Java公司面试题集锦(四)
151、Spring中自动装配的方式有哪些?
答:
- no:不进行自动装配,手动设置Bean的依赖关系。
- byName:根据Bean的名字进行自动装配。
- byType:根据Bean的类型进行自动装配。
- constructor:类似于byType,不过是应用于构造器的参数,如果正好有一个Bean与构造器的参数类型相同则可以自动装配,否则会导致错误。
- autodetect:如果有默认的构造器,则通过constructor的方式进行自动装配,否则使用byType的方式进行自动装配。
说明:自动装配没有自定义装配方式那么精确,而且不能自动装配简单属性(基本类型、字符串等),在使用时应注意。152、Spring中如何使用注解来配置Bean?有哪些相关的注解?
答:首先需要在Spring配置文件中增加如下配置:
<context:component-scan base-package="org.example"/>然后可以用@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository注解来标注需要由Spring IoC容器进行对象托管的类。这几个注解没有本质区别,只不过@Controller通常用于控制器,@Service通常用于业务逻辑类,@Repository通常用于仓储类(例如我们的DAO实现类),普通的类用@Component来标注。
153、Spring支持的事务管理类型有哪些?你在项目中使用哪种方式?
答:Spring支持编程式事务管理和声明式事务管理。许多Spring框架的用户选择声明式事务管理,因为这种方式和应用程序的关联较少,因此更加符合轻量级容器的概念。声明式事务管理要优于编程式事务管理,尽管在灵活性方面它弱于编程式事务管理,因为编程式事务允许你通过代码控制业务。
事务分为全局事务和局部事务。全局事务由应用服务器管理,需要底层服务器JTA支持(如WebLogic、WildFly等)。局部事务和底层采用的持久化方案有关,例如使用JDBC进行持久化时,需要使用Connetion对象来操作事务;而采用Hibernate进行持久化时,需要使用Session对象来操作事务。
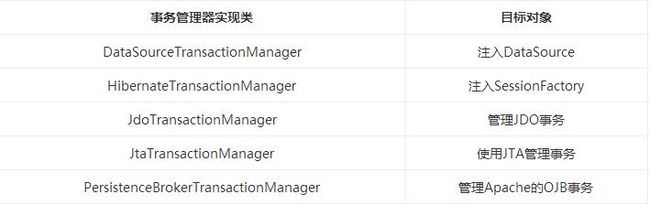
Spring提供了如下所示的事务管理器。
这些事务的父接口都是PlatformTransactionManager。Spring的事务管理机制是一种典型的策略模式,PlatformTransactionManager代表事务管理接口,该接口定义了三个方法,该接口并不知道底层如何管理事务,但是它的实现类必须提供getTransaction()方法(开启事务)、commit()方法(提交事务)、rollback()方法(回滚事务)的多态实现,这样就可以用不同的实现类代表不同的事务管理策略。使用JTA全局事务策略时,需要底层应用服务器支持,而不同的应用服务器所提供的JTA全局事务可能存在细节上的差异,因此实际配置全局事务管理器是可能需要使用JtaTransactionManager的子类,如:WebLogicJtaTransactionManager(Oracle的WebLogic服务器提供)、UowJtaTransactionManager(IBM的WebSphere服务器提供)等。
编程式事务管理如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.jackfrued"/>
<bean id="propertyConfig" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config. PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location">
<value>jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName">
<value>${db.driver}</value>
</property>
<property name="url">
<value>${db.url}</value>
</property>
<property name="username">
<value>${db.username}</value>
</property>
<property name="password">
<value>${db.password}</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
</bean>
<!-- JDBC事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource. DataSourceTransactionManager" scope="singleton">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 声明事务模板 -->
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support. TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager">
<ref bean="transactionManager" />
</property>
</bean>
</beans>package com.jackfrued.dao.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import com.jackfrued.dao.EmpDao;
import com.jackfrued.entity.Emp;
@Repository
public class EmpDaoImpl implements EmpDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public boolean save(Emp emp) {
String sql = "insert into emp values (?,?,?)";
return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, emp.getId(), emp.getName(), emp.getBirthday()) == 1;
}
}package com.jackfrued.biz.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionCallbackWithoutResult;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
import com.jackfrued.biz.EmpService;
import com.jackfrued.dao.EmpDao;
import com.jackfrued.entity.Emp;
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate txTemplate;
@Autowired
private EmpDao empDao;
@Override
public void addEmp(final Emp emp) {
txTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus txStatus) {
empDao.save(emp);
}
});
}
}声明式事务如下图所示,以Spring整合Hibernate 3为例,包括完整的DAO和业务逻辑代码。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd">
<!-- 配置由Spring IoC容器托管的对象对应的被注解的类所在的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.jackfrued" />
<!-- 配置通过自动生成代理实现AOP功能 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<!-- 配置数据库连接池 (DBCP) -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<!-- 配置驱动程序类 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<!-- 配置连接数据库的URL -->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myweb" />
<!-- 配置访问数据库的用户名 -->
<property name="username" value="root" />
<!-- 配置访问数据库的口令 -->
<property name="password" value="123456" />
<!-- 配置最大连接数 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="150" />
<!-- 配置最小空闲连接数 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="5" />
<!-- 配置最大空闲连接数 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="20" />
<!-- 配置初始连接数 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="10" />
<!-- 配置连接被泄露时是否生成日志 -->
<property name="logAbandoned" value="true" />
<!-- 配置是否删除超时连接 -->
<property name="removeAbandoned" value="true" />
<!-- 配置删除超时连接的超时门限值(以秒为单位) -->
<property name="removeAbandonedTimeout" value="120" />
<!-- 配置超时等待时间(以毫秒为单位) -->
<property name="maxWait" value="5000" />
<!-- 配置空闲连接回收器线程运行的时间间隔(以毫秒为单位) -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="300000" />
<!-- 配置连接空闲多长时间后(以毫秒为单位)被断开连接 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="60000" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置Spring提供的支持注解ORM映射的Hibernate会话工厂 -->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 通过setter注入数据源属性 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!-- 配置实体类所在的包 -->
