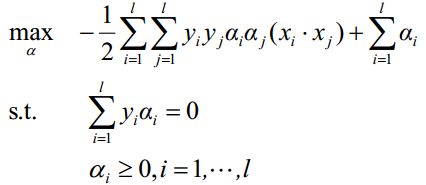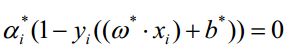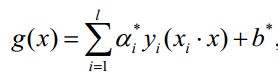SparkML之分类(三)支持向量机(SVM)
一、数学原理
支持向量机(SVM)是由Vladimir N. Vapnik和 Alexey Ya. Chervonenkis在1963年提出的。SVM的提出解决了当时在机
器学习领域的“维数灾难”,“过学习”等问题。它在机器学习领域可以用于分类和回归(更多信息可以参考文献1)。
SVM在回归可以解决股票价格回归等问题,但是在回归上SVM还是很局限,SVM大部分会和分类放在一起。所以本节
主要讲的是SVM的分类问题。
1、支持向量分类机的基本原理
给的训练集:
其中![]() ,
,![]() 称为输入空间,空间中的每一个点
称为输入空间,空间中的每一个点![]() 都是由n个属性组成,
都是由n个属性组成,![]() 。寻找
。寻找![]() 上的
上的
一个实值函数![]() ,以便使用分类函数
,以便使用分类函数
![]()
对,给定一个![]() ,都可以得到相应的
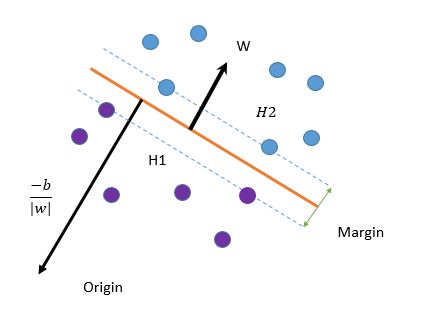
,都可以得到相应的![]() .对于這样的分类问题,希望结合下图可以更加清晰原理
.对于這样的分类问题,希望结合下图可以更加清晰原理
SVM算法的目的就是找出一个超平面(函数),能够把不一样的类(点)能够分开,上面的橙色线就是我们要找的
超平面(函数)。现在我们定义这个超平面(函数)的表达式:
![]()
其中![]() 称为权重,
称为权重,![]() 为偏执。
为偏执。
对于![]() 的取值来决定划分的界定,我们一般选择
的取值来决定划分的界定,我们一般选择 ![]()
现在我们来证明:当训练集样本为线性可分时,存在唯一的规范超平面![]() ,使得:
,使得:
证明:超平面存在是显然的,现在来证明唯一性
假设有两个:
又因为:
那么由条件可以得到:![]() ,
,
证明完毕--------------------------------------------------------
那么现在来确定![]() 和
和![]() 的数值。
的数值。
当![]() =-1的点落在f(x)<0一边,当
=-1的点落在f(x)<0一边,当![]() =1的点落在f(x)>0一边,使得:
=1的点落在f(x)>0一边,使得:
对于![]() 类的样本点,其Margin的数值为:
类的样本点,其Margin的数值为:
对于![]() 类的样本点,其Margin的数值为:
类的样本点,其Margin的数值为:
于是寻找最优的划分转化为如下的二次规划问题:
利用Lagrange乘子法得到最优解
引入Lagrange乘子:
其中,![]() 为Lagrange乘子,对各个变量求导:
为Lagrange乘子,对各个变量求导:
带入 Lagrange 函数化为原问题的 Lagrange 对偶问题:
load sample_svm_data.txt
Data = sample_svm_data;
% Data是 322*17的矩阵
% 第一列为标签,2到17列为量化的特征
%数据前7份用于训练,后3份用于测试
splitePoint = ceil(0.7*length(Data));
trainData = Data(1:splitePoint,:);
testData = Data(splitePoint:end,:);
yesID = find(trainData(:,1)==1);%标记为1的ID
noID = find(trainData(:,1)==0);%标记为0的ID
yesData = trainData(yesID,2:end);%取出标记为1的数据
noData = trainData(noID,2:end);%取出标记为0的数据
%规划
H = eye(17);H(17,17) = 0;%用于存放w,b的待定系数,b对应最后一个
yesMatrix = [yesData,ones(length(yesData),1)];
noMatrix = [noData,ones(length(noData),1)];
a = [-yesMatrix;noMatrix];
b = -ones(length(trainData),1);
[wb,fval,flag] = quadprog(H,[],a,b);%wb为所求系数
test = [testData(:,2:end),ones(length(testData),1)];
g = test*wb;
g1 = find(g>0)'; %标记为1的
g0 = find(g<0)'; %标记为0的
%检测效果
it = 0;
for i = 1:length(g0)
if testData(g0(i),1) == 0
it = it+1;
end
end
for i = 1:length(g1)
if testData(g1(i),1) == 1
it = it+1;
end
end
%正确率
rate = it/length(testData)
%rate = 0.5361
发现效果不是很好,所以一般在确定SVM的f(x)时候,最常用的就是引入Lagrange乘子
Spark源码分析
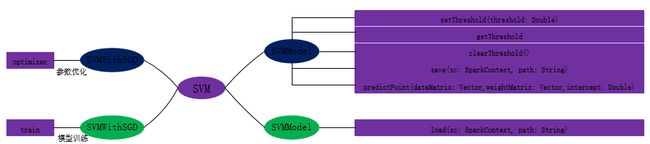
package org.apache.spark.mllib.classification
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.annotation.Since
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.impl.GLMClassificationModel
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vector
import org.apache.spark.mllib.optimization._
import org.apache.spark.mllib.pmml.PMMLExportable
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression._
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.{DataValidators, Loader, Saveable}
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
/**
* Model for Support Vector Machines (SVMs).
