SparkML之聚类(一)Kmeans聚类
------------------------------目录--------------------------------------------------
Kmeans理论
Matlab实现
Spark源码分析
Spark源码
Spark实验
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Kmeans聚类理论可以访问http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes7a.pdf
可以总结下面三点
1、初始化K个聚类中心点
2、计算每个点到K个聚类中心的距离
3、根据距离,寻找更好的K个聚类中心点
问题1:怎么确定这K个了?随机选择还是有算法确定
解答:我们可以随机选择这K个点,也可以用算法确定这K个点,一般用K-mean++算法进行对K个点的选择
详细的K-mean++算法访问(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-means%2B%2B和http://theory.stanford.edu/~sergei/papers/vldb12-kmpar.pdf.),具体流程如下:
1、从输入的数据集中随机选择一个点作为第一个聚类中心C1
2、计算每个数据点到C1的距离,保存在D(x)中
3、选择D(x)中最大距离的那个数据点作为第二个聚类中心C2
4、计算每个数据点到C1、C2的距离,那个聚类中心里这个数据点近,那么这个数据点就数据这个聚类中心
那么此时,所有的数据点分为2类,一类是依附于C1,另一类是依附于C2
问题2:当K大于2怎么办?那么是不是我们依附于C1、C2的距离都放在一个D(X),在按照那个距离最大,选哪个
解答:這是可以的!算法嘛,总是希望做的和别人有更优之处,要想更优,那么就得考虑更多,下面就是考虑更多的
结果
5、计算每个数据点到最近聚类中心的距离![]() (比如4中,计算C1类的点到C1的距离,C2类的点到C2的距离),之后
(比如4中,计算C1类的点到C1的距离,C2类的点到C2的距离),之后
对所有的距离进行求和得到Sum
6、取(0,sum)之间的一个随机值记为temp,让temp = temp - ![]() (i = 1,2,...),当temp <0 的那一刻,就取这个(i)
(i = 1,2,...),当temp <0 的那一刻,就取这个(i)
点,那么这个i点就是下一个聚类中心
7、就這样一直寻找到第K个点
现在结合matlab编写函数进行讲解
数据和代码,百度云链接;链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mh9ldnM 密码:dcz4
%导入数据
filename = 'C:\Users\andrew\Desktop\kmeans\IrisData.txt';
delimiter = '\t';
startRow = 2;
formatSpec = '%f%f%f%f%s%[^\n\r]';
fileID = fopen(filename,'r');
dataArray = textscan(fileID, formatSpec, 'Delimiter', delimiter, 'HeaderLines' ,startRow-1, 'ReturnOnError', false);
VarName1 = dataArray{:, 1};
Sepalwidth = dataArray{:, 2};%萼片宽
Petallength = dataArray{:, 3};%花瓣长度
Petalwidth = dataArray{:, 4};%花瓣宽度
Species = dataArray{:, 5};%种类
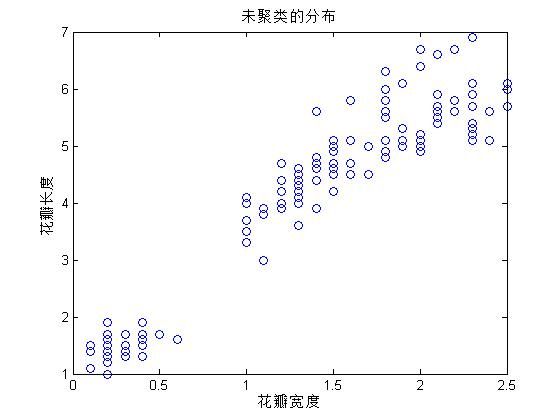
%查看样本的分布情况
figure(1)
plot(Petalwidth,Petallength,'o')
xlabel('花瓣宽度')
ylabel('花瓣长度')
title('未聚类的分布')
%为了更加直观,把不同的种类用不同的符号标记出来
%1到50的种类为: I. setosa
%51到100的种类为: I. versicolor
%101到150的种类为:I. virginica
figure(2)
hold on
plot(Petalwidth(1:50),Petallength(1:50),'rs','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g','MarkerSize',10)
plot(Petalwidth(51:100),Petallength(51:100),'mo','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor',[.49 1 .63],'MarkerSize',10)
plot(Petalwidth(101:end),Petallength(101:end),'rh','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','r','MarkerSize',10)
xlabel('花瓣宽度')
ylabel('花瓣长度')
title('实际类别分布情况')
hold off
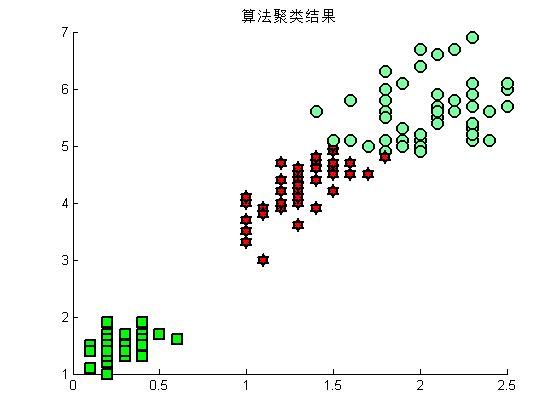
%调用 自己编写的kmeans,看看效果
X = [Petalwidth,Petallength];
[cid,nr,centers] = mykmeans(X,3);
figure(3)
hold on
for i = 1:length(Petalwidth)
if cid(i) ==1
plot(Petalwidth(i),Petallength(i),'rs','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','g','MarkerSize',10)
end
if cid(i) ==2
plot(Petalwidth(i),Petallength(i),'mo','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor',[.49 1 .63],'MarkerSize',10)
end
if cid(i) ==3
plot(Petalwidth(i),Petallength(i),'rh','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFaceColor','r','MarkerSize',10)
end
end
title('算法聚类结果')
hold off
%centers =
%
% 2.0478 5.6261
% 0.2460 1.4620
% 1.3593 4.2926
function [cid,nr,centers] = mykmeans(X,k)
%参数说明
% X:数据集(n*m)
% k:输入的聚类中心个数
% cid:每一个数据输入那一类
% nr:每个数据的个数
% centers:每个类的聚合中心(集合)
%%寻找初始的k个聚类中心
[n,m]=size(X);
cid = zeros(1,n);
nr = zeros(1,k);
%从输入的数据集中随机找出k个聚类中心
temp = randperm(n);
a = temp(1:k);
nc= X(a',:);
%开始对k个聚类中心进行优化
maxIter = 100;
iter = 1;
while iter < maxIter
for i = 1:n
dist = sum((repmat(X(i,:),k,1)-nc).^2,2);
