【一天一道LeetCode】#72. Edit Distance
一天一道LeetCode
本系列文章已全部上传至我的github,地址:ZeeCoder‘s Github
欢迎大家关注我的新浪微博,我的新浪微博
欢迎转载,转载请注明出处
(一)题目
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps ?>required to convert word1 to word2. (each operation is counted as 1 step.)
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
a) Insert a character
b) Delete a character
c) Replace a character
(二)解题
这道题一拿到就觉得需要用到动态规划,于是考虑到用递归来解决,三种情况,依次进行,可是随着递归的加深,自然而然就超时了!
/* 注:此代码没有过多测试,如有错误,请各位留言指出 */
class Solution {
public:
int minDis = 1000000;
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
vector<int> minpath(10000,10000);
getMinDis(word1,word2,0,0,minpath);
return minDis;
}
void getMinDis(string word1, string word2, int idx, int count,vector<int>& minpath)
{
if(minpath[idx] <= count) return; //为了减少递归深度,可是还是超时了
if (word1 == word2) { minDis = minDis < count ? minDis : count; return; }
//如果该位上相等则继续
if(idx < word1.size() && idx < word2.size() && word1[idx] == word2[idx]) getMinDis(word1, word2, idx + 1, count,minpath);
else {
if (idx < word1.size())//idx小于word1的时候才能删除
{
string tword1 = word1;
tword1.erase(tword1.begin() + idx);
getMinDis(tword1, word2, idx, count + 1,minpath);
}
if (idx < word2.size()) //插入话需要idx小于Word2的长度
{
string tword1 = word1;
tword1.insert(idx, 1, word2[idx]);
getMinDis(tword1, word2, idx + 1, count + 1,minpath);
}
if (idx < word1.size() && idx < word2.size())//替换则需要都小于
{
string tword1 = word1;
tword1[idx] = word2[idx];
getMinDis(tword1, word2, idx + 1, count + 1,minpath);
}
}
}
};下面,主角出现了!看到这个算法真正觉得算法的美妙了,由繁化简!
首先我们定义一个数组,dp[i][j],这个数组代表了word1的0~i转换到word2的0~j需要的最小步数。很显然,该矩阵应该初始化为:dp[0][i] = i和dp[i][0] = i,如下图(以ACE->ADEF为例):
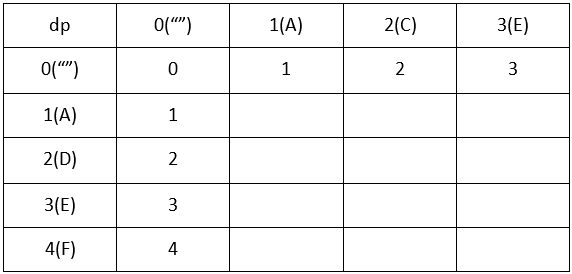
那么,下面我们来看看动态规划最重要的状态转移方程。
1、插入操作:
dp[1][1]表示从A到A,dp[0][1]表示从”“到A,那么word1插入一个A就得到A,所以dp[1][1] = dp[0][1]+1
2、删除操作:
dp[1][1]表示从A到A,dp[1][0]表示从A到””,那么word1需要删除一个A,所以dp[1][1] = dp[1][0]+1
3、替换操作:
dp[1][1]表示从A到A\,dp[0][0]表示从”“到”“,那么dp[1][1] = dp[0][0];
dp[2][2]表示从AC到AD,需要替换操作,所以dp[2][2] = dp[1][1]+1;
看到这里大概都明白了这个算法的步骤了,dp[1][1]到底等于多少呢?
答案显而易见,dp[1][1]等于三者中的最小值。
算法到最后,矩阵dp得值看下图:
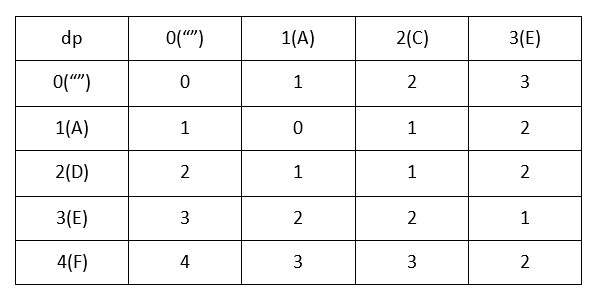
说这么多,代码见真招!
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int row = word1.length();
int col = word2.length();
//初始化
vector<vector<int>> dpath(row+1,vector<int>(col+1,0));
for(int i = 0 ; i < col+1 ; i++)/
{
dpath[0][i] = i;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < row+1 ;i++)
{
dpath[i][0] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i < row+1 ;i++)
{
for(int j = 1 ; j < col+1;j++)
{
//三者取最小
dpath[i][j] = min(dpath[i-1][j]+1,dpath[i][j-1]+1);
dpath[i][j] = min(dpath[i][j],dpath[i-1][j-1]+(word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]?0:1));
}
}
return dpath[row][col];
}
};