Java开发基础
Integer
Integer i = 100;
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(100);
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
Integer i = 100;
Integer j = 100;
System.out.println(i == j);
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
- Integer非线程安全,例如i + +,i - -,多线程访问无法保证一致性。
Integer i = new Integer(0);
public void test() {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
i++;
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * j);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
i--;
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * j);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
});
t2.start();
}
- java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger:一个提供原子操作的Integer的类。
- 内部通过volatile实现多线程可见性。使用原生Unsafe类实现同步修改。unsafe.compareAndSwapInt:比较obj的offset处内存位置中的值和期望的值,如果相同则更新,并返回TRUE。
public final int get();
public final int getAndSet(int newValue);
public final int getAndIncrement();
public final int getAndDecrement();
public final int getAndAdd(int delta);
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void test() {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
i.getAndIncrement();
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * j);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
i.getAndDecrement();
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * j);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
});
t2.start();
}
- 当我们使用VO或Form封装前端传入的参数时,数值型参数我们是定义成int还是Integer?
String
- 一个字符串常量只有一个拷贝,不可变性,内容存放常量池。
String str0 = "123";
String str1 = "123";
String str2 = "12" + "3";
static final String str = "3";
String str3 = "12" + str;
System.out.println(str0 == str1);
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
String str3 = new String("123");
String str4 = new String("123");
System.out.println(str3 == str4);
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str);
public boolean startsWith(String prefix);
public boolean matches(String regex);
public static String format(String format, Object... args);
public String[] split(String regex);
- StringBuffer、StringBuilder
StringBuilder线程不安全,StringBuffer线程安全(synchronized)。
定义常量时,使用String。速度快。
- StringUtils(Commons, Spring)
>>> org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils
public static boolean isEmpty(String str);
public static boolean isBlank(String str);
public static boolean contains(String str, String searchStr);
public static String join(Object[] array, String separator);
StringUtils.join(["a", "b", "c"], "-") = "a-b-c"
public static String rightPad(String str, int size, char padChar);
StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 5, 'z') = "batzz"
public static boolean isAlpha(String str);
public static boolean isAlphanumeric(String str);
public static String abbreviate(String str, int maxWidth);
StringUtils.abbreviate("abcdefg", 6) = "abc..."
>>> org.springframework.util.StringUtils
public static String getFilename(String path);
public static String getFilenameExtension(String path);
>>> org.apache.commons.lang.builder.ToStringBuilder
public static String reflectionToString(Object object, ToStringStyle style);
Array
String[] arr1 = new String[6];
String[] arr2 = {"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"};
String[] arr3 = new String[]{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"};
>>> java.util.Arrays
public static void sort(Object[] a);
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key);
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a);
public static String toString(Object[] a);
>>> org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils
public static void reverse(Object array[]);
public static Object[] addAll(Object array1[], Object array2[]);
public static boolean contains(Object array[], Object objectToFind);
public static int indexOf(Object array[], Object objectToFind);
public static Object[] remove(Object array[], int index);
List
List<Object> lst = new ArrayList<Object>();
- ArrayList增长机制,源码。
- 特性:插入慢(当数据到一定量时),遍历速度快。
private transient Object[] elementData;
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1);
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
public E get(int index) {
RangeCheck(index);
return (E) elementData[index];
}
- LinkedList源码。
- 特性:插入速度快,遍历速度慢。
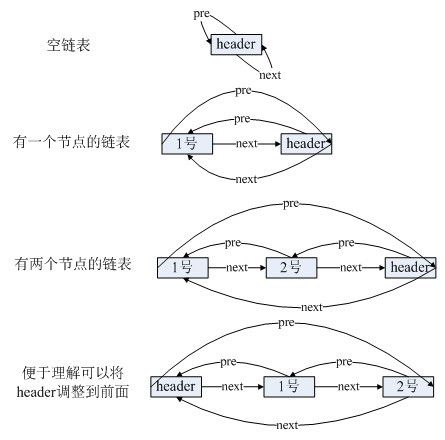
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
private static class Entry<E> {
E element;
Entry<E> next;
Entry<E> previous;
...
