VS2010 C++ 学习笔记(一) 引用 函数参数默认值 函数重载 内联inline
慕课网的C++ 视频。 视频链接 链接,讲的蛮不错,搭配 《Visual C++2008入门经典(中文高清版)》,有2010版的。
学习ing,做个笔记。
1.引用
2.函数参数默认值
3.函数重载
4.内联函数 inline
/************************************************
/*bool 类型 命名空间 输入输出
/*要求:
/* 使用一函数,找出一个整形数组中最大值或最小值
/*************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h> //system("pause")的头文件
using namespace std;
int getMaxOrMin(int *arr, int arr_len, bool isMax);
int main(void)
{
cout<<" hi "<<endl;
int arr1[5] = {2,5,6,4,9};
bool isMAx = false;
cin >> isMAx;
cout << getMaxOrMin(arr1, 5, isMAx) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int getMaxOrMin(int *arr, int arr_len, bool isMax)
{
int temp = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr_len; i++)
{
if (isMax)
{
if (temp < arr[i])//get max
{
temp = arr[i];
}
}
else
{
if (temp > arr[i])//get min
{
temp = arr[i];
}
}
}
return temp;
}
1 为 Ture ,求Max, 值为9
0 为False, 求Min, 值为2
1.引用
指针类型引用 *&指针引用明 = 指针;
引用的好处,左边为C语言方式,右边为C++ 引用方式。交换两个数的值。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
//int a = 10;
int &b = NULL; //引用,没有实体。会出现引用错误.
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*
错误 1 error C2440: “初始化”: 无法从“int”转换为“int &”
e:\linbo\visual studio 2010\projects\test\test\test.cpp 9 1 test
*/
引用,没有实体。会出现引用错误.
c++中的引用与指针的区别
★ 相同点:
1. 都是地址的概念;
指针指向一块内存,它的内容是所指内存的地址;引用是某块内存的别名。
★ 区别:
1. 指针是一个实体,而引用仅是个别名;
2. 引用使用时无需解引用(*),指针需要解引用;
3. 引用只能在定义时被初始化一次,之后不可变;指针可变;引用“从一而终” ^_^
4. 引用没有 const,指针有 const,const 的指针不可变;
5. 引用不能为空,指针可以为空;
6. “sizeof 引用”得到的是所指向的变量(对象)的大小,而“sizeof 指针”得到的是指针本身(所指向的变量或对象的地址)的大小;
7. 指针和引用的自增(++)运算意义不一样;
引用的一些规则如下:
(1)引用被创建的同时必须被初始化(指针则可以在任何时候被初始化)。
(2)不能有NULL 引用,引用必须与合法的存储单元关联(指针则可以是NULL)。
(3)一旦引用被初始化,就不能改变引用的关系(指针则可以随时改变所指的对象)。
2.函数参数默认值
有默认值的参数必须在参数列表的最右端。
fun(20) 即:i = 20,j,k为默认参数
fun(20,30)即:i=20,j=30,k为默认值
fun(20,30,40)即:i=20,j=30,k=40
*****************************************************************************************************************************************
3.函数重载
相同函数的识别是依靠参数类型,参数个数,参数顺序进行识别。
*******************************************************************************************************************************************************************
4.内敛函数inline
通常3的步骤用时不长,1,2两个步骤用时较长。
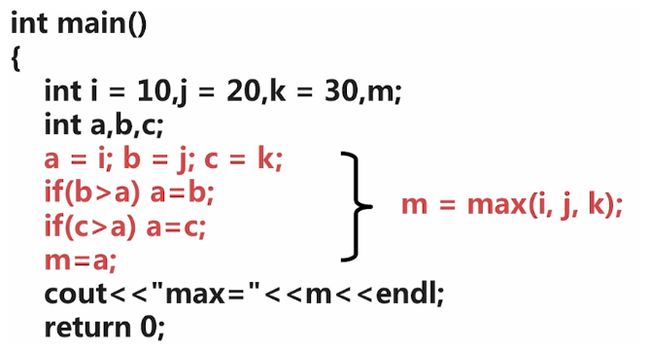
一inline函数,如下。实际上展开为下图。
上图函数实际展开。
fun(20) 即:i = 20,j,k为默认参数
fun(20,30)即:i=20,j=30,k为默认值
fun(20,30,40)即:i=20,j=30,k=40
***************************************************************************
函数参数重载
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
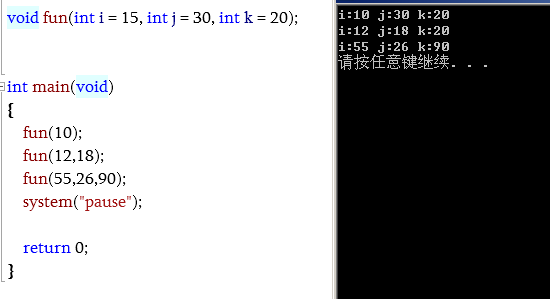
void fun(int i = 15, int j = 30, int k = 20);
int main(void)
{
fun(10);
fun(12,18);
fun(55,26,90);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void fun(int i, int j, int k)
{
cout << "i:" << i << " j:" << j << " k:" << k << endl;
}
************************************************************************
函数重载
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void fun(int i = 15, int j = 30, int k = 20);
void fun(double i , double j);
int main(void)
{
fun(1.1, 2.3); //void fun(double i , double j);
fun(12,18);//void fun(int i = 15, int j = 30, int k = 20);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void fun(int i, int j, int k)
{
cout << "i:" << i << " j:" << j << " k:" << k << endl;
}
void fun(double i , double j)
{
cout << "i:" << i << " j:" << j << endl;
}

***************************************************************************
inline
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline void fun(int i = 15, int j = 30, int k = 20);
inline void fun(double i , double j);
int main(void)
{
fun(1.1, 2.3); //void fun(double i , double j);
fun(12,18);//void fun(int i = 15, int j = 30, int k = 20);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void fun(int i, int j, int k)
{
cout << "i:" << i << " j:" << j << " k:" << k << endl;
}
void fun(double i , double j)
{
cout << "i:" << i << " j:" << j << endl;
}
*********************************************************************
单元巩固
使用函数的重载完成返回最大值的方法。
现在有一个数组,定义一个方法getMax(),利用函数的重载,分别实现:
1、随意取出数组中的两个元素,传到方法getMax()中,可以返回较大的一个元素。
2、将整个数组传到方法getMax()中,可以返回数组中最大的一个元素。
使用函数的重载完成返回最大值的方法。
现在有一个数组,定义一个方法getMax(),利用函数的重载,分别实现:
1、随意取出数组中的两个元素,传到方法getMax()中,可以返回较大的一个元素。
2、将整个数组传到方法getMax()中,可以返回数组中最大的一个元素。
/**************************************************************/
/* 单元巩固
使用函数的重载完成返回最大值的方法。
现在有一个数组,定义一个方法getMax(),利用函数的重载,分别实现:
1、随意取出数组中的两个元素,传到方法getMax()中,可以返回较大的一个元素。
2、将整个数组传到方法getMax()中,可以返回数组中最大的一个元素。
*/
/**************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int getMax(int *arr, int arr_len);
int getMax(int a, int b);
int main(void)
{
int arr[3] = { 5, 7, 3};
cout << getMax(arr, 3) << endl; //int getMax(int *arr, int arr_len);
cout << getMax(8, 7) << endl;//int getMax(int a, int b);
//system("pause");
}
int getMax(int *arr, int arr_len)
{
int max_temp = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr_len; i++)
{
if ( max_temp < arr[i])
{
max_temp = arr[i];
}
}
return max_temp;
}
int getMax(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b; //a>b 为true 执行a,为false 执行b
}

*****************************************