[~,ind] = min(dist);
cid(i) = ind;
end
for i = 1:k
ind = find(cid==i);
nc(i,:) = mean(X(ind,:));
nr(i) = length(ind);
end
iter = iter + 1;
end
tempMaxiter = 2;
tempIter = 1;
tempMove = 1;
while tempIter < tempMaxiter && tempMove ~= 0
tempMove = 0;
for i = 1:n
dist = sum((repmat(X(i,:),k,1)-nc).^2,2);
r = cid(i);
dadj = nr./(nr+1).*dist';
[~,ind] = min(dadj);
if ind ~= r
cid(i) = ind;
ic = find(cid==ind);
nc(ind,:) = mean(X(ic,:));
tempMove = 1;
end
end
tempIter = tempIter+1;
end
centers = nc;
end
SparkML源码分析
Spark对于Kmeans算法程序一共有:KMeans类和KMeans同名对象。
VectorWithNorm类(自行设定norm,为fastSquaredDistance函数服务)
KMeansModel类和KMeansModel同名对象
作用:
KMeans类:
设定训练的参数(聚类中心数目:k,最大迭代次数: maxIterations并行数:runs(默认是1),
初始化算法:initializationMode,种子:seed,收敛值:Epsilon等)
训练模型(run):初始化中心(随机方法和K-mean++算法),聚类中心点计算(runAlogorithm)
初始化并行度(initKMeansParallel)
KMeans同名对象
对不同输入格式,书写train方法
找里各个聚类中心最近的点(findClosest)和计算距离(pointCost)
快速距离计算(fastSquaredDistance)
KMeansModel类
计算每个样本到最近聚类中心的距离(computeCost)
保存模型(save)
预测(predict)
KMeansModel同名对象
导入模型(load)
当前模型的版本号处理(object SaveLoadV1_0)
spark源码:
Kmeans类
@Since("0.8.0") class KMeans private ( private var k: Int, private var maxIterations: Int, private var runs: Int, private var initializationMode: String, private var initializationSteps: Int, private var epsilon: Double, private var seed: Long) extends Serializable with Logging { /** * Constructs a KMeans instance with default parameters: {k: 2, maxIterations: 20, runs: 1, * initializationMode: "k-means||", initializationSteps: 5, epsilon: 1e-4, seed: random}. */ //构造函数: //默认情况下:分2类,20次迭代,1个并行,输出化模型选择KMeans.K_MEANS_PARALLEL,初始steps为5 //epsilon = 0.0001, @Since("0.8.0") def this() = this(2, 20, 1, KMeans.K_MEANS_PARALLEL, 5, 1e-4, Utils.random.nextLong()) /** * Number of clusters to create (k). */ @Since("1.4.0") def getK: Int = k /** * Set the number of clusters to create (k). Default: 2. */ @Since("0.8.0") def setK(k: Int): this.type = { this.k = k this } /** * Maximum number of iterations allowed. */ @Since("1.4.0") def getMaxIterations: Int = maxIterations /** * Set maximum number of iterations allowed. Default: 20. */ @Since("0.8.0") def setMaxIterations(maxIterations: Int): this.type = { this.maxIterations = maxIterations this } /** * The initialization algorithm. This can be either "random" or "k-means||". */ @Since("1.4.0") def getInitializationMode: String = initializationMode /** * Set the initialization algorithm. This can be either "random" to choose random points as * initial cluster centers, or "k-means||" to use a parallel variant of k-means++ * (Bahmani et al., Scalable K-Means++, VLDB 2012). Default: k-means||. */ @Since("0.8.0") def setInitializationMode(initializationMode: String): this.type = { KMeans.validateInitMode(initializationMode) this.initializationMode = initializationMode this } /** * :: Experimental :: * Number of runs of the algorithm to execute in parallel. */ @Since("1.4.0") @deprecated("Support for runs is deprecated. This param will have no effect in 2.0.0.", "1.6.0") def getRuns: Int = runs /** * :: Experimental :: * Set the number of runs of the algorithm to execute in parallel. We initialize the algorithm * this many times with random starting conditions (configured by the initialization mode), then * return the best clustering found over any run. Default: 1. */ @Since("0.8.0") @deprecated("Support for runs is deprecated. This param will