android 使用Scroller实现美团悬浮框,网易左右滑动菜单效果
Scroller类其实就是对View的scrollTo()以及ScrollBy()方法封装以及优化,比如我们熟悉的网易客户端主界面的侧滑菜单,如果要实现当滑动超过一半的时候回弹的效果,而不是一下子就回到了最终点,view的scrollTo(),scrollBy()方法是没有做这个功能的,而Scroller类就做了这些优化,使用起来更方便,如果对View的那个二个方法很真的懂了的话,讲Scroller就很容易懂,不懂的话可以去看下我另外一篇关于View的scrollTo()和scrollBy()方法,自认为讲的比较详细,讲Scroller类首先从它的构造花函数讲起,在API 11之前就2个构造函数,API 11后添加了一个新的构造函数,
/** * Create a Scroller with the default duration and interpolator. */ public Scroller(Context context) { this(context, null); } /** * Create a Scroller with the specified interpolator. If the interpolator is * null, the default (viscous) interpolator will be used. "Flywheel" behavior will * be in effect for apps targeting Honeycomb or newer. */ public Scroller(Context context, Interpolator interpolator) { this(context, interpolator, context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB); } /** * Create a Scroller with the specified interpolator. If the interpolator is * null, the default (viscous) interpolator will be used. Specify whether or * not to support progressive "flywheel" behavior in flinging. */ public Scroller(Context context, Interpolator interpolator, boolean flywheel) { mFinished = true; if (interpolator == null) { mInterpolator = new ViscousFluidInterpolator(); } else { mInterpolator = interpolator; } mPpi = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density * 160.0f; mDeceleration = computeDeceleration(ViewConfiguration.getScrollFriction()); mFlywheel = flywheel; mPhysicalCoeff = computeDeceleration(0.84f); // look and feel tuning }第一个构造函数很简单,就一个Context形参,无需做过多的介绍
第二个构造函数,第一个形参还是Context,第二个形参是插补器,里面封装了很多动画效果,
第三个构造函数有三个形参,最后一个形参是boolean值,是API 11后有的,什么意思先留在这里
今天就不讲Interpolator 这个类的使用,因为它会涉及很多子类,每个子类对应的动画效果不一样,到时候会讲动画系列会好好讲下,
现在看下Scroller类都给我们提供了哪些方法可以给我们调用,
public final boolean isFinished() {} 判断滑动是否结束
public final int getDuration() {} 返回滑动所需的时间(单位为毫秒)
public final int getCurrX() {} 返回当前x轴偏移量
public final int getCurrY() {} 返回当前y轴偏移量
public float getCurrVelocity(){}返回当前滚动的速度
public final void forceFinished(boolean finished) {}强制终止滚动
public final int getStartX() {} 返回滚动起始点x轴偏移量
public final int getStartY() {} 返回滚动起始点y轴偏移量
public final int getFinalX() {}返回滚动结束x轴的偏移量
public final int getFinalY() {}返回滚动结束y轴的偏移量
public boolean computeScrollOffset() {} 判断是否滑动结束,
public void setFinalX(int newX) {} 设置x轴方向终止偏移量
public void setFinalY(int newY) {} 设置y轴方向终止偏移量
public int timePassed() {}返回开始滑动经过的时间
public void extendDuration(int extend) {}延迟extend 秒再滑动
public void abortAnimation() {}终止动画执行
public void fling(int startX, int startY, int velocityX, int velocityY,int minX, int maxX, int minY, int maxY) {} 快速滑动松开手势惯性滑动
使用Scroller类实现view的滑动一般就三个步骤
第一步:创建Scroller类的对象
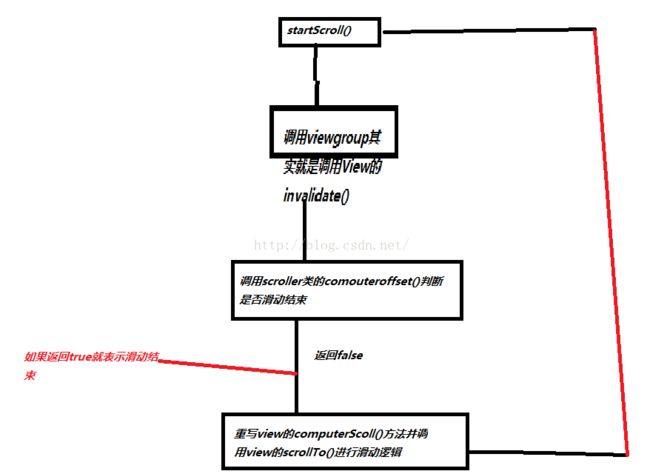
第二步:调用Scroller类的startScroll()方法,先看下它的源码:
/** * Start scrolling by providing a starting point, the distance to travel, * and the duration of the scroll. * * @param startX Starting horizontal scroll offset in pixels. Positive * numbers will scroll the content to the left. * @param startY Starting vertical scroll offset in pixels. Positive numbers * will scroll the content up. * @param dx Horizontal distance to travel. Positive numbers will scroll the * content to the left. * @param dy Vertical distance to travel. Positive numbers will scroll the * content up. * @param duration Duration of the scroll in milliseconds. */ public void startScroll(int startX, int startY, int dx, int dy, int duration) { mMode = SCROLL_MODE; mFinished = false; mDuration = duration; mStartTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis(); mStartX = startX; mStartY = startY; mFinalX = startX + dx; mFinalY = startY + dy; mDeltaX = dx; mDeltaY = dy; mDurationReciprocal = 1.0f / (float) mDuration; }你会发现这个方法其实一堆赋值操作,并没有帮你实现滑动的逻辑,滑动的逻辑其实还是调用View的scrollTo()方法,startScroll()方法就是初始化了一些滑动的数据
第三步:调用Scroller类的computeScrollOffset()方法判断是否滑动到了终点,如果没有滑动到终点的话就重写View的computeScroll()方法,这个方法在View中是空实现,所以重写这个方法实现你继续滑动的逻辑,为什么会调用这个方法呢?结合源码分析:
首先会调用ViewGroup中的invalidate()方法,因为ViewGroup是继承自View的,而ViewGroup并没有重写invalidate()方法,所以调用的是View中的invalidate()方法:
/** * Invalidate the whole view. If the view is visible, * {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} will be called at some point in * the future. This must be called from a UI thread. To call from a non-UI thread, * call {@link #postInvalidate()}. */ public void invalidate() { invalidate(true); }调用如下方法:
/** * This is where the invalidate() work actually happens. A full invalidate() * causes the drawing cache to be invalidated, but this function can be called with * invalidateCache set to false to skip that invalidation step for cases that do not * need it (for example, a component that remains at the same dimensions with the same * content). * * @param invalidateCache Whether the drawing cache for this view should be invalidated as * well. This is usually true for a full invalidate, but may be set to false if the * View's contents or dimensions have not changed. */ void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) { if (skipInvalidate()) { return; } if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) || (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED || isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque) { mLastIsOpaque = isOpaque(); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWN; mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DIRTY; if (invalidateCache) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; } final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo; final ViewParent p = mParent; //noinspection PointlessBooleanExpression,ConstantConditions if (!HardwareRenderer.RENDER_DIRTY_REGIONS) { if (p != null && ai != null && ai.mHardwareAccelerated) { // fast-track for GL-enabled applications; just invalidate the whole hierarchy // with a null dirty rect, which tells the ViewAncestor to redraw everything p.invalidateChild(this, null); return; } } if (p != null && ai != null) { final Rect r = ai.mTmpInvalRect;//把ai定义的矩形赋值给r r.set(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop);//设置矩形的区域 也就是2个坐标点 // Don't call invalidate -- we don't want to internally scroll // our own bounds p.invalidateChild(this, r);//调用ViewGroup中的重新绘制子view的方法,因为ViewGroup是实现了ViewParent()接口 } } }ViewGroup中的invalidateChild(View view,Rect rect)
/** * Don't call or override this method. It is used for the implementation of * the view hierarchy. */ public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) { ViewParent parent = this; final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo; if (attachInfo != null) { // If the child is drawing an animation, we want to copy this flag onto // ourselves and the parent to make sure the invalidate request goes // through final boolean drawAnimation = (child.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION) == PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION; // Check whether the child that requests the invalidate is fully opaque // Views being animated or transformed are not considered opaque because we may // be invalidating their old position and need the parent to paint behind them. Matrix childMatrix = child.getMatrix(); final boolean isOpaque = child.isOpaque() && !drawAnimation && child.getAnimation() == null && childMatrix.isIdentity(); // Mark the child as dirty, using the appropriate flag // Make sure we do not set both flags at the same time int opaqueFlag = isOpaque ? PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE : PFLAG_DIRTY; if (child.mLayerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; child.mLocalDirtyRect.union(dirty); } final int[] location = attachInfo.mInvalidateChildLocation; location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = child.mLeft; location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = child.mTop; if (!childMatrix.isIdentity() || (mGroupFlags & ViewGroup.FLAG_SUPPORT_STATIC_TRANSFORMATIONS) != 0) { RectF boundingRect = attachInfo.mTmpTransformRect; boundingRect.set(dirty); Matrix transformMatrix; if ((mGroupFlags & ViewGroup.FLAG_SUPPORT_STATIC_TRANSFORMATIONS) != 0) { Transformation t = attachInfo.mTmpTransformation; boolean transformed = getChildStaticTransformation(child, t); if (transformed) { transformMatrix = attachInfo.mTmpMatrix; transformMatrix.set(t.getMatrix()); if (!childMatrix.isIdentity()) { transformMatrix.preConcat(childMatrix); } } else { transformMatrix = childMatrix; } } else { transformMatrix = childMatrix; } transformMatrix.mapRect(boundingRect); dirty.set((int) (boundingRect.left - 0.5f), (int) (boundingRect.top - 0.5f), (int) (boundingRect.right + 0.5f), (int) (boundingRect.bottom + 0.5f)); } do { View view = null; if (parent instanceof View) { view = (View) parent; } if (drawAnimation) { if (view != null) { view.mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION; } else if (parent instanceof ViewRootImpl) { ((ViewRootImpl) parent).mIsAnimating = true; } } // If the parent is dirty opaque or not dirty, mark it dirty with the opaque // flag coming from the child that initiated the invalidate if (view != null) { if ((view.mViewFlags & FADING_EDGE_MASK) != 0 && view.getSolidColor() == 0) { opaqueFlag = PFLAG_DIRTY; } if ((view.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) != PFLAG_DIRTY) { view.mPrivateFlags = (view.mPrivateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | opaqueFlag; } } parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty); if (view != null) { // Account for transform on current parent Matrix m = view.getMatrix(); if (!m.isIdentity()) { RectF boundingRect = attachInfo.mTmpTransformRect; boundingRect.set(dirty); m.mapRect(boundingRect); dirty.set((int) (boundingRect.left - 0.5f), (int) (boundingRect.top - 0.5f), (int) (boundingRect.right + 0.5f), (int) (boundingRect.bottom + 0.5f)); } } } while (parent != null); } }在上面的代码中使用了do...while循环先判断这个view是不是ViewGroup 如果不是还是对View的坐标进行计算,然后会走到这个函数
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