<property name="packagesToScan" value="com.jackfrued.entity" />
<!-- 配置Hibernate的相关属性 -->
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<!-- 在项目调试完成后要删除show_sql和format_sql属性否则对性能有显著影响 -->
<value>
hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Spring提供的Hibernate事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<!-- 通过setter注入Hibernate会话工厂 -->
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置基于注解配置声明式事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven />
</beans>package com.jackfrued.dao;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryBean;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryResult;
/** * 数据访问对象接口(以对象为单位封装CRUD操作) * @author 骆昊 * * @param <E> 实体类型 * @param <K> 实体标识字段的类型 */
public interface BaseDao <E, K extends Serializable> {
/** * 新增 * @param entity 业务实体对象 * @return 增加成功返回实体对象的标识 */
public K save(E entity);
/** * 删除 * @param entity 业务实体对象 */
public void delete(E entity);
/** * 根据ID删除 * @param id 业务实体对象的标识 * @return 删除成功返回true否则返回false */
public boolean deleteById(K id);
/** * 修改 * @param entity 业务实体对象 * @return 修改成功返回true否则返回false */
public void update(E entity);
/** * 根据ID查找业务实体对象 * @param id 业务实体对象的标识 * @return 业务实体对象对象或null */
public E findById(K id);
/** * 根据ID查找业务实体对象 * @param id 业务实体对象的标识 * @param lazy 是否使用延迟加载 * @return 业务实体对象对象 */
public E findById(K id, boolean lazy);
/** * 查找所有业务实体对象 * @return 装所有业务实体对象的列表容器 */
public List<E> findAll();
/** * 分页查找业务实体对象 * @param page 页码 * @param size 页面大小 * @return 查询结果对象 */
public QueryResult<E> findByPage(int page, int size);
/** * 分页查找业务实体对象 * @param queryBean 查询条件对象 * @param page 页码 * @param size 页面大小 * @return 查询结果对象 */
public QueryResult<E> findByPage(QueryBean queryBean, int page, int size);
}package com.jackfrued.dao;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryBean;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryResult;
/** * BaseDao的缺省适配器 * @author 骆昊 * * @param <E> 实体类型 * @param <K> 实体标识字段的类型 */
public abstract class BaseDaoAdapter<E, K extends Serializable> implements BaseDao<E, K> {
@Override
public K save(E entity) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void delete(E entity) {
}
@Override
public boolean deleteById(K id) {
E entity = findById(id);
if(entity != null) {
delete(entity);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void update(E entity) {
}
@Override
public E findById(K id) {
return null;
}
@Override
public E findById(K id, boolean lazy) {
return null;
}
@Override
public List<E> findAll() {
return null;
}
@Override
public QueryResult<E> findByPage(int page, int size) {
return null;
}
@Override
public QueryResult<E> findByPage(QueryBean queryBean, int page, int size) {
return null;
}
}package com.jackfrued.dao;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import com.jackfrued.comm.HQLQueryBean;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryBean;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryResult;
/** * 基于Hibernate的BaseDao实现类 * @author 骆昊 * * @param <E> 实体类型 * @param <K> 主键类型 */
@SuppressWarnings(value = {"unchecked"})
public abstract class BaseDaoHibernateImpl<E, K extends Serializable> extends BaseDaoAdapter<E, K> {
@Autowired
protected SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private Class<?> entityClass; // 业务实体的类对象
private String entityName; // 业务实体的名字
public BaseDaoHibernateImpl() {
ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType) this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
entityClass = (Class<?>) pt.getActualTypeArguments()[0];
entityName = entityClass.getSimpleName();
}
@Override
public K save(E entity) {
return (K) sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().save(entity);
}
@Override
public void delete(E entity) {
sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().delete(entity);
}
@Override
public void update(E entity) {
sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().update(entity);
}
@Override
public E findById(K id) {
return findById(id, false);
}
@Override
public E findById(K id, boolean lazy) {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
return (E) (lazy? session.load(entityClass, id) : session.get(entityClass, id));
}
@Override
public List<E> findAll() {
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().createCriteria(entityClass).list();
}
@Override
public QueryResult<E> findByPage(int page, int size) {
return new QueryResult<E>(
findByHQLAndPage("from " + entityName , page, size),
getCountByHQL("select count(*) from " + entityName)
);
}
@Override
public QueryResult<E> findByPage(QueryBean queryBean, int page, int size) {
if(queryBean instanceof HQLQueryBean) {
HQLQueryBean hqlQueryBean = (HQLQueryBean) queryBean;
return new QueryResult<E>(
