Struts2学习第一天——struts2基本流程与配置
| 文档版本 | 开发工具 | 测试平台 | 工程名字 | 日期 | 作者 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1.0 | 2016.06.12 | lutianfei | none |
struts2框架
什么是框架,框架有什么用?
- 框架 是 实现部分功能的代码 (半成品),使用框架简化企业级软件开发 ,提高开发效率。
- 学习框架 ,清楚的知道框架能做什么? 还有哪些工作需要自己编码实现 ?
什么是struts2框架,它有什么用?
- Struts 2是在 struts 1和WebWork的技术基础上进行了合并的全新的Struts 2框架。
- 其全新的Struts 2的体系结构与Struts 1的体系结构差别巨大。Struts 2以WebWork为核心
- struts2=struts1+webwork;
- struts2框架是apache产品。
- struts2是一个标准的mvc框架。
- javaweb中的model2模式就是一个mvc模式。 model2=servlet+jsp+javaBean
- struts2框架只能在
javaweb开发中使用的。 - 使用struts2框架,可以简化我们的web开发,并且降低程序的耦合度。
XWork—它是webwork核心,提供了很多核心功能:
- 前端拦截机(interceptor)
- 运行时表单属性验证
- 类型转换
- 强大的表达式语言(OGNL – the Object Graph Navigation Language)
- IoC(Inversion of Control反转控制)容器等
类似于struts2框架的产品 :
- struts1 webwork jsf springmvc
- ssh—struts2 spring hibernate
- ssi—springmvc spring ibatis
Strust2 核心功能
- 允许POJO(Plain Old Java Objects)对象 作为Action
- Action的execute 方法不再与Servlet API耦合,更易测试
- 支持更多视图技术(JSP、FreeMarker、Velocity)
- 基于Spring AOP思想的拦截器机制,更易扩展
- 更强大、更易用输入校验功能
- 整合Ajax支持
struts2快速入门
- index.jsp——>HelloServlet——–>hello.jsp web开发流程.
index.jsp——>HelloAction———>hello.jsp struts2流程
Struts2的下载和安装
- http://struts.apache.org/download.cgi 下载Struts2 最新版
struts2的目录结构:
- apps: 该文件夹包含了基于struts2 的示例应用,这些示例应用对于学习者是非常有用的;例子程序
war后缀表示web压缩文件 - docs : 该文件夹下包含了struts2 相关文档,包括struts2 快速入门、struts2的文档以及API文档等
- lib : 该文件夹下包含了Struts2框架和核心类库,以及struts2第三方插件类库
- 开发时没必要将lib目录下jar文件全部复制到项目中
- src : 该文件夹下包含了Struts2框架的全部源代码
- core 它是struts2的源代码
- xwork-core struts2底层使用了xwork,xwork的源代码
- apps: 该文件夹包含了基于struts2 的示例应用,这些示例应用对于学习者是非常有用的;例子程序
1.导入jar包
- 下载struts2的jar包 struts-2.3.15.1-all 版本.