}
public boolean add(E e) {
addBefore(e, header);
return true;
}
private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) {
Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous);
newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;
newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;
size++;
modCount++;
return newEntry;
}
public E get(int index) {
return entry(index).element;
}
private Entry<E> entry(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
Entry<E> e = header;
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)
e = e.next;
} else {
for (int i = size; i > index; i--)
e = e.previous;
}
return e;
}
- 两者比较:链表插入数据速度快的说法是相对的,在数据量很小的时候,ArrayList的插入速度不仅不比LinkedList慢,而且还快很多。只有当数据量达到一定量,这个特性才会体现出来,使用时根据场景选择。
- 工具类
>>> java.util.Collections
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list);
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c);
public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... elements);
>>> org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils
public static boolean isEmpty(Collection coll);
public static Collection removeAll(Collection collection, Collection remove);
public static Collection union(Collection a, Collection b);
public static Collection intersection(Collection a, Collection b);
public static Collection disjunction(Collection a, Collection b);
public static Collection subtract(Collection a, Collection b);
>>> com.google.common.collect.Lists
List<String> lst = new ArrayList<String>();
lst.add("a");
lst.add("b");
lst.add("c");
Lists.newArrayList("a", "b", "c");
Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(3);
Lists.newLinkedList();
- CopyOnWriteArrayList。可并发的ArrayList,读写分离。
List<String> lst = new ArrayList<String>();
lst.add("a");
lst.add("b");
lst.add("c");
for (Iterator<String> itor = lst.iterator(); itor.hasNext(); ) {
if ("b".equals(itor.next())) {
lst.remove(itor.next());
}
}
for (Iterator<String> itor = lst.iterator(); itor.hasNext(); ) {
if ("a".equals(itor.next())) {
itor.remove();
}
}
List<String> lst = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
Map
- Map作为最基本的数据结果,在代码中出现频率非常大。Java JDK、C++ STL都对其有很好的支持。
- HashMap、Hashtable内部维护了一个Entry数组。不同的是Hashtable对操作的方法都使用了synchronized确保线程安全。
- HashTable中hash数组默认大小是11,增加的方式是 old * 2 + 1。HashMap中hash数组的默认大小是16,而且一定是2的指数。
- 加载因子:Hsah表中元素的填满的程度。加载因子越大,填满的元素越多,空间利用率高,Hash冲突的机会大。加载因子越小,填满的元素越少,冲突的机会减小,空间浪费多了。
冲突的机会越大,则查找的成本越高。反之,查找的成本越小。
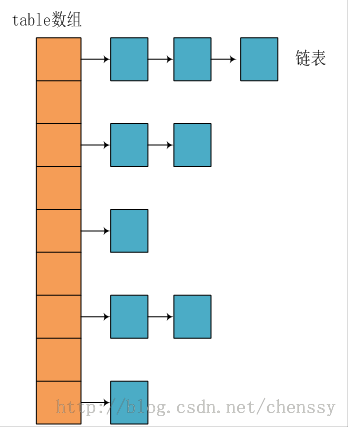
JDK源码:
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). */
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(4);
map.put("1", "1");
map.put("2", "2");
map.put("3", "3");
map.put("4", "4");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(4, 1);
TreeMap内部通过红黑树保证取出来的是排序后的键值对。插入、删除需要维护平衡会牺牲一些效率。但如果要按自然顺序或自定义顺序遍历键,那么TreeMap会更好。Comparable, Comparator. TreeMap详解
TreeSet内部通过TreeMap实现。TreeSet元素实现Comparable接口或自定义比较器。
HashMap效率高线程不安全,Hashtable线程安全但效率不高。ConcurrentHashMap折中办法。
Guava增强的集合
- Multiset:可重复的Set。HashMultiset,内部HashMap实现。
List<Integer> lst = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3);
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (Integer i : lst) {
Integer count = map.get(i);
if (count == null) {
map.put(i, 1);
} else {
map.put(i, count + 1);
}
}
System.out.println(map.get(2));
Multiset<Integer> set = HashMultiset.create();
set.addAll(lst);
int count = set.count(2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(set.toArray()));
- BiMap:一个双向映射的Map,强制Value唯一性。
BiMap<String, String> map = HashBiMap.create();
map.put("M", "1");
map.put("F", "2");
map.put("F", "1");
map.forcePut("F", "3");
System.out.println(map.get("F"));
System.out.println(map.inverse().get("1"));
- Multimap:一个Key对应多个Value,比Map
Map<String, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<String, List<Integer>>();
Multimap<String, Integer> multimap = ArrayListMultimap.create();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
multimap.put((i % 2 == 0) ? "m" : "n", i);
}
System.out.println("size: " + multimap.size());
System.out.println("keys: " + multimap.keys());
System.out.println(multimap.get("m").toString());
System.out.println(multimap.get("n").toString());
System.out.println(multimap.containsValue(10));
反射
- Java反射机制主要提供了以下功能:在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类;在运行时构造任意一个类的对象;在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法;在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法;生成动态代理。
class User {
private String name;
public Integer age;
private String getName() {
return name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public static void Test() {
System.out.println("Test");
}
}
Class clazz = User.class;
User user = (User)clazz.newInstance();
user.age = 10;
clazz.getSimpleName();
clazz.getName();
clazz.getPackage();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
Object value = clazz.getField("age").get(user);
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
Object result = clazz.getMethod("getAge").invoke(user);
clazz.getMethod("Test").invoke(null);
PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor("name", clazz);
pd.getReadMethod().getName();
Bean属性复制
- Commons BeanUtils PropertyUtils, Spring BeanUtils
- Commons的BeanUtils.copyProperties()会对类型转换,如:Integer默认0。Spring的BeanUtils.copyProperties()不会。
- Commons的PropertyUtils.copyProperties()对属性的类型强校验。
- 类型转换:org.apache.commons.beanutils.converters
public class User1 {
private Integer age;
private Integer name;
}
public class User2 {
private Integer age;
private String name;
}
User1 u1 = new User1();
User2 u2 = new User2();
org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils.copyProperties(u2, u1);
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties(u1, u2);
org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils.copyProperties(u2, u1);
User1 u1 = new User1();
u1.setName(123);
User2 u2 = new User2();
org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils.copyProperties(u2, u1);
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties(u1, u2);
org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils.copyProperties(u2, u1);