findByHQLAndPage(hqlQueryBean.getQueryString(), page, size, hqlQueryBean.getParameters()),
getCountByHQL(hqlQueryBean.getCountString(), hqlQueryBean.getParameters())
);
}
return null;
}
/** * 根据HQL和可变参数列表进行查询 * @param hql 基于HQL的查询语句 * @param params 可变参数列表 * @return 持有查询结果的列表容器或空列表容器 */
protected List<E> findByHQL(String hql, Object... params) {
return this.findByHQL(hql, getParamList(params));
}
/** * 根据HQL和参数列表进行查询 * @param hql 基于HQL的查询语句 * @param params 查询参数列表 * @return 持有查询结果的列表容器或空列表容器 */
protected List<E> findByHQL(String hql, List<Object> params) {
List<E> list = createQuery(hql, params).list();
return list != null && list.size() > 0 ? list : Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
}
/** * 根据HQL和参数列表进行分页查询 * @param hql 基于HQL的查询语句 * @page 页码 * @size 页面大小 * @param params 可变参数列表 * @return 持有查询结果的列表容器或空列表容器 */
protected List<E> findByHQLAndPage(String hql, int page, int size, Object... params) {
return this.findByHQLAndPage(hql, page, size, getParamList(params));
}
/** * 根据HQL和参数列表进行分页查询 * @param hql 基于HQL的查询语句 * @page 页码 * @size 页面大小 * @param params 查询参数列表 * @return 持有查询结果的列表容器或空列表容器 */
protected List<E> findByHQLAndPage(String hql, int page, int size, List<Object> params) {
List<E> list = createQuery(hql, params)
.setFirstResult((page - 1) * size)
.setMaxResults(size)
.list();
return list != null && list.size() > 0 ? list : Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
}
/** * 查询满足条件的记录数 * @param hql 基于HQL的查询语句 * @param params 可变参数列表 * @return 满足查询条件的总记录数 */
protected long getCountByHQL(String hql, Object... params) {
return this.getCountByHQL(hql, getParamList(params));
}
/** * 查询满足条件的记录数 * @param hql 基于HQL的查询语句 * @param params 参数列表容器 * @return 满足查询条件的总记录数 */
protected long getCountByHQL(String hql, List<Object> params) {
return (Long) createQuery(hql, params).uniqueResult();
}
// 创建Hibernate查询对象(Query)
private Query createQuery(String hql, List<Object> params) {
Query query = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().createQuery(hql);
for(int i = 0; i < params.size(); i++) {
query.setParameter(i, params.get(i));
}
return query;
}
// 将可变参数列表组装成列表容器
private List<Object> getParamList(Object... params) {
List<Object> paramList = new ArrayList<>();
if(params != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
paramList.add(params[i]);
}
}
return paramList.size() == 0? Collections.EMPTY_LIST : paramList;
}
}package com.jackfrued.comm;
import java.util.List;
/** * 查询条件的接口 * @author 骆昊 * */
public interface QueryBean {
/** * 添加排序字段 * @param fieldName 用于排序的字段 * @param asc 升序还是降序 * @return 查询条件对象自身(方便级联编程) */
public QueryBean addOrder(String fieldName, boolean asc);
/** * 添加排序字段 * @param available 是否添加此排序字段 * @param fieldName 用于排序的字段 * @param asc 升序还是降序 * @return 查询条件对象自身(方便级联编程) */
public QueryBean addOrder(boolean available, String fieldName, boolean asc);
/** * 添加查询条件 * @param condition 条件 * @param params 替换掉条件中参数占位符的参数 * @return 查询条件对象自身(方便级联编程) */
public QueryBean addCondition(String condition, Object... params);
/** * 添加查询条件 * @param available 是否需要添加此条件 * @param condition 条件 * @param params 替换掉条件中参数占位符的参数 * @return 查询条件对象自身(方便级联编程) */
public QueryBean addCondition(boolean available, String condition, Object... params);
/** * 获得查询语句 * @return 查询语句 */
public String getQueryString();
/** * 获取查询记录数的查询语句 * @return 查询记录数的查询语句 */
public String getCountString();
/** * 获得查询参数 * @return 查询参数的列表容器 */
public List<Object> getParameters();
}package com.jackfrued.comm;
import java.util.List;
/** * 查询结果 * @author 骆昊 * * @param <T> 泛型参数 */
public class QueryResult<T> {
private List<T> result; // 持有查询结果的列表容器
private long totalRecords; // 查询到的总记录数
/** * 构造器 */
public QueryResult() {
}
/** * 构造器 * @param result 持有查询结果的列表容器 * @param totalRecords 查询到的总记录数 */
public QueryResult(List<T> result, long totalRecords) {
this.result = result;
this.totalRecords = totalRecords;
}
public List<T> getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(List<T> result) {
this.result = result;
}
public long getTotalRecords() {
return totalRecords;
}
public void setTotalRecords(long totalRecords) {
this.totalRecords = totalRecords;
}
}package com.jackfrued.dao;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryResult;
import com.jackfrued.entity.Dept;
/** * 部门数据访问对象接口 * @author 骆昊 * */
public interface DeptDao extends BaseDao<Dept, Integer> {
/** * 分页查询顶级部门 * @param page 页码 * @param size 页码大小 * @return 查询结果对象 */
public QueryResult<Dept> findTopDeptByPage(int page, int size);
}package com.jackfrued.dao.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryResult;
import com.jackfrued.dao.BaseDaoHibernateImpl;
import com.jackfrued.dao.DeptDao;
import com.jackfrued.entity.Dept;
@Repository
public class DeptDaoImpl extends BaseDaoHibernateImpl<Dept, Integer> implements DeptDao {
private static final String HQL_FIND_TOP_DEPT = " from Dept as d where d.superiorDept is null ";
@Override
public QueryResult<Dept> findTopDeptByPage(int page, int size) {
List<Dept> list = findByHQLAndPage(HQL_FIND_TOP_DEPT, page, size);
long totalRecords = getCountByHQL(" select count(*) " + HQL_FIND_TOP_DEPT);
return new QueryResult<>(list, totalRecords);
}
}package com.jackfrued.comm;
import java.util.List;
/** * 分页器 * @author 骆昊 * * @param <T> 分页数据对象的类型 */
public class PageBean<T> {
private static final int DEFAUL_INIT_PAGE = 1;
private static final int DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE = 10;
private static final int DEFAULT_PAGE_COUNT = 5;
private List<T> data; // 分页数据
private PageRange pageRange; // 页码范围
private int totalPage; // 总页数
private int size; // 页面大小
private int currentPage; // 当前页码
private int pageCount; // 页码数量
/** * 构造器 * @param currentPage 当前页码 * @param size 页码大小 * @param pageCount 页码数量 */
public PageBean(int currentPage, int size, int pageCount) {
this.currentPage = currentPage > 0 ? currentPage : 1;
this.size = size > 0 ? size : DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
this.pageCount = pageCount > 0 ? size : DEFAULT_PAGE_COUNT;
}
/** * 构造器 * @param currentPage 当前页码 * @param size 页码大小 */
public PageBean(int currentPage, int size) {
this(currentPage, size, DEFAULT_PAGE_COUNT);
}
/** * 构造器 * @param currentPage 当前页码 */
public PageBean(int currentPage) {
this(currentPage, DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE, DEFAULT_PAGE_COUNT);
}
/** * 构造器 */
public PageBean() {
this(DEFAUL_INIT_PAGE, DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE, DEFAULT_PAGE_COUNT);
}
public List<T> getData() {
return data;
}
public int getStartPage() {
return pageRange != null ? pageRange.getStartPage() : 1;
}
public int getEndPage() {
return pageRange != null ? pageRange.getEndPage() : 1;
}
public long getTotalPage() {
return totalPage;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getCurrentPage() {
return currentPage;
}
/** * 将查询结果转换为分页数据 * @param queryResult 查询结果对象 */
public void transferQueryResult(QueryResult<T> queryResult) {
long totalRecords = queryResult.getTotalRecords();
data = queryResult.getResult();
totalPage = (int) ((totalRecords + size - 1) / size);
totalPage = totalPage >= 0 ? totalPage : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
this.pageRange = new PageRange(pageCount, currentPage, totalPage);
}
}package com.jackfrued.comm;
/** * 页码范围 * @author 骆昊 * */
public class PageRange {
private int startPage; // 起始页码
private int endPage; // 终止页码
/** * 构造器 * @param pageCount 总共显示几个页码 * @param currentPage 当前页码 * @param totalPage 总页数 */
public PageRange(int pageCount, int currentPage, int totalPage) {
startPage = currentPage - (pageCount - 1) / 2;
endPage = currentPage + pageCount / 2;
if(startPage < 1) {
startPage = 1;
endPage = totalPage > pageCount ? pageCount : totalPage;
}
if (endPage > totalPage) {
endPage = totalPage;
startPage = (endPage - pageCount > 0) ? endPage - pageCount + 1 : 1;
}
}
/** * 获得起始页页码 * @return 起始页页码 */
public int getStartPage() {
return startPage;
}
/** * 获得终止页页码 * @return 终止页页码 */
public int getEndPage() {
return endPage;
}
}package com.jackfrued.biz;
import com.jackfrued.comm.PageBean;
import com.jackfrued.entity.Dept;
/** * 部门业务逻辑接口 * @author 骆昊 * */
public interface DeptService {
/** * 创建新的部门 * @param department 部门对象 * @return 创建成功返回true否则返回false */
public boolean createNewDepartment(Dept department);
/** * 删除指定部门 * @param id 要删除的部门的编号 * @return 删除成功返回true否则返回false */
public boolean deleteDepartment(Integer id);
/** * 分页获取顶级部门 * @param page 页码 * @param size 页码大小 * @return 部门对象的分页器对象 */
public PageBean<Dept> getTopDeptByPage(int page, int size);
}package com.jackfrued.biz.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.jackfrued.biz.DeptService;
import com.jackfrued.comm.PageBean;
import com.jackfrued.comm.QueryResult;
import com.jackfrued.dao.DeptDao;
import com.jackfrued.entity.Dept;
@Service
@Transactional // 声明式事务的注解
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptDao deptDao;
@Override
public boolean createNewDepartment(Dept department) {
return deptDao.save(department) != null;
}
@Override
public boolean deleteDepartment(Integer id) {
return deptDao.deleteById(id);
}
@Override
public PageBean<Dept> getTopDeptByPage(int page, int size) {
QueryResult<Dept> queryResult = deptDao.findTopDeptByPage(page, size);
PageBean<Dept> pageBean = new PageBean<>(page, size);
pageBean.transferQueryResult(queryResult);
return pageBean;
}
}154、如何在Web项目中配置Spring的IoC容器?
答:如果需要在Web项目中使用Spring的IoC容器,可以在Web项目配置文件web.xml中做出如下配置:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>155、如何在Web项目中配置Spring MVC?
答:要使用Spring MVC需要在Web项目配置文件中配置其前端控制器DispatcherServlet,如下所示:
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>说明:上面的配置中使用了*.html的后缀映射,这样做一方面不能够通过URL推断采用了何种服务器端的技术,另一方面可以欺骗搜索引擎,因为搜索引擎不会搜索动态页面,这种做法称为伪静态化。156、Spring MVC的工作原理是怎样的?
