MySQL用户权限管理
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/xyang81/article/details/51822252
用户权限管理主要有以下作用:
1. 可以限制用户访问哪些库、哪些表
2. 可以限制用户对哪些表执行SELECT、CREATE、DELETE、DELETE、ALTER等操作
3. 可以限制用户登录的IP或域名
4. 可以限制用户自己的权限是否可以授权给别的用户
一、用户授权
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'yangxin'@'%' identified by 'yangxin123456' with grant option;- all privileges:表示将所有权限授予给用户。也可指定具体的权限,如:SELECT、CREATE、DROP等。
- on:表示这些权限对哪些数据库和表生效,格式:数据库名.表名,这里写“*”表示所有数据库,所有表。如果我要指定将权限应用到test库的user表中,可以这么写:test.user
- to:将权限授予哪个用户。格式:”用户名”@”登录IP或域名”。%表示没有限制,在任何主机都可以登录。比如:”yangxin”@”192.168.0.%”,表示yangxin这个用户只能在192.168.0IP段登录
- identified by:指定用户的登录密码
- with grant option:表示允许用户将自己的权限授权给其它用户
可以使用GRANT给用户添加权限,权限会自动叠加,不会覆盖之前授予的权限,比如你先给用户添加一个SELECT权限,后来又给用户添加了一个INSERT权限,那么该用户就同时拥有了SELECT和INSERT权限。
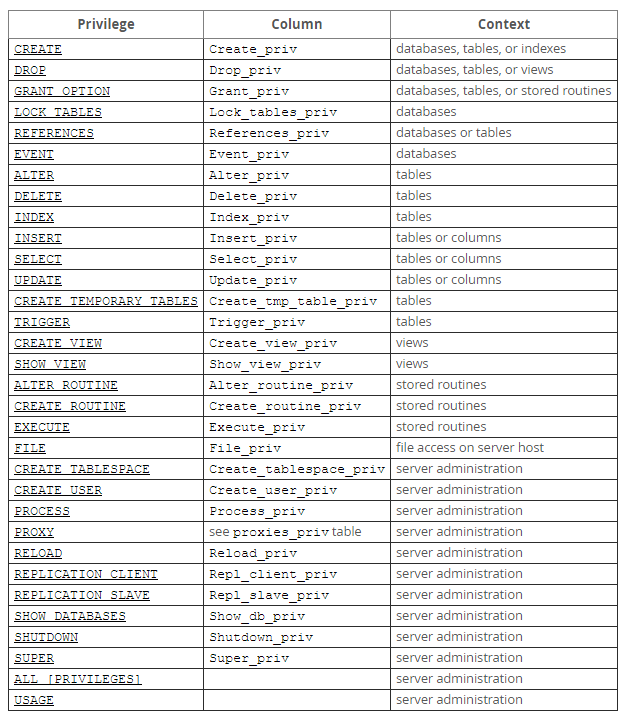
用户详情的权限列表请参考MySQL官网说明:http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/privileges-provided.html
二、刷新权限
对用户做了权限变更之后,一定记得重新加载一下权限,将权限信息从内存中写入数据库。
mysql> flush privileges;三、查看用户权限
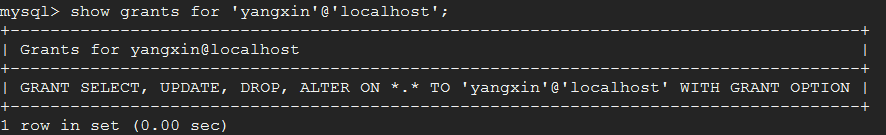
mysql> grant select,create,drop,update,alter on *.* to 'yangxin'@'localhost' identified by 'yangxin0917' with grant option;
mysql> show grants for 'yangxin'@'localhost';四、回收权限
删除yangxin这个用户的create权限,该用户将不能创建数据库和表。
mysql> revoke create on *.* from 'yangxin@localhost';
mysql> flush privileges;五、删除用户
mysql> select host,user from user; +---------------+---------+
| host | user | +---------------+---------+
| % | root |
| % | test3 |
| % | yx |
| 192.168.0.% | root |
| 192.168.0.% | test2 |
| 192.168.0.109 | test |
| ::1 | yangxin |
| localhost | yangxin | +---------------+---------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop user 'yangxin'@'localhost';六、用户重命名
shell> rename user 'test3'@'%' to 'test1'@'%';七、修改密码
1> 更新mysql.user表
mysql> use mysql;
# mysql5.7之前
mysql> update user set password=password('123456') where user='root';
# mysql5.7之后
mysql> update user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root';
mysql> flush privileges;2> 用set password命令
语法:set password for ‘用户名’@’登录地址’=password(‘密码’)
mysql> set password for 'root'@'localhost'=password('123456');3> mysqladmin
语法:mysqladmin -u用户名 -p旧的密码 password 新密码
mysql> mysqladmin -uroot -p123456 password 1234abcd注意:mysqladmin位于mysql安装目录的bin目录下
八、忘记密码
1> 添加登录跳过权限检查配置
修改my.cnf,在mysqld配置节点添加skip-grant-tables配置
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables2> 重新启动mysql服务
shell> service mysqld restart3> 修改密码
此时在终端用mysql命令登录时不需要用户密码,然后按照修改密码的第一种方式将密码修改即可。
4> 还原登录权限跳过检查配置
将my.cnf中mysqld节点的skip-grant-tables配置删除,然后重新启动服务即可。