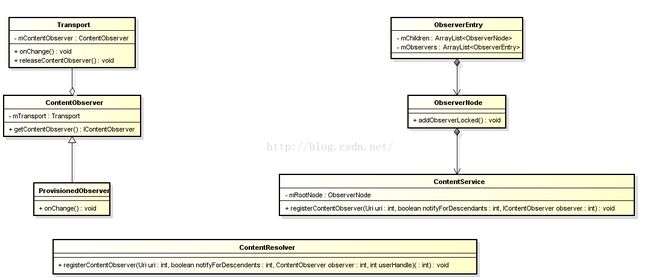
Android ContentObserver 学习
当我们查询数据中某个值是否变化时,通常很耗时费力,数据量大时可能还需要开辟线程来做这种事,急需一种及时反馈机制来处理这种问题,ContentObserver的提供的很
好的解决方案。
ContentObserver为内容观察着,目的就是捕捉内容的变化,当所观察的Uri发生变化时,就会被触发,当然有内容观察者就离不开内容提供者。
内容观察者实现
下面以Android源码中的ProvisionedObserver展开分析:
class ProvisionedObserver extends ContentObserver {
public ProvisionedObserver(Handler handler) {
super(handler);
}
public void onChange(boolean selfChange) {
final boolean wasProvisioned = mProvisioned;
final boolean isProvisioned = deviceIsProvisioned();
// latch: never unprovision
mProvisioned = wasProvisioned || isProvisioned;
if (MORE_DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Provisioning change: was=" + wasProvisioned
+ " is=" + isProvisioned + " now=" + mProvisioned);
}
synchronized (mQueueLock) {
if (mProvisioned && !wasProvisioned && mEnabled) {
// we're now good to go, so start the backup alarms
if (MORE_DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Now provisioned, so starting backups");
startBackupAlarmsLocked(FIRST_BACKUP_INTERVAL);
}
}
}
}ProvisionedObserver作为ContentObserver的子类主要实现了一个onChange,构造时传入了一个hander,方法其实就是观察的内容发生变化时会被触发调用,但是handler的
作用被没有体现出来,我们再看ContentObserver类的方法dispatchChange
/**
* Dispatches a change notification to the observer. Includes the changed
* content Uri when available and also the user whose content changed.
* <p>
* If a {@link Handler} was supplied to the {@link ContentObserver} constructor,
* then a call to the {@link #onChange} method is posted to the handler's message queue.
* Otherwise, the {@link #onChange} method is invoked immediately on this thread.
* </p>
*
* @param selfChange True if this is a self-change notification.
* @param uri The Uri of the changed content, or null if unknown.
* @param userId The user whose content changed.
*/
private void dispatchChange(boolean selfChange, Uri uri, int userId) {
if (mHandler == null) {
onChange(selfChange, uri, userId);
} else {
mHandler.post(new NotificationRunnable(selfChange, uri, userId));
}
}?如果传入的handler是null,则会调用父类自身的onChange,反之就会通过NotificationRunnable调用到ProvisionedObserver的onChange方法,而dispatchChange是在内部
类Transport 的onChange方法中完成
private static final class Transport extends IContentObserver.Stub {
private ContentObserver mContentObserver;
public Transport(ContentObserver contentObserver) {
mContentObserver = contentObserver;
}
@Override
public void onChange(boolean selfChange, Uri uri, int userId) {
ContentObserver contentObserver = mContentObserver;
if (contentObserver != null) {
contentObserver.dispatchChange(selfChange, uri, userId);
}
}
public void releaseContentObserver() {
mContentObserver = null;
}
}?似乎分析到这里,发现接截止在Transport.onChange
注册流程分析
下面看看ProvisionedObserver的注册
final ContentResolver resolver = context.getContentResolver(); mProvisionedObserver = new ProvisionedObserver(mBackupHandler); resolver.registerContentObserver( Settings.Global.getUriFor(Settings.Global.DEVICE_PROVISIONED), false, mProvisionedObserver);接着进入文件ContentResolver.java的registerContentObserver
/**
* Register an observer class that gets callbacks when data identified by a
* given content URI changes.
*
* @param uri The URI to watch for changes. This can be a specific row URI, or a base URI
* for a whole class of content.
* @param notifyForDescendents If <code>true</code> changes to URIs beginning with <code>uri</code>
* will also cause notifications to be sent. If <code>false</code> only changes to the exact URI
* specified by <em>uri</em> will cause notifications to be sent. If <code>true</code>, any URI values
* at or below the specified URI will also trigger a match.
* @param observer The object that receives callbacks when changes occur.
* @see #unregisterContentObserver
*/
public final void registerContentObserver(Uri uri, boolean notifyForDescendents,
ContentObserver observer)
{
registerContentObserver(uri, notifyForDescendents, observer, UserHandle.myUserId());
}
/** @hide - designated user version */
public final void registerContentObserver(Uri uri, boolean notifyForDescendents,
ContentObserver observer, int userHandle)
{
try {
getContentService().registerContentObserver(uri, notifyForDescendents,
observer.getContentObserver(), userHandle);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
getContentService().registerContentObserver(uri, notifyForDescendents,
observer.getContentObserver(), userHandle); 会进入ContentService.registerContentObserve中
public void registerContentObserver(Uri uri, boolean notifyForDescendants,
IContentObserver observer, int userHandle) {
if (observer == null || uri == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must pass a valid uri and observer");
}
enforceCrossUserPermission(userHandle,
"no permission to observe other users' provider view");
if (userHandle < 0) {
if (userHandle == UserHandle.USER_CURRENT) {
userHandle = ActivityManager.getCurrentUser();
} else if (userHandle != UserHandle.USER_ALL) {
throw new InvalidParameterException("Bad user handle for registerContentObserver: "
+ userHandle);
}
}
synchronized (mRootNode) {
mRootNode.addObserverLocked(uri, observer, notifyForDescendants, mRootNode,
Binder.getCallingUid(), Binder.getCallingPid(), userHandle);
if (false) Log.v(TAG, "Registered observer " + observer + " at " + uri +
" with notifyForDescendants " + notifyForDescendants);
}
}其中observer就是ProvisionedObserver.getContentObserver,如下
/**
* Gets access to the binder transport object. Not for public consumption.