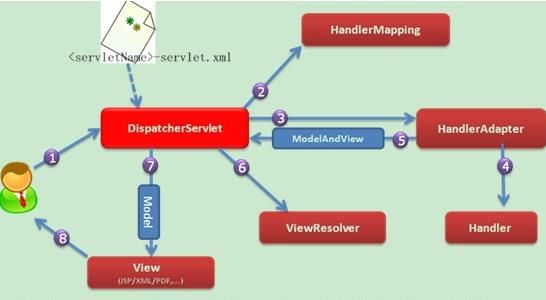
答:Spring MVC的工作原理如下图所示:
① 客户端的所有请求都交给前端控制器DispatcherServlet来处理,它会负责调用系统的其他模块来真正处理用户的请求。
② DispatcherServlet收到请求后,将根据请求的信息(包括URL、HTTP协议方法、请求头、请求参数、Cookie等)以及HandlerMapping的配置找到处理该请求的Handler(任何一个对象都可以作为请求的Handler)。
③在这个地方Spring会通过HandlerAdapter对该处理器进行封装。
④ HandlerAdapter是一个适配器,它用统一的接口对各种Handler中的方法进行调用。
⑤ Handler完成对用户请求的处理后,会返回一个ModelAndView对象给DispatcherServlet,ModelAndView顾名思义,包含了数据模型以及相应的视图的信息。
⑥ ModelAndView的视图是逻辑视图,DispatcherServlet还要借助ViewResolver完成从逻辑视图到真实视图对象的解析工作。
⑦ 当得到真正的视图对象后,DispatcherServlet会利用视图对象对模型数据进行渲染。
⑧ 客户端得到响应,可能是一个普通的HTML页面,也可以是XML或JSON字符串,还可以是一张图片或者一个PDF文件。
157、如何在Spring IoC容器中配置数据源?
答:
DBCP配置:
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>C3P0配置:
<bean id="dataSource"
class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>提示: DBCP的详细配置在第153题中已经完整的展示过了。158、如何配置配置事务增强?
答:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional -->
<bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/>
<!-- the transactional advice -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<!-- the transactional semantics... -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- all methods starting with 'get' are read-only -->
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<!-- other methods use the default transaction settings (see below) -->
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- ensure that the above transactional advice runs for any execution of an operation defined by the FooService interface -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="fooServiceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.FooService.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="fooServiceOperation"/>
</aop:config>
<!-- don't forget the DataSource -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl"/>
<property name="username" value="scott"/>
<property name="password" value="tiger"/>
</bean>
<!-- similarly, don't forget the PlatformTransactionManager -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- other <bean/> definitions here -->
</beans>159、选择使用Spring框架的原因(Spring框架为企业级开发带来的好处有哪些)?
答:可以从以下几个方面作答:
- 非侵入式:支持基于POJO的编程模式,不强制性的要求实现Spring框架中的接口或继承Spring框架中的类。
- IoC容器:IoC容器帮助应用程序管理对象以及对象之间的依赖关系,对象之间的依赖关系如果发生了改变只需要修改配置文件而不是修改代码,因为代码的修改可能意味着项目的重新构建和完整的回归测试。有了IoC容器,程序员再也不需要自己编写工厂、单例,这一点特别符合Spring的精神”不要重复的发明轮子”。
- AOP(面向切面编程):将所有的横切关注功能封装到切面(aspect)中,通过配置的方式将横切关注功能动态添加到目标代码上,进一步实现了业务逻辑和系统服务之间的分离。另一方面,有了AOP程序员可以省去很多自己写代理类的工作。
- MVC:Spring的MVC框架是非常优秀的,从各个方面都可以甩Struts 2几条街,为Web表示层提供了更好的解决方案。
- 事务管理:Spring以宽广的胸怀接纳多种持久层技术,并且为其提供了声明式的事务管理,在不需要任何一行代码的情况下就能够完成事务管理。
- 其他:选择Spring框架的原因还远不止于此,Spring为Java企业级开发提供了一站式选择,你可以在需要的时候使用它的部分和全部,更重要的是,你甚至可以在感觉不到Spring存在的情况下,在你的项目中使用Spring提供的各种优秀的功能。
160、Spring IoC容器配置Bean的方式?
答:
- 基于XML文件进行配置。
- 基于注解进行配置。
- 基于Java程序进行配置(Spring 3+)
package com.jackfrued.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
@Autowired
private Car car;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
}package com.jackfrued.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Car {
private String brand;
private int maxSpeed;
public Car(String brand, int maxSpeed) {
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed=" + maxSpeed + "]";
}
}package com.jackfrued.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.jackfrued.bean.Car;
import com.jackfrued.bean.Person;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Car car() {
return new Car("Benz", 320);
}
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person("骆昊", 34);
}
}package com.jackfrued.test;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.jackfrued.bean.Person;
import com.jackfrued.config.AppConfig;
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TWR (Java 7+)
try(ConfigurableApplicationContext factory = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class)) {
Person person = factory.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
}161、阐述Spring框架中Bean的生命周期?
答:
① Spring IoC容器找到关于Bean的定义并实例化该Bean。
② Spring IoC容器对Bean进行依赖注入。
③ 如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,则将该Bean的id传给setBeanName方法。
④ 如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,则将BeanFactory对象传给setBeanFactory方法。
⑤ 如果Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,则调用其postProcessBeforeInitialization方法。
⑥ 如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,则调用其afterPropertySet方法。
⑦ 如果有和Bean关联的BeanPostProcessors对象,则这些对象的postProcessAfterInitialization方法被调用。
⑧ 当销毁Bean实例时,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,则调用其destroy方法。
162、依赖注入时如何注入集合属性?
答:可以在定义Bean属性时,通过 / / / 分别为其注入列表、集合、映射和键值都是字符串的映射属性。
163、Spring中的自动装配有哪些限制?