*
* @param weights 每个变量的权重.
* @param intercept SVM模型的偏置项
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
class SVMModel @Since("1.1.0") (
@Since("1.0.0") override val weights: Vector,
@Since("0.8.0") override val intercept: Double)
extends GeneralizedLinearModel(weights, intercept) with ClassificationModel with Serializable
with Saveable with PMMLExportable {
//偏置项设置为0.0
private var threshold: Option[Double] = Some(0.0)
//自己设置偏执(来决定什么时候为正,什么时候为负)
@Since("1.0.0")
def setThreshold(threshold: Double): this.type = {
this.threshold = Some(threshold)
this
}
//返回设置的偏执项(如果有的话),
@Since("1.3.0")
def getThreshold: Option[Double] = threshold
//清除偏置项(在计算的时候对于大部分预测回归都是会這么做)
@Since("1.0.0")
def clearThreshold(): this.type = {
threshold = None
this
}
def predictPoint(dataMatrix: Vector,weightMatrix: Vector,intercept: Double)
override protected def predictPoint(
dataMatrix: Vector,
weightMatrix: Vector,
intercept: Double) = {
val margin = weightMatrix.toBreeze.dot(dataMatrix.toBreeze) + intercept
threshold match {
case Some(t) => if (margin > t) 1.0 else 0.0
case None => margin
}
}
//模型的保存
@Since("1.3.0")
override def save(sc: SparkContext, path: String): Unit = {
GLMClassificationModel.SaveLoadV1_0.save(sc, path, this.getClass.getName,
numFeatures = weights.size, numClasses = 2, weights, intercept, threshold)
}
override protected def formatVersion: String = "1.0"
//重写toString方法
override def toString: String = {
s"${super.toString}, numClasses = 2, threshold = ${threshold.getOrElse("None")}"
}
}
@Since("1.3.0")
//SVMModel类的同名对象
object SVMModel extends Loader[SVMModel] {
@Since("1.3.0")
//加载模型(之前自己保存的)
override def load(sc: SparkContext, path: String): SVMModel = {
//输入给的的路径,导出元数据(之前训练好的)
val (loadedClassName, version, metadata) = Loader.loadMetadata(sc, path)
// Hard-code class name string in case it changes in the future
val classNameV1_0 = "org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.SVMModel"
(loadedClassName, version) match {
case (className, "1.0") if className == classNameV1_0 =>
val (numFeatures, numClasses) = ClassificationModel.getNumFeaturesClasses(metadata)
val data = GLMClassificationModel.SaveLoadV1_0.loadData(sc, path, classNameV1_0)
val model = new SVMModel(data.weights, data.intercept)
assert(model.weights.size == numFeatures, s"SVMModel.load with numFeatures=$numFeatures" +
s" was given non-matching weights vector of size ${model.weights.size}")
assert(numClasses == 2,
s"SVMModel.load was given numClasses=$numClasses but only supports 2 classes")
data.threshold match {
case Some(t) => model.setThreshold(t)
case None => model.clearThreshold()
}
//返回的SVM模型
model
case _ => throw new Exception(
s"SVMModel.load did not recognize model with (className, format version):" +
s"($loadedClassName, $version). Supported:\n" +
s" ($classNameV1_0, 1.0)")
}
}
}
SVMWithSGD
/**
*用随机梯度下降训练SVM,默认采用L2正则化
* NOTE: Labels used in SVM should be {0, 1}.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
class SVMWithSGD private (
private var stepSize: Double,
private var numIterations: Int,
private var regParam: Double,
private var miniBatchFraction: Double)
extends GeneralizedLinearAlgorithm[SVMModel] with Serializable {
private val gradient = new HingeGradient()
private val updater = new SquaredL2Updater()
@Since("0.8.0")
//设置各种参数
override val optimizer = new GradientDescent(gradient, updater)
.setStepSize(stepSize)
.setNumIterations(numIterations)
.setRegParam(regParam)
.setMiniBatchFraction(miniBatchFraction)
override protected val validators = List(DataValidators.binaryLabelValidator)
/**
* 一个SVM默认参数: {stepSize: 1.0, numIterations: 100,
* regParm: 0.01, miniBatchFraction: 1.0}.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
def this() = this(1.0, 100, 0.01, 1.0)
override protected def createModel(weights: Vector, intercept: Double) = {
new SVMModel(weights, intercept)
}
}
/**
* Top-level methods for calling SVM. NOTE: Labels used in SVM should be {0, 1}.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
//SVMWithSGD的同名对象
//作用是利用构造函数,实现各种输入方式
object SVMWithSGD {
/**
* 对于给定的(label, features) pairs类型的RDD去训练SVM
*
* NOTE: Labels used in SVM should be {0, 1}.
