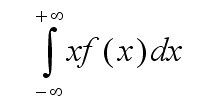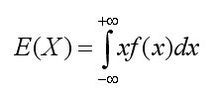uva10900 - So you want to be a 2n-aire? 概率 递推
Problem A: So you want to be a 2n-aire?
The player starts with a prize of $1, and is asked a sequence of n questions. For each question, he may- quit and keep his prize.
- answer the question. If wrong, he quits with nothing. If correct, the prize is doubled, and he continues with the next question.
Once each question is asked, the player is able to assess the probability p that he will be able to answer it. For each question, we assume that p is a random variable uniformly distributed over the range t .. 1.
Input is a number of lines, each with two numbers: an integer 1 ≤ n ≤ 30, and a real 0 ≤ t ≤ 1. Input is terminated by a line containing 0 0. This line should not be processed.
For each input n and t, print the player's expected prize, if he plays the best strategy. Output should be rounded to three fractional digits.
Sample input
1 0.5 1 0.3 2 0.6 24 0.25 0 0
Output for sample input
1.500 1.357 2.560 230.138
初始是1块钱,给你一个t,答对每道题的概率都在[t,1],可以选择答或不答,答对钱翻倍,答错一分钱都没了,选择不答就获得目前的钱数。回答者会做最优选择。
真心表示应该好好学概率论的。。哎~ 看了别人的,又把概率论书拿出来看了一下,算是明白了。。
如果用q[i]表示答对前i道题可以得到的钱数的期望(第i道题以后不确定),那么第i+1道题可以选择答或不答。如果不答就拿着2^i块钱走了,但是如果答呢?q[i+1]表示第i+1道题答对可以获得钱数的期望,设第i+1道题答对的概率为p,则答i+1题的期望就是p*q[i+1]+(1-p)*0=p*q[i+1]。如果p*q[i+1]>2^i,那么选择答题可能获得的钱比不答多,因为参加游戏的人会做最优选择,所以会选择答,反之不答。设分界点p=2^i/q[i+1],如果t>=p,一定选择答题,如果t<p,那么答对率在[t,p]之间的话选择不答,在[p,1]选择答。又因为答对率在[t,1]均匀分布,分布概率为1/(1-t),期望就是
∫t到p 2^i /(1-t) dx+∫p到1 x*q[i+1]/(1-t) dx
积分符号。。能看懂就行。。其实也可以yy,有(p-t)/(1-t)的概率不答,有(1-p)/(1-t)的概率答,答的话答对的概率是(1+p)/2。。答案也是对的,不过总感觉这样怪怪的。。
于是只要倒着递推q[i],q[0]就是最后的答案。
PS:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<algorithm>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
int N;
double a[40];
double T;
void init(){
a[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=31;i++) a[i]=a[i-1]*2;
}
double solve(){
double ret=a[N],p;
for(int i=N-1;i>=0;i--){
p=a[i]/ret;
if(p<=T) ret=ret*(1+T)/2;
else ret=(p-T)/(1-T)*a[i]+(1-p)/(1-T)*(p+1)/2*ret;
}
return ret;
}
int main(){
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
init();
while(scanf("%d%lf",&N,&T),N||T){
printf("%.3lf\n",solve());
}
return 0;
}