答:
- 如果使用了构造器注入或者setter注入,那么将覆盖自动装配的依赖关系。
- 基本数据类型的值、字符串字面量、类字面量无法使用自动装配来注入。
- 优先考虑使用显式的装配来进行更精确的依赖注入而不是使用自动装配。
164、在Web项目中如何获得Spring的IoC容器?
答:
WebApplicationContext ctx = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);- 大型网站在架构上应当考虑哪些问题?
答:
- 分层:分层是处理任何复杂系统最常见的手段之一,将系统横向切分成若干个层面,每个层面只承担单一的职责,然后通过下层为上层提供的基础设施和服务以及上层对下层的调用来形成一个完整的复杂的系统。计算机网络的开放系统互联参考模型(OSI/RM)和Internet的TCP/IP模型都是分层结构,大型网站的软件系统也可以使用分层的理念将其分为持久层(提供数据存储和访问服务)、业务层(处理业务逻辑,系统中最核心的部分)和表示层(系统交互、视图展示)。需要指出的是:(1)分层是逻辑上的划分,在物理上可以位于同一设备上也可以在不同的设备上部署不同的功能模块,这样可以使用更多的计算资源来应对用户的并发访问;(2)层与层之间应当有清晰的边界,这样分层才有意义,才更利于软件的开发和维护。
- 分割:分割是对软件的纵向切分。我们可以将大型网站的不同功能和服务分割开,形成高内聚低耦合的功能模块(单元)。在设计初期可以做一个粗粒度的分割,将网站分割为若干个功能模块,后期还可以进一步对每个模块进行细粒度的分割,这样一方面有助于软件的开发和维护,另一方面有助于分布式的部署,提供网站的并发处理能力和功能的扩展。
- 分布式:除了上面提到的内容,网站的静态资源(JavaScript、CSS、图片等)也可以采用独立分布式部署并采用独立的域名,这样可以减轻应用服务器的负载压力,也使得浏览器对资源的加载更快。数据的存取也应该是分布式的,传统的商业级关系型数据库产品基本上都支持分布式部署,而新生的NoSQL产品几乎都是分布式的。当然,网站后台的业务处理也要使用分布式技术,例如查询索引的构建、数据分析等,这些业务计算规模庞大,可以使用Hadoop以及MapReduce分布式计算框架来处理。
- 集群:集群使得有更多的服务器提供相同的服务,可以更好的提供对并发的支持。
- 缓存:所谓缓存就是用空间换取时间的技术,将数据尽可能放在距离计算最近的位置。使用缓存是网站优化的第一定律。我们通常说的CDN、反向代理、热点数据都是对缓存技术的使用。
- 异步:异步是实现软件实体之间解耦合的又一重要手段。异步架构是典型的生产者消费者模式,二者之间没有直接的调用关系,只要保持数据结构不变,彼此功能实现可以随意变化而不互相影响,这对网站的扩展非常有利。使用异步处理还可以提高系统可用性,加快网站的响应速度(用Ajax加载数据就是一种异步技术),同时还可以起到削峰作用(应对瞬时高并发)。";能推迟处理的都要推迟处理”是网站优化的第二定律,而异步是践行网站优化第二定律的重要手段。
- 冗余:各种服务器都要提供相应的冗余服务器以便在某台或某些服务器宕机时还能保证网站可以正常工作,同时也提供了灾难恢复的可能性。冗余是网站高可用性的重要保证。
166、你用过的网站前端优化的技术有哪些?
答:
① 浏览器访问优化:
- 减少HTTP请求数量:合并CSS、合并JavaScript、合并图片(CSS Sprite)
- 使用浏览器缓存:通过设置HTTP响应头中的Cache-Control和Expires属性,将CSS、JavaScript、图片等在浏览器中缓存,当这些静态资源需要更新时,可以更新HTML文件中的引用来让浏览器重新请求新的资源
- 启用压缩
- CSS前置,JavaScript后置
- 减少Cookie传输
② CDN加速:CDN(Content Distribute Network)的本质仍然是缓存,将数据缓存在离用户最近的地方,CDN通常部署在网络运营商的机房,不仅可以提升响应速度,还可以减少应用服务器的压力。当然,CDN缓存的通常都是静态资源。
③ 反向代理:反向代理相当于应用服务器的一个门面,可以保护网站的安全性,也可以实现负载均衡的功能,当然最重要的是它缓存了用户访问的热点资源,可以直接从反向代理将某些内容返回给用户浏览器。
167、你使用过的应用服务器优化技术有哪些?
