Android HandlerThread 使用介绍及简单解析
一 先看看官方介绍:
(1)HandlerThread继承自线程Thread,内部封装了有Looper。
public class HandlerThread extends Thread Handy class for starting a new thread that has a looper. The looper can then be used to create handler classes. Note that start() must still be called.(2)常用方法:
1、Looper getLooper()//返回一个与当前线程关联的Looper
This method returns the Looper associated with this thread. 2、int getThreadId() Returns the identifier of this thread. 3、boolean quit() // HandlerThread退出资源 Quits the handler thread's looper. 4、boolean quitSafely() Quits the handler thread's looper safely. 5、void run() //执行方法(工作线程) If this thread was constructed using a separate Runnable run object, then that Runnable object's run method is called; otherwise, this method does nothing and returns.二 HandlerThread DEMO
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context="com.troy.handlerthreaddemo.MainActivity">
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/ll_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:textSize="22dp" android:layout_marginBottom="18dp" android:text="三峡日泄洪流量时刻表" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv;
private HandlerThread mCheckMsgThread; //HandlerThread
private Handler mCheckMsgHandler; //工作线程的Handler
private boolean isUpdateInfo;
private static final int MSG_UPDATE_INFO = 0x110;
private Handler mUIHandler=new Handler();//与UI线程管理的Handler
private LinearLayout ll_container;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
ll_container=(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.ll_container);
initBackThread();//创建工作线程
}
private void initBackThread(){
mCheckMsgThread=new HandlerThread("check-message-coming");
mCheckMsgThread.start();
mCheckMsgHandler=new Handler(mCheckMsgThread.getLooper()){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
Log.i("TEST","msg.what :"+msg.what);
checkForUpdate();
if(isUpdateInfo){
mCheckMsgHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(MSG_UPDATE_INFO,1000);//自己触发自己
}
}
};
}
private void checkForUpdate(){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
mUIHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Date date=new Date();
DateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String time=format.format(date);
String result="当前泄洪流量: <font color='red'>%d</font> 立方/秒 <font color='gray'>%s</font>";
result=String.format(result,(int)(Math.random()*3000+1000),time);
TextView textView=new TextView(MainActivity.this);
textView.setTextSize(20);
textView.setPadding(0,5,0,5);
textView.setText(Html.fromHtml(result));
ll_container.addView(textView);
}
});
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume(){
super.onResume();
//开始查询
isUpdateInfo = true;
mCheckMsgHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_UPDATE_INFO);
}
@Override
protected void onPause(){
super.onPause();
//停止查询
isUpdateInfo = false;
mCheckMsgHandler.removeMessages(MSG_UPDATE_INFO);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
//释放资源
mCheckMsgThread.quit();
}
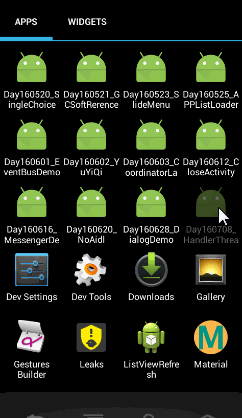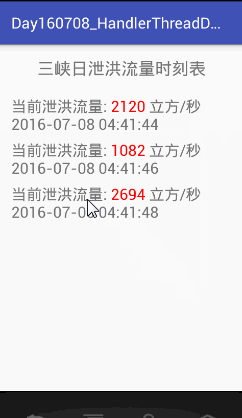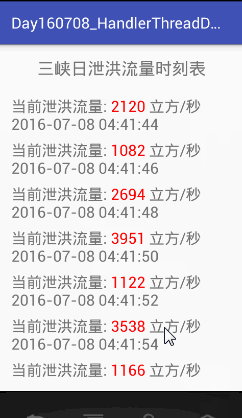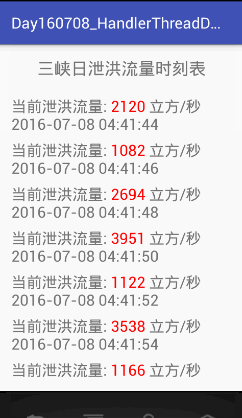
}运行结果如下:
三 源码分析:
HandlerThread.java:
HandlerThread的创建:
public HandlerThread(String name) {//构造方法
super(name);
mPriority = Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT;
}
public HandlerThread(String name, int priority) {//可设置线程优先级 int THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT // 默认应用的优先级
super(name);
mPriority = priority;
}
HandlerThread的启动:
@Override
public void run() {
mTid = Process.myTid();
Looper.prepare();
synchronized (this) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
notifyAll();
}
Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority);//设置线程的优先级
onLooperPrepared();
Looper.loop();//开启消息循环
mTid = -1;
}
可以看到run()方法中调用了Looper.prepare(),Loop.loop();
prepare()呢,中创建了一个Looper对象,并且把该对象放到了该线程范围内的变量中(sThreadLocal),在Looper对象的构造过程中,初始化了一个MessageQueue,作为该Looper对象成员变量。loop()就开启了,不断的循环从MessageQueue中取消息处理了,当没有消息的时候会阻塞,有消息的到来的时候会唤醒。
那么,mCheckMsgThread.getLooper()做了什么:
/** * This method returns the Looper associated with this thread. If this thread not been started * or for any reason is isAlive() returns false, this method will return null. If this thread * has been started, this method will block until the looper has been initialized. * @return The looper. */
public Looper getLooper() {
if (!isAlive()) {
return null;
}
// If the thread has been started, wait until the looper has been created.
synchronized (this) {
while (isAlive() && mLooper == null) {
try {
wait();//如果mLooper为空的时候,就等待,直到 mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); 由notifyAll();来唤醒;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
return mLooper;
}mCheckMsgThread.getLooper()返回的就是我们在run方法中创建的mLooper。
参考致谢:
1 Android HandlerThread 完全解析