI->Socket = s;
SI->BytesSEND = 0;
SI->BytesRECV = 0;
SocketArray[TotalSockets] = SI;
TotalSockets++;
return(TRUE);
}
void FreeSocketInformation(DWORD Index)
{
LPSOCKET_INFORMATION SI = SocketArray[Index];
DWORD i;
closesocket(SI->Socket);
printf("Closing socket number %d\n", SI->Socket);
GlobalFree(SI);
// Squash the socket array
for (i = Index; i < TotalSockets; i++)
{
SocketArray[i] = SocketArray[i + 1];
}
TotalSockets--;
}
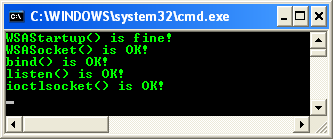
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.
---------------------------------------------------------------
The Client Test Program Example
The following program example is a client that will be used to test all the server/receiver program created in this chapter. This program uses TCP protocol.
Add the following source code.
// Description:
// This sample is the echo client. It connects to the TCP server,
// sends data, and reads data back from the server.
//
// Command Line Options:
// client [-p:x] [-s:IP] [-n:x] [-o]
// -p:x Remote port to send to
// -s:IP Server's IP address or hostname
// -n:x Number of times to send message
// -o Send messages only; don't receive
//
// Link to ws2_32.lib
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define DEFAULT_COUNT 20
#define DEFAULT_PORT 5150
#define DEFAULT_BUFFER 2048
#define DEFAULT_MESSAGE "\'A test message from client\'"
char szServer[128], // Server to connect to
szMessage[1024]; // Message to send to sever
int iPort = DEFAULT_PORT; // Port on server to connect to
DWORD dwCount = DEFAULT_COUNT; // Number of times to send message
BOOL bSendOnly = FALSE; // Send data only; don't receive
// Function: usage:
// Description: Print usage information and exit
void usage()
{
printf("Chapter5TestClient: client [-p:x] [-s:IP] [-n:x] [-o]\n\n");
printf(" -p:x Remote port to send to\n");
printf(" -s:IP Server's IP address or hostname\n");
printf(" -n:x Number of times to send message\n");
printf(" -o Send messages only; don't receive\n");
printf("\n");
}
// Function: ValidateArgs
// Description:
// Parse the command line arguments, and set some global flags
// to indicate what actions to perform
void ValidateArgs(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i;
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++)
{
if ((argv[i][0] == '-') || (argv[i][0] == '/'))
{
switch (tolower(argv[i][1]))
{
case 'p': // Remote port
if (strlen(argv[i]) > 3)
iPort = atoi(&argv[i][3]);
break;
case 's': // Server
if (strlen(argv[i]) > 3)
strcpy_s(szServer, sizeof(szServer),&argv[i][3]);
break;
case 'n': // Number of times to send message
if (strlen(argv[i]) > 3)
dwCount = atol(&argv[i][3]);
break;
case 'o': // Only send message; don't receive
bSendOnly = TRUE;
break;
default:
usage();
break;
}
}
}
}
// Function: main
// Description:
// Main thread of execution. Initialize Winsock, parse the
// command line arguments, create a socket, connect to the
// server, and then send and receive data.
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
WSADATA wsd;
SOCKET sClient;
char szBuffer[DEFAULT_BUFFER];
int ret, i;
struct sockaddr_in server;
struct hostent *host = NULL;
if(argc < 2)
{
usage();
exit(1);
}
// Parse the command line and load Winsock
ValidateArgs(argc, argv);
if (WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), & wsd) != 0)
{
printf("Failed to load Winsock library! Error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("Winsock library loaded successfully!\n");
strcpy_s(szMessage, sizeof(szMessage),DEFAULT_MESSAGE);
// Create the socket, and attempt to connect to the server
sClient = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (sClient == INVALID_SOCKET)
{
printf("socket() failed with error code %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("socket() looks fine!\n");
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(iPort);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(szServer);
// If the supplied server address wasn't in the form
// "aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd" it's a hostname, so try to resolve it
if (server.sin_addr.s_addr == INADDR_NONE)
{
host = gethostbyname(szServer);
if (host == NULL)
{
printf("Unable to resolve server %s\n", szServer);
return 1;
}
else
printf("The hostname resolved successfully!\n");
CopyMemory(&server.sin_addr, host->h_addr_list[0], host->h_length);
}
if (connect(sClient, (struct sockaddr *)&server, sizeof(server)) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("connect() failed with error code %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 1;
}
else
printf("connect() is pretty damn fine!\n");
// Send and receive data
printf("Sending and receiving data if any...\n");
for(i = 0; i < (int)dwCount; i++)
{
ret = send(sClient, szMessage, strlen(szMessage), 0);
if (ret == 0)
break;
else if (ret == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("send() failed with error code %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
break;
}
printf("send() should be fine. Send %d bytes\n", ret);
if (!bSendOnly)
{
ret = recv(sClient, szBuffer, DEFAULT_BUFFER, 0);
if (ret == 0) // Graceful close
{
printf("It is a graceful close!\n");
break;
}
else if (ret == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("recv() failed with error code %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
break;
}
szBuffer[ret] = '\0';
printf("recv() is OK. Received %d bytes: %s\n", ret, szBuffer);
}
}
if(closesocket(sClient) == 0)
printf("closesocket() is OK!\n");
else
printf("closesocket() failed with error code %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
if (WSACleanup() == 0)
printf("WSACleanup() is fine!\n");
else
printf("WSACleanup() failed with error code %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return 0;
}
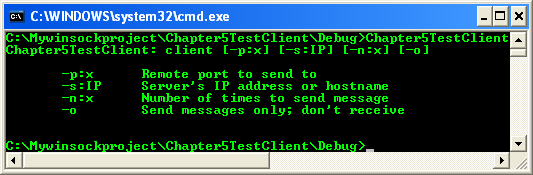
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.