/** * Don't call or override this method. It is used for the implementation of * the view hierarchy. * * This implementation returns null if this ViewGroup does not have a parent, * if this ViewGroup is already fully invalidated or if the dirty rectangle * does not intersect with this ViewGroup's bounds. */ public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) { if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWN) == PFLAG_DRAWN || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) { if ((mGroupFlags & (FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE | FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE)) != FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE) { dirty.offset(location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] - mScrollX, location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] - mScrollY); if ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == 0) { dirty.union(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } final int left = mLeft; final int top = mTop; if ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) { if (!dirty.intersect(0, 0, mRight - left, mBottom - top)) { dirty.setEmpty(); } } mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = left; location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = top; if (mLayerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; mLocalDirtyRect.union(dirty); } return mParent; } else { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWN & ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = mLeft; location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = mTop; if ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) { dirty.set(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } else { // in case the dirty rect extends outside the bounds of this container dirty.union(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } if (mLayerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; mLocalDirtyRect.union(dirty); } return mParent; } } return null; }研究卡在这里 不知道怎么进行下去,如果有知道的可以请教下,在下感谢不尽,在这就当它进行到了View的draw()方法,在网上查资料看到郭大神的博客是这么讲的,但是我没找到根据,为了这博客能继续写下去,就认为是到了draw(Canvas canvas)方法里:
public void draw(Canvas canvas) { if (mClipBounds != null) { canvas.clipRect(mClipBounds); } final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags; final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE && (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState); mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN; /* * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed * in the appropriate order: * * 1. Draw the background * 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading * 3. Draw view's content * 4. Draw children * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) */ // Step 1, draw the background, if needed int saveCount; if (!dirtyOpaque) { final Drawable background = mBackground; if (background != null) { final int scrollX = mScrollX; final int scrollY = mScrollY; if (mBackgroundSizeChanged) { background.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); mBackgroundSizeChanged = false; } if ((scrollX | scrollY) == 0) { background.draw(canvas); } else { canvas.translate(scrollX, scrollY); background.draw(canvas); canvas.translate(-scrollX, -scrollY); } } } // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case) final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0; boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0; if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) { // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); (绘制子view内容) // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas);(如果是ViewGroup的话,绘制子view就要重写这个dispatchDraw()方法,这个在讲tv中gridview的放大效果用到,如果是view就不必须重写了,) // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) onDrawScrollBars(canvas); if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) { mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas); } // we're done... return; } /* * Here we do the full fledged routine... * (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less, * this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been * done above) */ boolean drawTop = false; boolean drawBottom = false; boolean drawLeft = false; boolean drawRight = false; float topFadeStrength = 0.0f; float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f; float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f; float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f; // Step 2, save the canvas' layers int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft; final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired(); if (offsetRequired) { paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset(); } int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft; int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft; int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired); int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired); if (offsetRequired) { right += getRightPaddingOffset(); bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset(); } final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache; final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength; int length = (int) fadeHeight; // clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap // overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) { length = (bottom - top) / 2; } // also clip horizontal fades if necessary if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) { length = (right - left) / 2; } if (verticalEdges) { topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength())); drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength())); drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; } if (horizontalEdges) { leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength())); drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength())); drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; } saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount(); int solidColor = getSolidColor(); if (solidColor == 0) { final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG; if (drawTop) { canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags); } if (drawBottom) { canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags); } if (drawLeft) { canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags); } if (drawRight) { canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags); } } else { scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor); } // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas);//绘制子view的内容 所以它必须在ViewGroup类中 // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint; final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix; final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader; if (drawTop) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength); matrix.postTranslate(left, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p); } if (drawBottom) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(180); matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p); } if (drawLeft) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(-90); matrix.postTranslate(left, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p); } if (drawRight) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(90); matrix.postTranslate(right, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p); } canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) onDrawScrollBars(canvas); if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) { mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas); } }现在进入到ViewGroup中的dispatchDraw()
/** * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { final int count = mChildrenCount;//获取ViewGroup子view的个数 final View[] children = mChildren; 子view的数组 int flags = mGroupFlags; if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) { final boolean cache = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE) == FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE; final boolean buildCache = !isHardwareAccelerated(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//遍历所有的view final View child = children[i];//取出每个子view if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {//判断是否可见(不可见不绘制) final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();//获取LayoutParams attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, count); bindLayoutAnimation(child); if (cache) {//是否缓存 child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true); if (buildCache) { child.buildDrawingCache(true); } } } } final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController; if (controller.willOverlap()) { mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE; } controller.start(); mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION; mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE; if (cache) { mGroupFlags |= FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE; } if (mAnimationListener != null) { mAnimationListener.onAnimationStart(controller.getAnimation()); } } int saveCount = 0; final boolean clipToPadding = (flags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK; if (clipToPadding) { saveCount = canvas.save(); canvas.clipRect(mScrollX + mPaddingLeft, mScrollY + mPaddingTop, mScrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight, mScrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom); } // We will draw our child's animation, let's reset the flag mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION; mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED; boolean more = false; final long drawingTime = getDrawingTime(); if ((flags & FLAG_USE_CHILD_DRAWING_ORDER) == 0) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); } } } else { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = children[getChildDrawingOrder(count, i)]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); } } } // Draw any disappearing views that have animations if (mDisappearingChildren != null) { final ArrayList<View> disappearingChildren = mDisappearingChildren; final int disappearingCount = disappearingChildren.size() - 1; // Go backwards -- we may delete as animations finish for (int i = disappearingCount; i >= 0; i--) { final View child = disappearingChildren.get(i); more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);//遍历子view并绘制内容上去 } } if (debugDraw()) { onDebugDraw(canvas); } if (clipToPadding) { canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); } // mGroupFlags might have been updated by drawChild() flags = mGroupFlags; if ((flags & FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) == FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) { invalidate(true); } if ((flags & FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE) == 0 && (flags & FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER) == 0 && mLayoutAnimationController.isDone() && !more) { // We want to erase the drawing cache and notify the listener after the // next frame is drawn because one extra invalidate() is caused by // drawChild() after the animation is over mGroupFlags |= FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER; final Runnable end = new Runnable() { public void run() { notifyAnimationListener(); } }; post(end); } }