- Struts运行必要jar包
- struts2-core-2.3.1.1.jar:Struts 2框架的核心类库
- xwork-core-2.3.1.1.jar:Command模式框架,WebWork和Struts2都基于xwork
- ognl-3.0.3.jar:对象图导航语言(Object Graph Navigation Language),struts2框架通过其读写对象的属性
- freemarker-2.3.18.jar:Struts 2的UI标签的模板使用FreeMarker编写
- commons-logging-1.1.x.jar:ASF出品的日志包,Struts 2框架使用这个日志,包来支持Log4J和JDK 1.4+的日志记录。
- commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar: 文件上传组件,2.1.6版本后需要加入此文件
- commons-io-2.0.1.jar:传文件依赖的jar包
- commons-lang-2.5.jar:对java.lang包的增强
- 开发中为了方便导入,可以使用app/struts2-blank.war 携带jar包
注意:在struts2开发,一般情况下最少导入的jar包,去
apps下的struts2-blank示例程序中copy。将war后缀改为rar后解压。2.创建index.jsp,hello.jsp页面
- 在index.jsp (发起请求页面)
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/hello">第一次使用struts2</a>
- hello.jsp (结果页面)
<h1>你好,Struts2<h1>
- 结果页面显示 struts2框架访问成功
- 在index.jsp (发起请求页面)
3.对struts2框架进行配置
- 1.web.xml文件中配置前端控制器(核心控制器)—–就是一个Filter
- 目的:是为了让struts2框架可以运行。
- 过滤器配置
/*, 但是struts2 默认处理.action结尾请求,分发到相应Action类
- 1.web.xml文件中配置前端控制器(核心控制器)—–就是一个Filter
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>* 2.创建一个struts.xml配置文件 ,这个是struts2框架配置文件。
* 目的:是为了struts2框架流程可以执行。
* 名称:struts.xml
* 位置:src下(classes下)
- 4.创建一个HelloAction类
- 要求,在HelloAction类中创建一个返回值是String类型的方法,注意,无参数。
public class HelloAction {
public String say(){
System.out.println("hello world");
return "good"; // 结果页面命名
}
}struts2 的Action类似以前编写的Servlet程序,可以处理用户提交请求,但是Struts2的Action可以POJO对象
5.在struts.xml文件中配置HelloAction
<package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<action name="hello" class="cn.itcast.action.HelloAction" method="say">
<result name="good">/hello.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>- 6.在index.jsp中添加连接,测试
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/hello">第一次使用struts2</a>- 在地址栏中输入:http://localhost/struts2_day01/index.jsp 访问连接,就可以看到
- HelloAction类中的say方法执行了,也跳转到了hello.jsp.
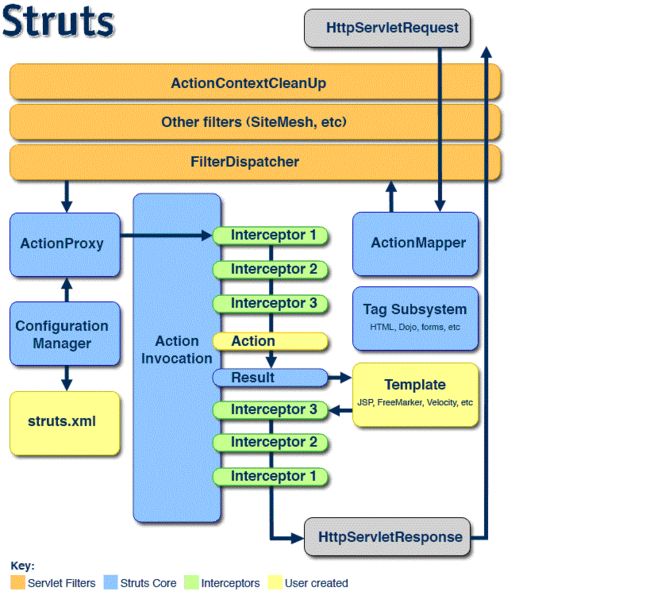
Struts2 处理流程
- 对入门程序进行流程分析
模仿struts2流程完成入门程序
- index.jsp
- hello.jsp
- HelloAction
struts.xml
1.创建一个Filter—-StrutsFilter
- 2.在web.xml文件中配置StrutsFilter
<filter>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<filter-class>cn.itcast.filter.StrutsFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>- 3.在StrutsFilter中完成拦截操作,并访问Action中的方法,跳转到hello.jsp页面操作.
// 2.1 得到请求资源路径
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
String path = uri.substring(contextPath.length() + 1);
// System.out.println(path); // hello
// 2.2 使用path去struts.xml文件中查找某一个<action name=path>这个标签
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
// 得到struts.xml文件的document对象。
Document document = reader.read(new File(this.getClass()
.getResource("/struts.xml").getPath()));
Element actionElement = (Element) document
.selectSingleNode("//action[@name='" + path + "']"); // 查找<action name='hello'>这样的标签
if (actionElement != null) {
// 得到<action>标签上的class属性以及method属性
String className = actionElement.attributeValue("class"); // 得到了action类的名称
String methodName = actionElement.attributeValue("method");// 得到action类中的方法名称。
// 2.3通过反射,得到Class对象,得到Method对象
Class actionClass = Class.forName(className);
Method method = actionClass.getDeclaredMethod(methodName);
// 2.4 让method执行.
String returnValue = (String) method.invoke(actionClass
.newInstance()); // 是让action类中的方法执行,并获取方法的返回值。
// 2.5
// 使用returnValue去action下查找其子元素result的name属性值,与returnValue做对比。
Element resultElement = actionElement.element("result");
String nameValue = resultElement.attributeValue("name");
if (returnValue.equals(nameValue)) {
// 2.6得到了要跳转的路径。
String skipPath = resultElement.getText();
// System.out.println(skipPath);
request.getRequestDispatcher(skipPath).forward(request,
response);
return;
}
}struts2的流程分析以及工具配置
1.流程分析
- 请求 –> StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter 核心控制器 –> Interceptors 拦截器(实现代码功能 ) –> Action 的execute –> 结果页面 Result
- 拦截器 在
struts-default.xml定义 - 执行拦截器 是 defaultStack 中引用拦截器
2.关于手动配置struts.xml文件中提示操作
- 如果安装Aptana编辑器 ,请不要用Aptana自带xml编辑器 编写struts2配置文件
- struts.xml提示来自于 DTD约束,
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
- 如果可以上网,自动缓存dtd,提供提示功能
- 如果不能上网,也可以配置本地DTD提示
- 提示配置说明
- dtd文件的名称空间:http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd
- 提示文件的路径:\struts-2.3.15.1-all\struts-2.3.15.1\src\core\src\main\resources\struts-2.3.dtd
3.关联struts2源文件
- 如果是com.opensymphony.xxx : 在xwork-core下
- 如果是org.apache.struts2 : 在core下
4.使用插件
struts2-config-browser-plugin-2.3.15.1- 提供在浏览器中查看 struts2 配置加载情况
- 将解压struts2/lib/struts2-config-browser-plugin-2.3.7.jar 复制WEB-INF/lib下
- 访问 http://localhost/struts2_day01/config-browser/index.action 查看 struts2配置加载情况
struts2配置(重点)
1.struts2配置文件加载顺序
- struts2框架要能执行,必须先加载
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter - 在StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的init方法中对Dispatcher进行了初始化.
- 在Dispatcher类中定义的init方法内就描述了struts2配置文件加载的顺序
init_DefaultProperties(); // [1] ---------- org/apache/struts2/default.properties
init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations(); // [2] --- struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml
init_LegacyStrutsProperties(); // [3] --- 自定义struts.properties
init_CustomConfigurationProviders(); // [5] ----- 自定义配置提供
init_FilterInitParameters() ; // [6] ----- web.xml
init_AliasStandardObjects() ; // [7] ---- Bean加载 1.default.properties文件
- 作用:定义了struts2框架中所有常量
- 位置: org/apache/struts2/default.properties
2.struts-default.xml
- 作用:配置了bean,interceptor,result等。
- 位置:在struts的core核心jar包.
- struts-plugin.xml
- 它是struts2框架中所使用的插件的配置文件。
struts.xml
- 我们使struts2所使用的配置文件。
3.自定义的struts.properties
- 就是可以自定义常量。
4.web.xml
- 可以理解为由Struts2框架加载的。
在开发中,后加载文件中的配置会将先加载文件中的配置覆盖。
- default.properties
- struts-default.xml
- struts.xml
2.关于Action的配置
1.
<package>作用:是用于声明一个包。用于管理action。- 1.name 它用于声明一个包名,包名不能重复,也就是它是唯一的。
- 2.namespace 它与action标签的name属性合并确定了一个唯一访问action的路径。
- 3.extends 它代表继承的包名。
- 4.abstrace 它可以取值为true/false,如果为true,代表这个包是用于被继承的。
2
<action>用于声明一个action- 1.name 就是action的一个名称,它是唯一的(在同包内) 它与package中的namespace确定了访问action的路径。
- 2.class Action类的全名
- 3.method 要访问的Action类中的方法的名称,方法无参数 ,返回值为String.如果不写,默认跳转到
execute函数。
3.
<result>用于确定返回结果类型- 1.name 它与action中的method方法返回值做对比,确定跳转路径。
关于action配置其它细节
1.关于默认值问题
<package namespace="默认值">namespace的默认值是<action class="默认值" method="默认值">
- class的默认值是 : com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport
- method的默认值是 : execute
<result name="默认值">name的默认值是 “success”
2.关于访问action的路径问题
- 当action的配置是:
<package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<action name="hello" class="cn.itcast.action.DefaultAction">
<result>/hello.jsp</result>
</action>
</package> * 此时输入: http://localhost/struts2_day01_2/a/b/c/hello 也访问到了action。
* 原因:struts2中的action被访问时,它会首先查找
* 1.namespace="/a/b/c" action的name=hello 没有.
* 2.namespace="/a/b action的name=hello 没有
* 3.namespace="/a" action的name=hello 没有
* 4.namespace="/" action的name=hello 查找到了.
* 如果最后也查找不到,会报404错误.
* 3.默认的action。
* 作用:处理其它action处理不了的路径。
* `<default-action-ref name="action的名称" />`
* 当访问的路径,其它的action处理不了时,就会执行name指定的名称的action。
* 4.action的默认处理类
* 在action配置时,如果class不写。默认情况下是 com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport
* `<default-class-ref class="cn.itcast.action.DefaultAction"/>`
* 如上设置,在当前包下,默认处理action请求的处理类就为class指定的类。即:当`<action name="xxx" class="">`中class省略时,按照default-class-ref中的class设置认定对应的类。
关于常量配置
default.properties 它声明了struts中的常量。
问题:人为设置常量,可以在哪些位置设置 ?
- 1.struts.xml(应用最多)
<constant name="常量名称" value="常量值"></constant>
- 2.struts.properties(基本不使用)
- 3.web.xml(了解)
- 配置常量,是使用
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的初始化参数来配置的.
- 配置常量,是使用
- 1.struts.xml(应用最多)
<init-param>
<param-name>struts.action.extension</param-name>
<param-value>do,,</param-value>
</init-param>常用常量(struts.xml)
struts.action.extension=action,,: 这个常量用于指定strus2框架默认拦截的后缀名.<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"/>: 相当于request.setCharacterEncoding(“UTF-8”); 解决post请求乱码<constant name="struts.serve.static.browserCache" value="false"/>: false不缓存,true浏览器会缓存静态内容,产品环境设置true、开发环境设置false<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" />: 提供详细报错页面,修改struts.xml后不需要重启服务器 (要求)
struts.xml文件的分离:
- 目的:就是为了阅读方便。可以让一个模块一个配置文件,在struts.xml文件中通过
<include file="test.xml"/>导入其它的配置文件。
- 目的:就是为了阅读方便。可以让一个模块一个配置文件,在struts.xml文件中通过
Action
关于Action类的创建方式介绍
有三种方式
1.创建一个POJO类.
- 简单的Java对象(Plain Old Java Objects):指的是没有实现任何接口,没有继承任何父类(除了Object)
- 优点:无耦合。
- 缺点:所以工作都要自己实现。
在struts2框架底层是通过反射来操作
- struts2框架 读取
struts.xml获得 完整Action类名 - obj = Class.forName(“完整类名”).newInstance();
- Method m = Class.forName(“完整类名”).getMethod(“execute”);
- m.invoke(obj); 通过反射 执行 execute方法
- struts2框架 读取
2.创建一个类,实现Action接口
com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action- 优点:耦合低。提供了五种结果视图,定义了一个行为方法。
- 缺点:所有工作都要自己实现。
- 为了让用户开发的Action更加规范struts2提供了一个Action接口
- public static final String SUCCESS = “success”; // 数据处理成功 (成功页面)
- public static final String NONE = “none”; // 页面不跳转 return null; 效果一样
- public static final String ERROR = “error”; // 数据处理发送错误 (错误页面)
- public static final String INPUT = “input”; // 用户输入数据有误,通常用于表单数据校验 (输入页面)
- public static final String LOGIN = “login”; // 主要权限认证 (登陆页面)
3.创建一个类,继承自
ActionSupport类。com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport- ActionSupport类实现了Action接口。
- 优点 : 表单校验、错误信息设置、读取国际化信息 三个功能都支持.
- 缺点 : 耦合度高。
- 在开发中,第三种会使用的比较多.
关于action的访问方式
1.通过设置method的值,来确定访问action类中的哪一个方法.