have no effect in 2.0.0.", "1.6.0") def setRuns(runs: Int): this.type = { internalSetRuns(runs) } // Internal version of setRuns for Python API, this should be removed at the same time as setRuns // this is done to avoid deprecation warnings in our build. private[mllib] def internalSetRuns(runs: Int): this.type = { if (runs <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of runs must be positive") } if (runs != 1) { logWarning("Setting number of runs is deprecated and will have no effect in 2.0.0") } this.runs = runs this } /** * Number of steps for the k-means|| initialization mode */ @Since("1.4.0") def getInitializationSteps: Int = initializationSteps /** * Set the number of steps for the k-means|| initialization mode. This is an advanced * setting -- the default of 5 is almost always enough. Default: 5. */ @Since("0.8.0") def setInitializationSteps(initializationSteps: Int): this.type = { if (initializationSteps <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of initialization steps must be positive") } this.initializationSteps = initializationSteps this } /** * The distance threshold within which we've consider centers to have converged. */ @Since("1.4.0") def getEpsilon: Double = epsilon /** * Set the distance threshold within which we've consider centers to have converged. * If all centers move less than this Euclidean distance, we stop iterating one run. */ @Since("0.8.0") def setEpsilon(epsilon: Double): this.type = { this.epsilon = epsilon this } /** * The random seed for cluster initialization. */ @Since("1.4.0") def getSeed: Long = seed /** * Set the random seed for cluster initialization. */ @Since("1.4.0") def setSeed(seed: Long): this.type = { this.seed = seed this } // Initial cluster centers can be provided as a KMeansModel object rather than using the // random or k-means|| initializationMode private var initialModel: Option[KMeansModel] = None /** * Set the initial starting point, bypassing the random initialization or k-means|| * The condition model.k == this.k must be met, failure results * in an IllegalArgumentException. */ @Since("1.4.0") def setInitialModel(model: KMeansModel): this.type = { require(model.k == k, "mismatched cluster count") initialModel = Some(model) this } /** * Train a K-means model on the given set of points; `data` should be cached for high * performance, because this is an iterative algorithm. */ @Since("0.8.0") //训练模型的run方法 //官方提示说,因为迭代最好选择将数据进行缓存 def run(data: RDD[Vector]): KMeansModel = { if (data.getStorageLevel == StorageLevel.NONE) { logWarning("The input data is not directly cached, which may hurt performance if its" + " parent RDDs are also uncached.") } // Compute squared norms and cache them. //计算2范数,并且缓存 val norms = data.map(Vectors.norm(_, 2.0)) norms.persist() val zippedData = data.zip(norms).map { case (v, norm) => new VectorWithNorm(v, norm) } //调用runAlgorithm函数,实现K-Means算法, val model = runAlgorithm(zippedData) norms.unpersist() // Warn at the end of the run as well, for increased visibility. if (data.getStorageLevel == StorageLevel.NONE) { logWarning("The input data was not directly cached, which may hurt performance if its" + " parent RDDs are also uncached.") } model//返回模型 } /** * Implementation of K-Means algorithm. */ private def runAlgorithm(data: RDD[VectorWithNorm]): KMeansModel = { val sc = data.sparkContext val initStartTime = System.nanoTime() // Only one run is allowed when initialModel is given val numRuns = if (initialModel.nonEmpty) { if (runs > 1) logWarning("Ignoring runs; one run is allowed when initialModel is given.") 