自定义View之绘图篇(五):圆形水波
没有比害怕本身更害怕的了。——培根
自定义View之绘图篇(一):基础图形的绘制
自定义View之绘图篇(二):路径(Path)
自定义View之绘图篇(三):文字(Text)
自定义View之绘图篇(四):baseLine和FontMetrics
先来看看下面这张效果图,我们应该怎么去实现:
一、相关知识点
知识点1mPaint.setXfermode()方法的理解以及知识点2mPath.rQuadTo()贝塞尔曲线的绘制原理。那我们分别来看一看。
1、mPaint.setXfermode(Xfermode xfermode)
参数预览:
mPaint.setXfermode(new AvoidXfermode());
mPaint.setXfermode(new PixelXorXfermode());
mPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode());new AvoidXfermode(),new PixelXorXfermode()用法难度不大,基本也用不到,这里就不再细讲了。主要来看一下new PorterDuffXfermode()。
PorterDuffXfermode
PorterDuffXfermode的构造函数如下:
public PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode mode) 只有一个参数PorterDuff.Mode是枚举类型,值有18个,他们分别为:
Mode.CLEAR
Mode.SRC
Mode.DST
Mode.SRC_OVER
Mode.DST_OVER
Mode.SRC_IN
Mode.DST_IN
Mode.SRC_OUT
Mode.DST_OUT
Mode.SRC_ATOP
Mode.DST_ATOP
Mode.XOR
Mode.DARKEN
Mode.LIGHTEN
Mode.MULTIPLY
Mode.SCREEN
Mode.OVERLAY
Mode.ADD 敲一敲,看看每个函数的展示出来的效果是怎么样的。我们一起来看个例子:
public class TestView extends View {
private int width = 800;
private int height = 800;
private Bitmap dstBmp;
private Bitmap srcBmp;
private Paint mPaint;
public TestView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public TestView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public TestView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mPaint = new Paint();
//目标图
dstBmp = makeBitmap(width, height, 0);
//源图
srcBmp = makeBitmap(width, height, 1);
}
public Bitmap makeBitmap(int w, int h, int style) {
Bitmap bm = Bitmap.createBitmap(w, h, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas c = new Canvas(bm);
Paint p = new Paint();
p.setAntiAlias(true);
switch (style) {
case 0:
p.setColor(Color.parseColor("#ff00ff"));
c.drawOval(new RectF(0, 0, w, h), p);
break;
case 1:
p.setColor(Color.parseColor("#00ffff"));
c.drawRect(new RectF(0, 0, w, h), p);
break;
default:
}
return bm;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//xml文件中设置math_parent
//新建图层
int layerID = canvas.saveLayer(0,0,getWidth(),getHeight(),mPaint,Canvas.ALL_SAVE_FLAG);
canvas.drawBitmap(dstBmp, 0, 0, mPaint);
mPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
canvas.drawBitmap(srcBmp, width/2, height/2, mPaint);
mPaint.setXfermode(null);
canvas.restoreToCount(layerID);
}
}xml文件:
<com.github.ws.wavedemo.app.TestView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>效果图:
一起来看看其他枚举值的效果展示:
2、mPath.rQuadTo()
方法预览:
//二阶贝赛尔
public void quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)
public void rQuadTo(float dx1, float dy1, float dx2, float dy2)
//三阶贝赛尔
public void cubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2,float x3, float y3)
public void rCubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2,float x3, float y3)多r的方法,把上一个操作点作为起始点,相对值。
贝塞尔公式
1、一阶贝塞尔公式
效果图为:
P0为起点、P1为终点,t表示当前时间,B(t)表示公式的结果值。 曲线的意义就是公式结果B(t)随时间的变化,其取值所形成的轨迹。在动画中,黑色点表示在当前时间t下公式B(t)的取值。而红色的那条线就不在各个时间点下不同取值的B(t)所形成的轨迹。 对于一阶贝赛尔曲线,大家可以理解为在起始点和终点形成的这条直线上,匀速移动的点。
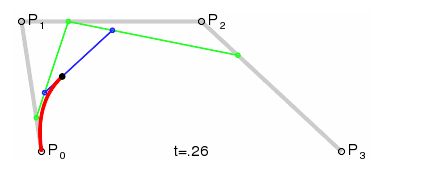
2、二阶贝塞尔公式
效果图为:
图中可以看出,P0是起点,P1是控制点,P2是终点。
3、三阶贝塞尔公式
效果图为:
公式你一定不要去背,知道就行。
水波效果的源码如下:
package com.github.ws.wavedemo.app;
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.PorterDuff;
import android.graphics.PorterDuffXfermode;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.LinearInterpolator;
/** * Created by Administrator on 5/16 0016. */
public class WaveLoadingView extends View {
private Context mContext;
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private Canvas mCanvas;
