how to use the MySQL subquery to write complex queries
ԭ�ĵ�ַ��http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-subquery/
A MySQL subquery is a query that is nested inside another query such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATEor DELETE. In addition, a MySQL subquery can be nested inside another subquery.
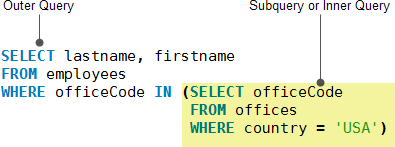
A MySQL subquery is also called an inner query while the query that contains the subquery is called an outer query.
You can use a subquery anywhere that you use an expression. In addition, you must enclose a subquery in parentheses.
1��MySQL subquery within a WHERE clause
1.1��MySQL subquery with comparison operators
You can use comparison operators e.g., =, >, <, etc., to compare a single value returned by the subquery with the expression in the WHERE clause.
SELECT customerNumber, checkNumber, amount FROM payments WHERE amount = ( SELECT MAX(amount) FROM payments );
In addition to the equality operator, you can use other comparison operators such as greater than (>), less than(<), etc.
SELECT customerNumber, checkNumber, amount FROM payments WHERE amount > ( SELECT AVG(amount) FROM payments );
1.2��MySQL subquery with IN and NOT IN operators
If a subquery returns more than one value, you can use other operators such as IN or NOT IN operator in the WHERE clause.
SELECT customername FROM customers WHERE customerNumber NOT IN( SELECT DISTINCT customernumber FROM orders );
1.3��MySQL subquery with EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
When a subquery is used with EXISTS or NOT EXISTS operator, a subquery returns a Boolean value of TRUE or FALSE. The subquery acts as an existence check.
SELECT customerName FROM customers WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT priceEach * quantityOrdered FROM orderdetails WHERE priceEach * quantityOrdered > 10000 GROUP BY orderNumber )
2��MySQL subquery in FROM clause
When you use a subquery in the FROM clause, the result set returned from a subquery is used as a table. This table is referred to as a derived table or materialized subquery.
SELECT MAX(items), MIN(items), FLOOR(AVG(items)) FROM ( SELECT orderNumber, COUNT(orderNumber) AS items FROM orderdetails GROUP BY orderNumber ) AS lineitems;
3��MySQL correlated subquery
In the previous examples, you notice that the subquery is independent. It means you can execute the subquery as a single query. However, a correlated subquery is a subquery that uses the information from the outer query. In other words, a correlated subquery depends on the outer query. A correlated subquery is evaluated once for each row in the outer query.
SELECT productname, buyprice FROM products AS p1 WHERE buyprice > ( SELECT AVG(buyprice) FROM products WHERE productline = p1.productline )