1 } else { runs } //聚类中心初始化 val centers = initialModel match { case Some(kMeansCenters) => { Array(kMeansCenters.clusterCenters.map(s => new VectorWithNorm(s))) } case None => { if (initializationMode == KMeans.RANDOM) { initRandom(data) } else { initKMeansParallel(data) } } } val initTimeInSeconds = (System.nanoTime() - initStartTime) / 1e9 logInfo(s"Initialization with $initializationMode took " + "%.3f".format(initTimeInSeconds) + " seconds.") val active = Array.fill(numRuns)(true) val costs = Array.fill(numRuns)(0.0) var activeRuns = new ArrayBuffer[Int] ++ (0 until numRuns) var iteration = 0 val iterationStartTime = System.nanoTime() // Execute iterations of Lloyd's algorithm until all runs have converged //使用Lloyd算法 //可以参考分析理论部分的5和6 //同时可以对比一下matlab的算法 //這里多了缓存,并行度的变量 while (iteration < maxIterations && !activeRuns.isEmpty) { type WeightedPoint = (Vector, Long) def mergeContribs(x: WeightedPoint, y: WeightedPoint): WeightedPoint = { axpy(1.0, x._1, y._1) (y._1, x._2 + y._2) } val activeCenters = activeRuns.map(r => centers(r)).toArray val costAccums = activeRuns.map(_ => sc.accumulator(0.0)) val bcActiveCenters = sc.broadcast(activeCenters) // Find the sum and count of points mapping to each center //理论分析的第五部分,对每个中心到各自的样本的距离进行计算 val totalContribs = data.mapPartitions { points => val thisActiveCenters = bcActiveCenters.value val runs = thisActiveCenters.length val k = thisActiveCenters(0).length val dims = thisActiveCenters(0)(0).vector.size val sums = Array.fill(runs, k)(Vectors.zeros(dims)) val counts = Array.fill(runs, k)(0L) points.foreach { point => (0 until runs).foreach { i => val (bestCenter, cost) = KMeans.findClosest(thisActiveCenters(i), point) costAccums(i) += cost val sum = sums(i)(bestCenter) axpy(1.0, point.vector, sum) counts(i)(bestCenter) += 1 } } //contribs = ((并行度,那个中心),某个聚类中心到各自样本之和,那个并行度下的那个聚类中心) val contribs = for (i <- 0 until runs; j <- 0 until k) yield { ((i, j), (sums(i)(j), counts(i)(j))) } contribs.iterator }.reduceByKey(mergeContribs).collectAsMap() bcActiveCenters.unpersist(blocking = false) // Update the cluster centers and costs for each active run for ((run, i) <- activeRuns.zipWithIndex) { var changed = false var j = 0 while (j < k) { val (sum, count) = totalContribs((i, j)) if (count != 0) { scal(1.0 / count, sum) val newCenter = new VectorWithNorm(sum) if (KMeans.fastSquaredDistance(newCenter, centers(run)(j)) > epsilon * epsilon) { changed = true } centers(run)(j) = newCenter } j += 1 } if (!changed) { active(run) = false logInfo("Run " + run + " finished in " + (iteration + 1) + " iterations") } costs(run) = costAccums(i).value } activeRuns = activeRuns.filter(active(_)) iteration += 1 } val iterationTimeInSeconds = (System.nanoTime() - iterationStartTime) / 1e9 logInfo(s"Iterations took " + "%.3f".format(iterationTimeInSeconds) + " seconds.") if (iteration == maxIterations) { logInfo(s"KMeans reached the max number of iterations: $maxIterations.") } else { logInfo(s"KMeans converged in $iteration iterations.") } val (minCost, bestRun) = costs.zipWithIndex.min logInfo(s"The cost for the best run is $minCost.") new KMeansModel(centers(bestRun).map(_.vector)) } /** * Initialize `runs` sets of cluster centers at random. */ //随机的寻找K个聚类中心 