*
* {@hide}
*/
public IContentObserver getContentObserver() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mTransport == null) {
mTransport = new Transport(this);
}
return mTransport;
}
}ContentService.registerContentObserver传入的observer也即是一个Transport,然后添加到mRootNode中
public void addObserverLocked(Uri uri, IContentObserver observer,
boolean notifyForDescendants, Object observersLock,
int uid, int pid, int userHandle) {
addObserverLocked(uri, 0, observer, notifyForDescendants, observersLock,
uid, pid, userHandle);
}
private void addObserverLocked(Uri uri, int index, IContentObserver observer,
boolean notifyForDescendants, Object observersLock,
int uid, int pid, int userHandle) {
// If this is the leaf node add the observer
if (index == countUriSegments(uri)) {
mObservers.add(new ObserverEntry(observer, notifyForDescendants, observersLock,
uid, pid, userHandle));
return;
}
// Look to see if the proper child already exists
String segment = getUriSegment(uri, index);
if (segment == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Uri (" + uri + ") used for observer");
}
int N = mChildren.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
ObserverNode node = mChildren.get(i);
if (node.mName.equals(segment)) {
node.addObserverLocked(uri, index + 1, observer, notifyForDescendants,
observersLock, uid, pid, userHandle);
return;
}
}
// No child found, create one
ObserverNode node = new ObserverNode(segment);
mChildren.add(node);
node.addObserverLocked(uri, index + 1, observer, notifyForDescendants,
observersLock, uid, pid, userHandle);
}在这个过程中,新增的内容观察者全部添加ContentService.mObservers链表中,等待触发。
触发流程
上面已经分析了,内容观察者的继承,注册,触发则有内容提供的源头来发起,也有ContentProvider来触发。通常数据变化发生在insert,delete,update三个操作中。
ContentProvider在完成insert,delete,update之后就会调用getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(url, null)来通知内容发生变化,至此整个注册,触发形成闭环。
ContentService.notifyChange触发函数如下:
/**
* Notify observers of a particular user's view of the provider.
* @param userHandle the user whose view of the provider is to be notified. May be
* the calling user without requiring any permission, otherwise the caller needs to
* hold the INTERACT_ACROSS_USERS_FULL permission. Pseudousers USER_ALL and
* USER_CURRENT are properly interpreted; no other pseudousers are allowed.
*/
@Override
public void notifyChange(Uri uri, IContentObserver observer,
boolean observerWantsSelfNotifications, boolean syncToNetwork,
int userHandle) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Notifying update of " + uri + " for user " + userHandle
+ " from observer " + observer + ", syncToNetwork " + syncToNetwork);
}
// Notify for any user other than the caller's own requires permission.
final int callingUserHandle = UserHandle.getCallingUserId();
if (userHandle != callingUserHandle) {
mContext.enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.INTERACT_ACROSS_USERS,
"no permission to notify other users");
}
// We passed the permission check; resolve pseudouser targets as appropriate
if (userHandle < 0) {
if (userHandle == UserHandle.USER_CURRENT) {
userHandle = ActivityManager.getCurrentUser();
} else if (userHandle != UserHandle.USER_ALL) {
throw new InvalidParameterException("Bad user handle for notifyChange: "
+ userHandle);
}
}
final int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
// This makes it so that future permission checks will be in the context of this
// process rather than the caller's process. We will restore this before returning.
long identityToken = clearCallingIdentity();
try {
ArrayList<ObserverCall> calls = new ArrayList<ObserverCall>();
synchronized (mRootNode) {
mRootNode.collectObserversLocked(uri, 0, observer, observerWantsSelfNotifications,
userHandle, calls);
}
final int numCalls = calls.size();
for (int i=0; i<numCalls; i++) {
ObserverCall oc = calls.get(i);
try {
oc.mObserver.onChange(oc.mSelfChange, uri, userHandle);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Notified " + oc.mObserver + " of " + "update at " + uri);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
synchronized (mRootNode) {
Log.w(TAG, "Found dead observer, removing");
IBinder binder = oc.mObserver.asBinder();
final ArrayList<ObserverNode.ObserverEntry> list
= oc.mNode.mObservers;
int numList = list.size();
for (int j=0; j<numList; j++) {
ObserverNode.ObserverEntry oe = list.get(j);
if (oe.observer.asBinder() == binder) {
list.remove(j);
j--;
numList--;
}
}
}
}
}
if (syncToNetwork) {
SyncManager syncManager = getSyncManager();
if (syncManager != null) {
syncManager.scheduleLocalSync(null /* all accounts */, callingUserHandle, uid,
uri.getAuthority());
}
}
} finally {
restoreCallingIdentity(identityToken);
}
}从观察者列表中获取内容观察者(Transport), 然后调用onChange.