private Path mWavePath;
private Paint mCirclePaint;
private Paint mWavePaint;
private int mCanvasSize;
private int mCircleRadius;
private int mCircleCenterX;
private int mCircleCenterY;
private int mWaveOriginX;
private int mWaveOriginY;
private int mWaveMoveX;
private int mWaveAmplitude = DEFAULT_WAVE_AMPLITUDE;
private int mWaveLength = DEFAULT_WAVE_LENGTH;
private static final int DEFAULT_WAVE_AMPLITUDE = 100;
private static final int DEFAULT_WAVE_LENGTH = 800;
public WaveLoadingView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public WaveLoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public WaveLoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
}
private void init(Context context) {
setLayerType(LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
mContext = context;
mCirclePaint=new Paint();
mCirclePaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#abc123"));
mCirclePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mWavePaint = new Paint();
mWavePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mWavePaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#D22D2E"));
mWavePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mWavePath = new Path();
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mCircleCenterX = w / 2;
mCircleCenterY = h / 2;
mCircleRadius = (int) (Math.min(mCircleCenterX, mCircleCenterY) * 0.615f);
mWaveOriginX = -mWaveLength;
mWaveOriginY = mCircleCenterX;
mBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(w, h, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
mCanvas = new Canvas(mBitmap);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = measureSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = measureSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int imageSize = (width < height) ? width : height;
setMeasuredDimension(imageSize, imageSize);
}
private int measureSize(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = mCanvasSize;
}
return result;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
mCanvasSize = canvas.getWidth();
if (canvas.getHeight() < mCanvasSize) {
mCanvasSize = canvas.getHeight();
}
int layerID = canvas.saveLayer(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight(), mWavePaint, Canvas.ALL_SAVE_FLAG);
mCanvas.drawCircle(mCircleCenterX, mCircleCenterY, mCircleRadius, mCirclePaint);
mWavePaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
mWavePath.reset();
mWavePaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#ff00ff"));
mWavePath.moveTo(mWaveOriginX + mWaveMoveX, mWaveOriginY);
for (int i = mWaveOriginX; i <= getWidth() + mWaveLength; i += mWaveLength) {
mWavePath.rQuadTo(mWaveLength / 4f, -mWaveAmplitude, mWaveLength / 2f, 0);
mWavePath.rQuadTo(mWaveLength / 4f, mWaveAmplitude, mWaveLength / 2f, 0);
}
mWavePath.lineTo(getWidth(), getHeight());
mWavePath.lineTo(0, getHeight());
mWavePath.close();
mCanvas.drawPath(mWavePath, mWavePaint);
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, 0, 0, null);
mWavePaint.setXfermode(null);
canvas.restoreToCount(layerID);
}
public void startAnim() {
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, Math.abs(mWaveLength));
animator.setDuration(1000);
animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
animator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
mWaveMoveX = (int) animation.getAnimatedValue();
postInvalidate();
}
});
animator.start();
}
}
今天太累了,有不懂的童鞋请给我留言。