private def initRandom(data: RDD[VectorWithNorm]) : Array[Array[VectorWithNorm]] = { // Sample all the cluster centers in one pass to avoid repeated scans val sample = data.takeSample(true, runs * k, new XORShiftRandom(this.seed).nextInt()).toSeq Array.tabulate(runs)(r => sample.slice(r * k, (r + 1) * k).map { v => new VectorWithNorm(Vectors.dense(v.vector.toArray), v.norm) }.toArray) } /** * Initialize `runs` sets of cluster centers using the k-means|| algorithm by Bahmani et al. * (Bahmani et al., Scalable K-Means++, VLDB 2012). This is a variant of k-means++ that tries * to find with dissimilar cluster centers by starting with a random center and then doing * passes where more centers are chosen with probability proportional to their squared distance * to the current cluster set. It results in a provable approximation to an optimal clustering. * * The original paper can be found at http://theory.stanford.edu/~sergei/papers/vldb12-kmpar.pdf. */ //用K-Means++理论 private def initKMeansParallel(data: RDD[VectorWithNorm]) : Array[Array[VectorWithNorm]] = { // Initialize empty centers and point costs. val centers = Array.tabulate(runs)(r => ArrayBuffer.empty[VectorWithNorm]) var costs = data.map(_ => Array.fill(runs)(Double.PositiveInfinity)) // Initialize each run's first center to a random point. val seed = new XORShiftRandom(this.seed).nextInt() val sample = data.takeSample(true, runs, seed).toSeq val newCenters = Array.tabulate(runs)(r => ArrayBuffer(sample(r).toDense)) /** Merges new centers to centers. */ def mergeNewCenters(): Unit = { var r = 0 while (r < runs) { centers(r) ++= newCenters(r) newCenters(r).clear() r += 1 } } // On each step, sample 2 * k points on average for each run with probability proportional // to their squared distance from that run's centers. Note that only distances between points // and new centers are computed in each iteration. var step = 0 while (step < initializationSteps) { val bcNewCenters = data.context.broadcast(newCenters) val preCosts = costs costs = data.zip(preCosts).map { case (point, cost) => Array.tabulate(runs) { r => math.min(KMeans.pointCost(bcNewCenters.value(r), point), cost(r)) } }.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK) val sumCosts = costs .aggregate(new Array[Double](runs))( seqOp = (s, v) => { // s += v var r = 0 while (r < runs) { s(r) += v(r) r += 1 } s }, combOp = (s0, s1) => { // s0 += s1 var r = 0 while (r < runs) { s0(r) += s1(r) r += 1 } s0 } ) bcNewCenters.unpersist(blocking = false) preCosts.unpersist(blocking = false) val chosen = data.zip(costs).mapPartitionsWithIndex { (index, pointsWithCosts) => val rand = new XORShiftRandom(seed ^ (step << 16) ^ index) pointsWithCosts.flatMap { case (p, c) => val rs = (0 until runs).filter { r => rand.nextDouble() < 2.0 * c(r) * k / sumCosts(r) } if (rs.length > 0) Some((p, rs)) else None } }.collect() mergeNewCenters() chosen.foreach { case (p, rs) => rs.foreach(newCenters(_) += p.toDense) } step += 1 } mergeNewCenters() costs.unpersist(blocking = false) // Finally, we might have a set of more than k candidate centers for each run; weigh each // candidate by the number of points in the dataset mapping to it and run a local k-means++ // on the weighted centers to pick just k of them val bcCenters = data.context.broadcast(centers) val weightMap = data.flatMap { p => Iterator.tabulate(runs) { r => ((r, KMeans.findClosest(bcCenters.value(r), p)._1), 1.0) } }.reduceByKey(_ + _).collectAsMap() bcCenters.unpersist(blocking = false) val finalCenters = (0 until runs).par.map { r => val myCenters = centers(r).toArray val myWeights = (0 until myCenters.length).map(i => weightMap.getOrElse((r, i), 0.0)).toArray LocalKMeans.kMeansPlusPlus(r, myCenters, myWeights, k, 30) } finalCenters.toArray } }KMeans同名对象