*
* @param input RDD of (label, array of features) pairs.
* @param numIterations Number of iterations of gradient descent to run.
* @param stepSize Step size to be used for each iteration of gradient descent.
* @param regParam Regularization parameter.
* @param miniBatchFraction Fraction of data to be used per iteration.
* @param initialWeights Initial set of weights to be used. Array should be equal in size to
* the number of features in the data.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
def train(
input: RDD[LabeledPoint],
numIterations: Int,
stepSize: Double,
regParam: Double,
miniBatchFraction: Double,
initialWeights: Vector): SVMModel = {
new SVMWithSGD(stepSize, numIterations, regParam, miniBatchFraction)
.run(input, initialWeights)
}
/**
* Train a SVM model given an RDD of (label, features) pairs. We run a fixed number
* of iterations of gradient descent using the specified step size. Each iteration uses
* `miniBatchFraction` fraction of the data to calculate the gradient.
* NOTE: Labels used in SVM should be {0, 1}
*
* @param input RDD of (label, array of features) pairs.
* @param numIterations Number of iterations of gradient descent to run.
* @param stepSize Step size to be used for each iteration of gradient descent.
* @param regParam Regularization parameter.
* @param miniBatchFraction Fraction of data to be used per iteration.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
def train(
input: RDD[LabeledPoint],
numIterations: Int,
stepSize: Double,
regParam: Double,
miniBatchFraction: Double): SVMModel = {
new SVMWithSGD(stepSize, numIterations, regParam, miniBatchFraction).run(input)
}
/**
* Train a SVM model given an RDD of (label, features) pairs. We run a fixed number
* of iterations of gradient descent using the specified step size. We use the entire data set to
* update the gradient in each iteration.
* NOTE: Labels used in SVM should be {0, 1}
*
* @param input RDD of (label, array of features) pairs.
* @param stepSize Step size to be used for each iteration of Gradient Descent.
* @param regParam Regularization parameter.
* @param numIterations Number of iterations of gradient descent to run.
* @return a SVMModel which has the weights and offset from training.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
def train(
input: RDD[LabeledPoint],
numIterations: Int,
stepSize: Double,
regParam: Double): SVMModel = {
train(input, numIterations, stepSize, regParam, 1.0)
}
/**
* Train a SVM model given an RDD of (label, features) pairs. We run a fixed number
* of iterations of gradient descent using a step size of 1.0. We use the entire data set to
* update the gradient in each iteration.
* NOTE: Labels used in SVM should be {0, 1}
*
* @param input RDD of (label, array of features) pairs.
* @param numIterations Number of iterations of gradient descent to run.
* @return a SVMModel which has the weights and offset from training.
*/
@Since("0.8.0")
def train(input: RDD[LabeledPoint], numIterations: Int): SVMModel = {
train(input, numIterations, 1.0, 0.01, 1.0)
}
}
Spark实验
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.{SVMModel, SVMWithSGD} import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.BinaryClassificationMetrics import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils object SVMWithSGDExample { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("SVMWithSGDExample").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) // Load training data in LIBSVM format. val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "C:\\Users\\alienware\\IdeaProjects\\sparkCore\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt") // Split data into training (60%) and test (40%). val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 11L) val training = splits(0).cache() val test = splits(1) // Run training algorithm to build the model val numIterations = 100 val model = SVMWithSGD.train(training, numIterations) // Clear the default threshold. model.clearThreshold() // Compute raw scores on the test set. val scoreAndLabels = test.map { point => val score = model.predict(point.features) (score, point.label) } // Get evaluation metrics. val metrics = new BinaryClassificationMetrics(scoreAndLabels) val auROC = metrics.areaUnderROC() println("Area under ROC = " + auROC) //Area under ROC = 1.0 // Save and load model model.save(sc, "target/tmp/scalaSVMWithSGDModel") val sameModel = SVMModel.load(sc, "target/tmp/scalaSVMWithSGDModel") sc.stop() } }
参考文献
1、https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine