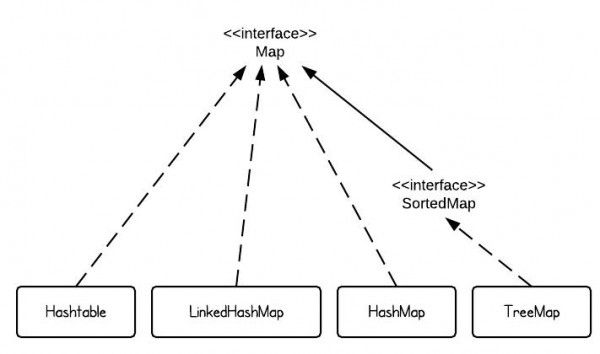
HashMap 、TreeMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap
HashMap
通过一个哈希表实现,无序
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Dog, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<Dog, Integer>();
Dog d1 = new Dog("red");
Dog d2 = new Dog("black");
Dog d3 = new Dog("white");
Dog d4 = new Dog("white");
hashMap.put(d1, 10);
hashMap.put(d2, 15);
hashMap.put(d3, 5);
hashMap.put(d4, 20);
//print size
System.out.println(hashMap.size());
//loop HashMap
for (Entry<Dog, Integer> entry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey().toString() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}输出:
4
white dog - 5
black dog - 15
red dog - 10
white dog - 20white dog被添加了2次,因为默认HashMap对象无法区分这两次的区别,需要添加实现hashCode 和 equals方法
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return ((Dog) o).color.equals(this.color);
}
public int hashCode() {
return color.length();
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}TreeMap
基于红黑树实现、根据Key排序的有序表
如果直接使用
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return ((Dog) o).color.equals(this.color);
}
public int hashCode() {
return color.length();
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog("red");
Dog d2 = new Dog("black");
Dog d3 = new Dog("white");
Dog d4 = new Dog("white");
TreeMap<Dog, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Dog, Integer>();
treeMap.put(d1, 10);
treeMap.put(d2, 15);
treeMap.put(d3, 5);
treeMap.put(d4, 20);
for (Entry<Dog, Integer> entry : treeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}将会抛出异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: collection.Dog cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
at java.util.TreeMap.put(Unknown Source)
需要对象实现Comparable接口
class Dog implements Comparable<Dog>{
String color;
int size;
Dog(String c, int s) {
color = c;
size = s;
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Dog o) {
return o.size - this.size;
}
}或者使用new TreeMap(comparator)构造器
TreeMap<Dog, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Dog, Integer>(
new Comparator<Dog>() {
@Override
public int compare(Dog o1, Dog o2) {
return o2.size - o1.size;
}
});Hashtable
线程同步的HashMap
LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的一个子类,它保留了HashMap的所有特点同时他也记录下了元素的插入顺序,如:
class Dog {
String color;
Dog(String c) {
color = c;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return ((Dog) o).color.equals(this.color);
}
public int hashCode() {
return color.length();
}
public String toString(){
return color + " dog";
}
}
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog("red");
Dog d2 = new Dog("black");
Dog d3 = new Dog("white");
Dog d4 = new Dog("white");
LinkedHashMap<Dog, Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<Dog, Integer>();
linkedHashMap.put(d1, 10);
linkedHashMap.put(d2, 15);
linkedHashMap.put(d3, 5);
linkedHashMap.put(d4, 20);
for (Entry<Dog, Integer> entry : linkedHashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " - " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}输出
red dog - 10
black dog - 15
white dog - 20和插入顺序一致