/** * Top-level methods for calling K-means clustering. */ @Since("0.8.0") object KMeans { // Initialization mode names @Since("0.8.0") val RANDOM = "random" @Since("0.8.0") val K_MEANS_PARALLEL = "k-means||" /** * Trains a k-means model using the given set of parameters. * * @param data Training points as an `RDD` of `Vector` types. * @param k Number of clusters to create. * @param maxIterations Maximum number of iterations allowed. * @param runs Number of runs to execute in parallel. The best model according to the cost * function will be returned. (default: 1) * @param initializationMode The initialization algorithm. This can either be "random" or * "k-means||". (default: "k-means||") * @param seed Random seed for cluster initialization. Default is to generate seed based * on system time. */ @Since("1.3.0") //输入分类数据:data,聚类中心数目:k,最大迭代次数: maxIterations //并行数:runs(默认是1),初始化算法:initializationMode,种子:seed //一共6个参数 def train( data: RDD[Vector], k: Int, maxIterations: Int, runs: Int, initializationMode: String, seed: Long): KMeansModel = { new KMeans().setK(k) .setMaxIterations(maxIterations) .internalSetRuns(runs) .setInitializationMode(initializationMode) .setSeed(seed) .run(data) } /** * Trains a k-means model using the given set of parameters. * * @param data Training points as an `RDD` of `Vector` types. * @param k Number of clusters to create. * @param maxIterations Maximum number of iterations allowed. * @param runs Number of runs to execute in parallel. The best model according to the cost * function will be returned. (default: 1) * @param initializationMode The initialization algorithm. This can either be "random" or * "k-means||". (default: "k-means||") */ @Since("0.8.0") //输入分类数据:data,聚类中心数目:k,最大迭代次数: maxIterations //并行数:runs(默认是1),初始化算法:initializationMode //一共5个参数 def train( data: RDD[Vector], k: Int, maxIterations: Int, runs: Int, initializationMode: String): KMeansModel = { new KMeans().setK(k) .setMaxIterations(maxIterations) .internalSetRuns(runs) .setInitializationMode(initializationMode) .run(data) } /** * Trains a k-means model using specified parameters and the default values for unspecified. */ //输入分类数据:data,聚类中心数目:k,最大迭代次数: maxIterations //一共3个参数 @Since("0.8.0") def train( data: RDD[Vector], k: Int, maxIterations: Int): KMeansModel = { train(data, k, maxIterations, 1, K_MEANS_PARALLEL) } /** * Trains a k-means model using specified parameters and the default values for unspecified. */ //输入分类数据:data,聚类中心数目:k,最大迭代次数: maxIterations //并行数:runs(默认是1) //一共4个参数 @Since("0.8.0") def train( data: RDD[Vector], k: Int, maxIterations: Int, runs: Int): KMeansModel = { train(data, k, maxIterations, runs, K_MEANS_PARALLEL) } /** * Returns the index of the closest center to the given point, as well as the squared distance. */ //找出点到所有聚类中心最近的一个聚类中心,返回:(bestIndex, bestDistance) private[mllib] def findClosest( centers: TraversableOnce[VectorWithNorm], point: VectorWithNorm): (Int, Double) = { var bestDistance = Double.PositiveInfinity var bestIndex = 0 var i = 0 centers.foreach { center => // Since `\|a - b\| \geq |\|a\| - \|b\||`, we can use this lower bound to avoid unnecessary // distance computation. var lowerBoundOfSqDist = center.norm - point.norm lowerBoundOfSqDist = lowerBoundOfSqDist * lowerBoundOfSqDist if (lowerBoundOfSqDist < bestDistance) { val distance: Double = fastSquaredDistance(center, point) if (distance < bestDistance) { bestDistance = distance bestIndex = i } } i += 1 } (bestIndex, bestDistance) } /** * Returns the K-means cost of a given point against the given cluster centers. */ //计算样本点和和中心点之间的距离 private[mllib] def pointCost( centers: TraversableOnce[VectorWithNorm], point: VectorWithNorm): Double = findClosest(centers, point)._2 /** * Returns the squared Euclidean distance between two vectors computed by * [[org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils#fastSquaredDistance]]. */ //返回两个点的2范数(距离) private[clustering] def fastSquaredDistance( v1: VectorWithNorm, v2: VectorWithNorm): Double = { MLUtils.fastSquaredDistance(v1.vector, v1.norm, v2.vector, v2.norm) } //验证初始化模型 private[spark] def validateInitMode(initMode: String): Boolean = { initMode match { case KMeans.RANDOM => true case KMeans.K_MEANS_PARALLEL => true case _ => false } } } KMeansModel /** * A vector with its norm for fast distance computation. * * @see [[org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.KMeans#fastSquaredDistance]] */ private[clustering] //自己定义 class VectorWithNorm(val vector: Vector, val norm: Double) extends Serializable { def this(vector: Vector) = this(vector, Vectors.norm(vector, 2.0)) def this(array: Array[Double]) = this(Vectors.dense(array)) /** Converts the vector to a dense vector. */ def toDense: VectorWithNorm = new VectorWithNorm(Vectors.dense(vector.toArray), norm) }
KMeansModel类
class KMeansModel @Since("1.1.0") (@Since("1.0.0") val clusterCenters: Array[Vector]) extends Saveable with Serializable with PMMLExportable { /** * A Java-friendly constructor that takes an Iterable of Vectors. */ @Since("1.4.0") def this(centers: java.lang.Iterable[Vector]) = this(centers.asScala.toArray) /** * Total number of clusters. */ @Since("0.8.0") def k: Int = clusterCenters.length /** * Returns the cluster index that a given point belongs to. */ @Since("0.8.0") def predict(point: Vector): Int = { KMeans.findClosest(clusterCentersWithNorm, new VectorWithNorm(point))._1 } /** * Maps given points to their cluster indices. */ @Since("1.0.0") def predict(points: RDD[Vector]): RDD[Int] = { val centersWithNorm = clusterCentersWithNorm val bcCentersWithNorm = points.context.broadcast(centersWithNorm) points.map(p => KMeans.findClosest(bcCentersWithNorm.value, new VectorWithNorm(p))._1) } /** * Maps given points to their cluster indices. */ @Since("1.0.0") def predict(points: JavaRDD[Vector]): JavaRDD[java.lang.Integer] = predict(points.rdd).toJavaRDD().asInstanceOf[JavaRDD[java.lang.Integer]] /** * Return the K-means cost (sum of squared distances of points to their nearest center) for this * model on the given data. */ @Since("0.8.0") def computeCost(data: RDD[Vector]): Double = { val centersWithNorm = clusterCentersWithNorm val bcCentersWithNorm = data.context.broadcast(centersWithNorm) data.map(p => KMeans.pointCost(bcCentersWithNorm.value, new VectorWithNorm(p))).sum() } private def clusterCentersWithNorm: Iterable[VectorWithNorm] = clusterCenters.map(new VectorWithNorm(_)) @Since("1.4.0") override def save(sc: SparkContext, path: String): Unit = { KMeansModel.SaveLoadV1_0.save(sc, this, path) } override protected def formatVersion: String = "1.0" }
KMeansModel同名对象
object KMeansModel extends Loader[KMeansModel] { @Since("1.4.0") override def load(sc: SparkContext, path: String): KMeansModel = { KMeansModel.SaveLoadV1_0.load(sc, path) } private case class Cluster(id: Int, point: Vector) private object Cluster { def apply(r: Row): Cluster = { Cluster(r.getInt(0), r.getAs[Vector](1)) } } private[clustering] object SaveLoadV1_0 { private val thisFormatVersion = "1.0" private[clustering] val thisClassName = "org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.KMeansModel" def save(sc: SparkContext, model: KMeansModel, path: String): Unit = { val sqlContext = SQLContext.getOrCreate(sc) import sqlContext.implicits._ val metadata = compact(render( ("class" -> thisClassName) ~ ("version" -> thisFormatVersion) ~ ("k" -> model.k))) sc.parallelize(Seq(metadata), 1).saveAsTextFile(Loader.metadataPath(path)) val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(model.clusterCenters.zipWithIndex).map { case (point, id) => Cluster(id, point) }.toDF() dataRDD.write.parquet(Loader.dataPath(path)) } def load(sc: SparkContext, path: String): KMeansModel = { implicit val formats = DefaultFormats val sqlContext = SQLContext.getOrCreate(sc) val (className, formatVersion, metadata) = Loader.loadMetadata(sc, path) assert(className == thisClassName) assert(formatVersion == thisFormatVersion) val k = (metadata \ "k").extract[Int] val centroids = sqlContext.read.parquet(Loader.dataPath(path)) Loader.checkSchema[Cluster](centroids.schema) val localCentroids = centroids.rdd.map(Cluster.apply).collect() assert(k == localCentroids.length) new KMeansModel(localCentroids.sortBy(_.id).map(_.point)) } } }
note:为了方便处理,这个数据和只是Matlab中的3,4列,而且是纯数字
package Cluster import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.{KMeans, KMeansModel} import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object myKmean { def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("KMeansExample").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) // Load and parse the data val data = sc.textFile("C:\\Users\\andrew\\Desktop\\kmeans\\IrisData.txt") println(data) data.collect.foreach(println) val parsedData = data.map(s => Vectors.dense(s.split('\t').map(_.toDouble))) parsedData.collect.foreach(println) // Cluster the data into two classes using KMeans val initMode = "K-means||" val numClusters = 3 val numIterations = 20 val clusters = KMeans.train(parsedData, numClusters, numIterations,1,initMode) clusters.clusterCenters.foreach(println) //聚类中心的坐标 //[5.595833333333332,2.0374999999999988] //[1.462,0.24599999999999994] //[4.269230769230769,1.3423076923076924] // Evaluate clustering by computing Within Set Sum of Squared Errors val WSSSE = clusters.computeCost(parsedData) println("Within Set Sum of Squared Errors = " + WSSSE) //Within Set Sum of Squared Errors = 31.371358974359016 // Save and load model clusters.save(sc, "target/org/apache/spark/KMeansExample/KMeansModel") val sameModel = KMeansModel.load(sc, "target/org/apache/spark/KMeansExample/KMeansModel") sc.stop() } }对比于matlab的聚合中心
centers =
2.0478 5.6261
0.2460 1.4620
1.3593 4.2926
//聚类中心的坐标
[5.595833333333332,2.0374999999999988]
[1.462,0.24599999999999994]
[4.269230769230769,1.3423076923076924]