- 当访问的是book_add,这时就会调用BookAction类中的add方法。
<action name="book_add" class="cn.itcast.action.BookAction" method="add"></action>
- 当访问的是book_update,这时就会调用BookAction类中的update方法。
<action name="book_update" class="cn.itcast.action.BookAction" method="update"></action>
- 当访问的是book_add,这时就会调用BookAction类中的add方法。
2.使用通配符来简化配置
- 1.在struts.xml文件中
<action name="*_*" class="cn.itcast.action.{1}Action" method="{2}"></action>
- 2.在jsp页面上
- book.jsp
- 1.在struts.xml文件中
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Book_add">book add</a><br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Book_update">book update</a><br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Book_delete">book delete</a><br>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/Book_search">book search</a><br>* 当访问book add时,这时的路径是 Book_add,那么对于struts.xml文件中.
* `*_*`代表匹配两个字符串
* {1} 匹配UserAction 用于执行class
* {2} 匹配login用于指定method执行方法 和结果页面
* 第一个星就是 Book
* 第二个星就是 add
* 对于{1}Action---->BookAction
* 对于method={2}--->method=add
* 使用通配符来配置注意事项:
* 1.必须定义一个统一的命名规范。
* 2.不建议使用过多的通配符,阅读不方便。
- 3.动态方法调用 (了解)
- 通过url动态指定调用Action哪个方法而无需配置
<action>的method属性 - 通过
!方法名指定调用Action哪个方法
- 通过url动态指定调用Action哪个方法而无需配置
struts.xml没有指定method属性,但
product!add.action就会执行ProductAction的add方法eg:在struts.xml文件中
<action name="book" class="cn.itcast.action.BookAction"></action>* 访问时路径: http://localhost/struts2_day01_2/book!add
* 就访问到了BookAction类中的add方法。
* 对于`book!add` 这就是动态方法调用。
* 注意:struts2框架支持动态方法调用,是因为在`default.properties`配置文件中设置了动态方法调用为**true**.
* 第108行 `struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation = true`
在struts2框架中获取servlet API
- 对于struts2框架,不建议直接使用servlet api;
在struts2中获取servlet api有三种方式
1.通过ActionContext来获取
- 1.获取一个ActionContext对象。
ActionContext context=ActionContext.getContext();:返回ActionContext实例对象
- 2.获取servlet api
- 注意:通过ActionContext获取的不是真正的Servlet api,而是一个Map集合。
- 1.context.getApplication() : 返回一个Map对象,存取ServletContext属性
- 2.context.getSession() : 返回一个Map对象,存取HttpSession属性
- 3.context.getParameter() : 得到的就相当于request.getParameterMap()
- 4.context.put(String,Object) : 相当于request.setAttribute(String,String);
- 5.context.get(key) 相当于 HttpServletRequest的getAttribute(String name)方法
- 6.context.setApplication(Map) 将该Map实例里key-value保存为ServletContext的属性名、属性值
- 7.setSession(Map) 将该Map实例里key-value保持为HttpSession的属性名、属性值
- 1.获取一个ActionContext对象。
2.注入方式获取(这种方式是真正的获取到了servlet api)
1.要求action类必须实现指定接口。
- ServletContextAware : 注入ServletContext对象
- ServletRequestAware :注入 request对象
- ServletResponseAware : 注入response对象
2.重定接口中的方法。
- private HttpServletRequest request;
- 3.声明一个web对象,使用接口中的方法的参数对声明的web对象赋值.
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}- 扩展:分析其实现:
- 是使用struts2中的一个interceptor完成的.
<interceptor name="servletConfig" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletConfigInterceptor"/>
if (action instanceof ServletRequestAware) { //判断action是否实现了ServletRequestAware接口
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) context.get(HTTP_REQUEST); //得到request对象.
((ServletRequestAware) action).setServletRequest(request);//将request对象通过action中重写的方法注入。
}- 3.通过ServletActionContext获取.
- 该方案可避免Action类实现XxxAware接口,但Action依然与Servlet API直接耦合
- 开发中优先使用ActionContext 这样可以避免耦合
- 在ServletActionContext中方法都是static。
- ServletActionContext.getRequest() : 获得request对象 (session)
- ServletActionContext.getResponse() : 获得response 对象
- ServletActionContext.getServletContext() : 获得ServletContext对象
- 静态方法没有线程问题,ThreadLocal
Result结果类型
Action处理请求后, 返回字符串(逻辑视图名), Struts2 根据逻辑视图名,决定响应哪个结果,需要在struts.xml 提供
<result>元素定义结果页面<result>标签属性- 1.name 与action中的method的返回值匹配,进行跳转.
- 2.type 作用:是用于定义跳转方式
- 对于type属性它的值有以下几种:
- 在struts-default.xml文件中定义了type可以取的值
<result-type name="chain" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionChainResult"/>
<result-type name="dispatcher" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ServletDispatcherResult" default="true"/>
<result-type name="freemarker" class="org.apache.struts2.views.freemarker.FreemarkerResult"/>
<result-type name="httpheader" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.HttpHeaderResult"/>
<result-type name="redirect" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ServletRedirectResult"/>
<result-type name="redirectAction" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ServletActionRedirectResult"/>
<result-type name="stream" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.StreamResult"/>
<result-type name="velocity" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.VelocityResult"/>
<result-type name="xslt" class="org.apache.struts2.views.xslt.XSLTResult"/>
<result-type name="plainText" class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.PlainTextResult" />必会: chain dispatcher redirect redirectAction stream
dispatcher:它代表的是请求转发,也是默认值。它一般用于从action跳转到页面。该结果类型有一个 location 参数, 它是一个默认参数
- dispatcher 结果类型将把控制权转发给应用程序里的某个资源.
- dispatcher 结果类型不能把控制权转发给一个外部资源. 若需要把控制权重定向到一个外部资源, 应该使用 redirect 结果类型
chain:它也相当于请求转发。它一般情况下用于从一个action跳转到另一个action。redirect:它代表的是重定向 它一般用于从action跳转到页面- redirect 结果类型接受下面这些参数:
redirectAction: 它代表的是重定向 它一般用于从action跳转另一个action。
- actionName: 指定 “目的地” 动作的名字. 它是默认属性
- namespace: 用来指定 “目的地” 动作的命名空间. 如果没有配置该参数, Struts 会把当前 Action 所在的命名空间作为 “目的地” 的命名空间
stream:代表的是服务器端返回的是一个流,一般用于下载。
了解: freemarker velocity
- 局部结果页面与全局结果页面
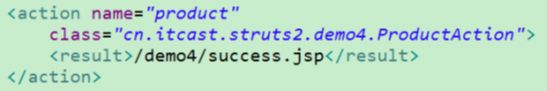
<action name="result" class="cn.itcast.struts2.demo6.ResultAction">
<!-- 局部结果 当前Action使用 -->
<result name="success">/demo6/result.jsp</result>
</action>
<global-results>
<!-- 全局结果 当前包中 所有Action都可以用-->
<result name="success">/demo6/result.jsp</result>
</global-results><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
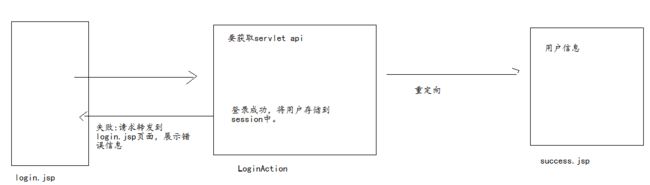
<package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<action name="login" class="cn.itcast.action.LoginAction">
<result name="failer">/login.jsp</result>
<result type="redirect">/success.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>- LoginAction.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<action name="login" class="cn.itcast.action.LoginAction">
<result name="failer">/login.jsp</result>
<result type="redirect">/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="login1" class="cn.itcast.action.Login1Action">
<result name="failer">/login1.jsp</result>
<result type="redirect">/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="login2" class="cn.itcast.action.Login2Action">
<result name="failer">/login2.jsp</result>
<result type="redirect">/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="login3" class="cn.itcast.action.Login3Action">
<result name="failer">/login3.jsp</result>
<result type="redirect">/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="list" class="cn.itcast.action.ListAction">
</action>
<action name="map" class="cn.itcast.action.MapAction">
</action>
</package>
</struts>- login.jsp & success.jsp
//login.jsp
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
${requestScope["login.message"] }<br>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="post">
username:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
password:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
//success.jsp
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
${username}
</body>
</html>