Value Object模式
1 理论知识
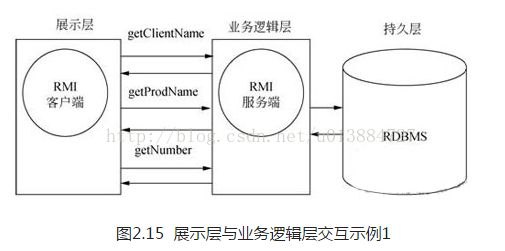
在J2EE软件开发中,通常会对系统模块进行分层。展示层主要负责数据的展示,定义数据库的UI组织模式;业务逻辑层负责具体的业务逻辑处理;持久层通常指数据库以及相关操作。在一个大型系统中,这些层次很有可能被分离,并部署在不同的服务器上。而在两个层次之间,可能通过远程过程调用RMI等方式进行通信。如图2.15所示,展示层组件作为RMI的客户端,通过中间的业务逻辑层取得一个订单(Order)的信息。假设一个订单由客户名、商品名和数量构成,那么一次交互过程可能由图2.15所描述的这样,RMI的客户端会与服务端进行3次交互,依次取得这些信息。
基于以上模式的通信方式是一种可行的解决方案,但是它存在两个严重的问题:
(1)对于获取一个订单对象而言,这个操作模式略显繁琐,且不具备较好的可维护性。
(2)前后累计进行了3次客户端与服务器的通信,性能成本较高。
为了解决这两个问题,就可以使用Value Object模式。Value Object模式提倡将一个对象的各个属性进行封装,将封装后的对象在网络中传递,从而使系统拥有更好的交互模型,并且减少网络通信数据,从而提高系统性能。使用Value Object模式对以上结构进行改良,定义对象Order,由Order对象维护客户名、商品名和数量等信息,而Order对象也就是Value Object,它必须是一个可串行化的对象。将Value Object模式应用到本例中,便可以得到如图2.16所示的结构。
在基于Value Object模式的结构中,为了获得一份订单信息,只需要进行一次网络通信,缩短了数据存取的响应时间,减少了网络数据流量。
注意:使用Value Object模式可以有效减少网络交互次数,提高远程调用方法的性能,也能使系统接口具有更好的可维护性。
2 代码实现
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface IOrderManager extends Remote{
Order getOrder(int id) throws RemoteException;
String getProductName(int id) throws RemoteException;
double getPrice(int id) throws RemoteException;
String getBrand(int id) throws RemoteException;
}
(2)RMI服务器端接口的实现:(必须继承类UnicastRemoteObject)
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
public class OrderManager extends UnicastRemoteObject implements IOrderManager {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected OrderManager() throws RemoteException {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public Order getOrder(int id) throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Order order=new Order();
order.setPrice(112.3);
order.setProductName("AIR-MAX");
return order;
}
@Override
public String getProductName(int id) throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "AIR-MAX";
}
@Override
public double getPrice(int id) throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 112.3;
}
@Override
public String getBrand(int id) throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "NIKE";
}
}(3)Value Object:(RMI传输的对象)
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Order implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3485578276309961802L;
private int id;
private String productName;
private double price;
private String brand;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getProductName() {
return productName;
}
public void setProductName(String productName) {
this.productName = productName;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}(4)业务逻辑层注册,并开启RMI服务器:
import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
public class OrderServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099); //注册RMI端口
IOrderManager manager=new OrderManager(); //RMI远程业务对象
Naming.rebind("OrderManager", manager); //绑定RMI对象
System.out.println("orderManager is ready");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}(5)客户端代码:
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.NotBoundException;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public class OrderClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
IOrderManager manager=(IOrderManager)Naming.lookup("OrderManager");
long begin=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
manager.getOrder(i);
}
System.out.println("耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-begin));
begin=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
manager.getPrice(i);
manager.getProductName(i);
manager.getBrand(i);
}
System.out.println("耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-begin));
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NotBoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
耗时:110 耗时:140注意:运行顺序,先运行Server端,注册RMI端口,绑定RMI对象,开启服务器;然后,运行client端。
由运行结果可以看出,对传输的数据进行有效的封装,可以明显提升RMI的性能。