答:
① 分布式缓存:缓存的本质就是内存中的哈希表,如果设计一个优质的哈希函数,那么理论上哈希表读写的渐近时间复杂度为O(1)。缓存主要用来存放那些读写比很高、变化很少的数据,这样应用程序读取数据时先到缓存中读取,如果没有或者数据已经失效再去访问数据库或文件系统,并根据拟定的规则将数据写入缓存。对网站数据的访问也符合二八定律(Pareto分布,幂律分布),即80%的访问都集中在20%的数据上,如果能够将这20%的数据缓存起来,那么系统的性能将得到显著的改善。当然,使用缓存需要解决以下几个问题:
- 频繁修改的数据;
- 数据不一致与脏读;
- 缓存雪崩(可以采用分布式缓存服务器集群加以解决,memcached是广泛采用的解决方案);
- 缓存预热;
- 缓存穿透(恶意持续请求不存在的数据)。
② 异步操作:可以使用消息队列将调用异步化,通过异步处理将短时间高并发产生的事件消息存储在消息队列中,从而起到削峰作用。电商网站在进行促销活动时,可以将用户的订单请求存入消息队列,这样可以抵御大量的并发订单请求对系统和数据库的冲击。目前,绝大多数的电商网站即便不进行促销活动,订单系统都采用了消息队列来处理。
③ 使用集群。
④ 代码优化:
- 多线程:基于Java的Web开发基本上都通过多线程的方式响应用户的并发请求,使用多线程技术在编程上要解决线程安全问题,主要可以考虑以下几个方面:A. 将对象设计为无状态对象(这和面向对象的编程观点是矛盾的,在面向对象的世界中被视为不良设计),这样就不会存在并发访问时对象状态不一致的问题。B. 在方法内部创建对象,这样对象由进入方法的线程创建,不会出现多个线程访问同一对象的问题。使用ThreadLocal将对象与线程绑定也是很好的做法,这一点在前面已经探讨过了。C. 对资源进行并发访问时应当使用合理的锁机制。
- 非阻塞I/O: 使用单线程和非阻塞I/O是目前公认的比多线程的方式更能充分发挥服务器性能的应用模式,基于Node.js构建的服务器就采用了这样的方式。Java在JDK 1.4中就引入了NIO(Non-blocking I/O),在Servlet 3规范中又引入了异步Servlet的概念,这些都为在服务器端采用非阻塞I/O提供了必要的基础。
- 资源复用:资源复用主要有两种方式,一是单例,二是对象池,我们使用的数据库连接池、线程池都是对象池化技术,这是典型的用空间换取时间的策略,另一方面也实现对资源的复用,从而避免了不必要的创建和释放资源所带来的开销。
168、什么是XSS攻击?什么是SQL注入攻击?什么是CSRF攻击?
答:
- XSS(Cross Site Script,跨站脚本攻击)是向网页中注入恶意脚本在用户浏览网页时在用户浏览器中执行恶意脚本的攻击方式。跨站脚本攻击分有两种形式:反射型攻击(诱使用户点击一个嵌入恶意脚本的链接以达到攻击的目标,目前有很多攻击者利用论坛、微博发布含有恶意脚本的URL就属于这种方式)和持久型攻击(将恶意脚本提交到被攻击网站的数据库中,用户浏览网页时,恶意脚本从数据库中被加载到页面执行,QQ邮箱的早期版本就曾经被利用作为持久型跨站脚本攻击的平台)。XSS虽然不是什么新鲜玩意,但是攻击的手法却不断翻新,防范XSS主要有两方面:消毒(对危险字符进行转义)和HttpOnly(防范XSS攻击者窃取Cookie数据)。
- SQL注入攻击是注入攻击最常见的形式(此外还有OS注入攻击(Struts 2的高危漏洞就是通过OGNL实施OS注入攻击导致的)),当服务器使用请求参数构造SQL语句时,恶意的SQL被嵌入到SQL中交给数据库执行。SQL注入攻击需要攻击者对数据库结构有所了解才能进行,攻击者想要获得表结构有多种方式:(1)如果使用开源系统搭建网站,数据库结构也是公开的(目前有很多现成的系统可以直接搭建论坛,电商网站,虽然方便快捷但是风险是必须要认真评估的);(2)错误回显(如果将服务器的错误信息直接显示在页面上,攻击者可以通过非法参数引发页面错误从而通过错误信息了解数据库结构,Web应用应当设置友好的错误页,一方面符合最小惊讶原则,一方面屏蔽掉可能给系统带来危险的错误回显信息);(3)盲注。防范SQL注入攻击也可以采用消毒的方式,通过正则表达式对请求参数进行验证,此外,参数绑定也是很好的手段,这样恶意的SQL会被当做SQL的参数而不是命令被执行,JDBC中的PreparedStatement就是支持参数绑定的语句对象,从性能和安全性上都明显优于Statement。
- CSRF攻击(Cross Site Request Forgery,跨站请求伪造)是攻击者通过跨站请求,以合法的用户身份进行非法操作(如转账或发帖等)。CSRF的原理是利用浏览器的Cookie或服务器的Session,盗取用户身份,其原理如下图所示。防范CSRF的主要手段是识别请求者的身份,主要有以下几种方式:(1)在表单中添加令牌(token);(2)验证码;(3)检查请求头中的Referer(前面提到防图片盗链接也是用的这种方式)。令牌和验证都具有一次消费性的特征,因此在原理上一致的,但是验证码是一种糟糕的用户体验,不是必要的情况下不要轻易使用验证码,目前很多网站的做法是如果在短时间内多次提交一个表单未获得成功后才要求提供验证码,这样会获得较好的用户体验。
补充:防火墙的架设是Web安全的重要保障,ModSecurity是开源的Web防火墙中的佼佼者。企业级防火墙的架设应当有两级防火墙,Web服务器和部分应用服务器可以架设在两级防火墙之间的DMZ,而数据和资源服务器应当架设在第二级防火墙之后。- 什么是领域模型(domain model)?贫血模型(anaemic domain model)和充血模型(rich domain model)有什么区别?
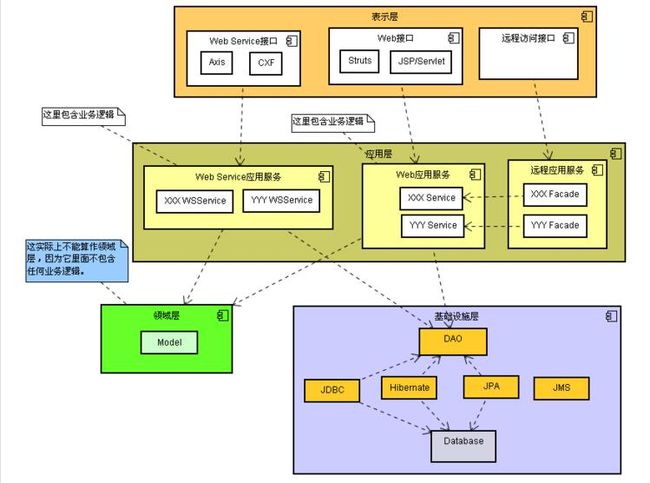
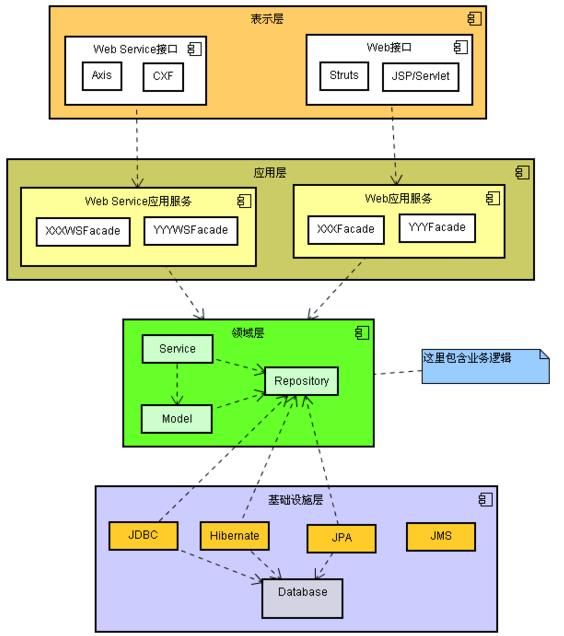
答:领域模型是领域内的概念类或现实世界中对象的可视化表示,又称为概念模型或分析对象模型,它专注于分析问题领域本身,发掘重要的业务领域概念,并建立业务领域概念之间的关系。贫血模型是指使用的领域对象中只有setter和getter方法(POJO),所有的业务逻辑都不包含在领域对象中而是放在业务逻辑层。有人将我们这里说的贫血模型进一步划分成失血模型(领域对象完全没有业务逻辑)和贫血模型(领域对象有少量的业务逻辑),我们这里就不对此加以区分了。充血模型将大多数业务逻辑和持久化放在领域对象中,业务逻辑(业务门面)只是完成对业务逻辑的封装、事务和权限等的处理。下面两张图分别展示了贫血模型和充血模型的分层架构。
贫血模型下组织领域逻辑通常使用事务脚本模式,让每个过程对应用户可能要做的一个动作,每个动作由一个过程来驱动。也就是说在设计业务逻辑接口的时候,每个方法对应着用户的一个操作,这种模式有以下几个有点:
- 它是一个大多数开发者都能够理解的简单过程模型(适合国内的绝大多数开发者)。
- 它能够与一个使用行数据入口或表数据入口的简单数据访问层很好的协作。
- 事务边界的显而易见,一个事务开始于脚本的开始,终止于脚本的结束,很容易通过代理(或切面)实现声明式事务。
然而,事务脚本模式的缺点也是很多的,随着领域逻辑复杂性的增加,系统的复杂性将迅速增加,程序结构将变得极度混乱。开源中国社区上有一篇很好的译文《贫血领域模型是如何导致糟糕的软件产生》对这个问题做了比较细致的阐述。
- 谈一谈测试驱动开发(TDD)的好处以及你的理解。
答:TDD是指在编写真正的功能实现代码之前先写测试代码,然后根据需要重构实现代码。在JUnit的作者Kent Beck的大作《测试驱动开发:实战与模式解析》(Test-Driven Development: by Example)一书中有这么一段内容:“消除恐惧和不确定性是编写测试驱动代码的重要原因”。因为编写代码时的恐惧会让你小心试探,让你回避沟通,让你羞于得到反馈,让你变得焦躁不安,而TDD是消除恐惧、让Java开发者更加自信更加乐于沟通的重要手段。TDD会带来的好处可能不会马上呈现,但是你在某个时候一定会发现,这些好处包括:
- 更清晰的代码 — 只写需要的代码
- 更好的设计
- 更出色的灵活性 — 鼓励程序员面向接口编程
- 更快速的反馈 — 不会到系统上线时才知道bug的存在
补充:敏捷软件开发的概念已经有很多年了,而且也部分的改变了软件开发这个行业,TDD也是敏捷开发所倡导的。TDD可以在多个层级上应用,包括单元测试(测试一个类中的代码)、集成测试(测试类之间的交互)、系统测试(测试运行的系统)和系统集成测试(测试运行的系统包括使用的第三方组件)。TDD的实施步骤是:红(失败测试)- 绿(通过测试) - 重构。关于实施TDD的详细步骤请参考另一篇文章《测试驱动开发之初窥门径》。
在使用TDD开发时,经常会遇到需要被测对象需要依赖其他子系统的情况,但是你希望将测试代码跟依赖项隔离,以保证测试代码仅仅针对当前被测对象或方法展开,这时候你需要的是测试替身。测试替身可以分为四类:
- 虚设替身:只传递但是不会使用到的对象,一般用于填充方法的参数列表
- 存根替身:总是返回相同的预设响应,其中可能包括一些虚设状态
- 伪装替身:可以取代真实版本的可用版本(比真实版本还是会差很多)
- 模拟替身:可以表示一系列期望值的对象,并且可以提供预设响应
Java世界中实现模拟替身的第三方工具非常多,包括EasyMock、Mockito、jMock等。