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) { return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime); }
然后调用子view本身的draw()方法:
/** * This method is called by ViewGroup.drawChild() to have each child view draw itself. * This draw() method is an implementation detail and is not intended to be overridden or * to be called from anywhere else other than ViewGroup.drawChild(). */ boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) { boolean useDisplayListProperties = mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated; boolean more = false; final boolean childHasIdentityMatrix = hasIdentityMatrix(); final int flags = parent.mGroupFlags; if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION) == ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION) { parent.getChildTransformation().clear(); parent.mGroupFlags &= ~ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } Transformation transformToApply = null; boolean concatMatrix = false; boolean scalingRequired = false; boolean caching; int layerType = getLayerType(); final boolean hardwareAccelerated = canvas.isHardwareAccelerated(); if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE) != 0 || (flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_ALWAYS_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE) != 0) { caching = true; // Auto-scaled apps are not hw-accelerated, no need to set scaling flag on DisplayList if (mAttachInfo != null) scalingRequired = mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired; } else { caching = (layerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) || hardwareAccelerated; } final Animation a = getAnimation(); if (a != null) { more = drawAnimation(parent, drawingTime, a, scalingRequired); concatMatrix = a.willChangeTransformationMatrix(); if (concatMatrix) { mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM; } transformToApply = parent.getChildTransformation(); } else { if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM) == PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM && mDisplayList != null) { // No longer animating: clear out old animation matrix mDisplayList.setAnimationMatrix(null); mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM; } if (!useDisplayListProperties && (flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_SUPPORT_STATIC_TRANSFORMATIONS) != 0) { final Transformation t = parent.getChildTransformation(); final boolean hasTransform = parent.getChildStaticTransformation(this, t); if (hasTransform) { final int transformType = t.getTransformationType(); transformToApply = transformType != Transformation.TYPE_IDENTITY ? t : null; concatMatrix = (transformType & Transformation.TYPE_MATRIX) != 0; } } } concatMatrix |= !childHasIdentityMatrix; // Sets the flag as early as possible to allow draw() implementations // to call invalidate() successfully when doing animations mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN; if (!concatMatrix && (flags & (ViewGroup.FLAG_SUPPORT_STATIC_TRANSFORMATIONS | ViewGroup.FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN)) == ViewGroup.FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN && canvas.quickReject(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom, Canvas.EdgeType.BW) && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION) == 0) { mPrivateFlags2 |= PFLAG2_VIEW_QUICK_REJECTED; return more; } mPrivateFlags2 &= ~PFLAG2_VIEW_QUICK_REJECTED; if (hardwareAccelerated) { // Clear INVALIDATED flag to allow invalidation to occur during rendering, but // retain the flag's value temporarily in the mRecreateDisplayList flag mRecreateDisplayList = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) == PFLAG_INVALIDATED; mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_INVALIDATED; } DisplayList displayList = null; Bitmap cache = null; boolean hasDisplayList = false; if (caching) { if (!hardwareAccelerated) { if (layerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { layerType = LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE; buildDrawingCache(true); } cache = getDrawingCache(true); } else { switch (layerType) { case LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE: if (useDisplayListProperties) { hasDisplayList = canHaveDisplayList(); } else { buildDrawingCache(true); cache = getDrawingCache(true); } break; case LAYER_TYPE_HARDWARE: if (useDisplayListProperties) { hasDisplayList = canHaveDisplayList(); } break; case LAYER_TYPE_NONE: // Delay getting the display list until animation-driven alpha values are // set up and possibly passed on to the view hasDisplayList = canHaveDisplayList(); break; } } } useDisplayListProperties &= hasDisplayList; if (useDisplayListProperties) { displayList = getDisplayList(); if (!displayList.isValid()) { // Uncommon, but possible. If a view is removed from the hierarchy during the call // to getDisplayList(), the display list will be marked invalid and we should not // try to use it again. displayList = null; hasDisplayList = false; useDisplayListProperties = false; } } int sx = 0; int sy = 0;把上面的调用顺序画一张图好理解下:if (!hasDisplayList) { computeScroll(); sx = mScrollX; sy = mScrollY; }{//在这进行调用了computeScroll()方法,如果有兴趣的可以去看下hasDisplayListfinal boolean hasNoCache = cache == null || hasDisplayList; final boolean offsetForScroll = cache == null && !hasDisplayList && layerType != LAYER_TYPE_HARDWARE; int restoreTo = -1; if (!useDisplayListProperties || transformToApply != null) { restoreTo = canvas.save(); } if (offsetForScroll) { canvas.translate(mLeft - sx, mTop - sy); } else { if (!useDisplayListProperties) { canvas.translate(mLeft, mTop); } if (scalingRequired) { if (useDisplayListProperties) { // TODO: Might not need this if we put everything inside the DL restoreTo = canvas.save(); } // mAttachInfo cannot be null, otherwise scalingRequired == false final float scale = 1.0f / mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale; canvas.scale(scale, scale); } } float alpha = useDisplayListProperties ? 1 : (getAlpha() * getTransitionAlpha()); if (transformToApply != null || alpha < 1 || !hasIdentityMatrix() || (mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA) == PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA) { if (transformToApply != null || !childHasIdentityMatrix) { int transX = 0; int transY = 0; if (offsetForScroll) { transX = -sx; transY = -sy; } if (transformToApply != null) { if (concatMatrix) { if (useDisplayListProperties) { displayList.setAnimationMatrix(transformToApply.getMatrix()); } else { // Undo the scroll translation, apply the transformation matrix, // then redo the scroll translate to get the correct result. canvas.translate(-transX, -transY); canvas.concat(transformToApply.getMatrix()); canvas.translate(transX, transY); } parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } float transformAlpha = transformToApply.getAlpha(); if (transformAlpha < 1) { alpha *= transformAlpha; parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } } if (!childHasIdentityMatrix && !useDisplayListProperties) { canvas.translate(-transX, -transY); canvas.concat(getMatrix()); canvas.translate(transX, transY); } } // Deal with alpha if it is or used to be <1 if (alpha < 1 || (mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA) == PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA) { if (alpha < 1) { mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA; } else { mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA; } parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; if (hasNoCache) { final int multipliedAlpha = (int) (255 * alpha); if (!onSetAlpha(multipliedAlpha)) { int layerFlags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG; if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) != 0 || layerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { layerFlags |= Canvas.CLIP_TO_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG; } if (useDisplayListProperties) { displayList.setAlpha(alpha * getAlpha() * getTransitionAlpha()); } else if (layerType == LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { final int scrollX = hasDisplayList ? 0 : sx; final int scrollY = hasDisplayList ? 0 : sy; canvas.saveLayerAlpha(scrollX, scrollY, scrollX + mRight - mLeft, scrollY + mBottom - mTop, multipliedAlpha, layerFlags); } } else { // Alpha is handled by the child directly, clobber the layer's alpha mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_ALPHA_SET; } } } } else if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_ALPHA_SET) == PFLAG_ALPHA_SET) { onSetAlpha(255); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_ALPHA_SET; } if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == ViewGroup.FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN && !useDisplayListProperties && cache == null) { if (offsetForScroll) { canvas.clipRect(sx, sy, sx + (mRight - mLeft), sy + (mBottom - mTop)); } else { if (!scalingRequired || cache == null) { canvas.clipRect(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } else { canvas.clipRect(0, 0, cache.getWidth(), cache.getHeight()); } } } if (!useDisplayListProperties && hasDisplayList) { displayList = getDisplayList(); if (!displayList.isValid()) { // Uncommon, but possible. If a view is removed from the hierarchy during the call // to getDisplayList(), the display list will be marked invalid and we should not // try to use it again. displayList = null; hasDisplayList = false; } } if (hasNoCache) { boolean layerRendered = false; if (layerType == LAYER_TYPE_HARDWARE && !useDisplayListProperties) { final HardwareLayer layer = getHardwareLayer(); if (layer != null && layer.isValid()) { mLayerPaint.setAlpha((int) (alpha * 255)); ((HardwareCanvas) canvas).drawHardwareLayer(layer, 0, 0, mLayerPaint); layerRendered = true; } else { final int scrollX = hasDisplayList ? 0 : sx; final int scrollY = hasDisplayList ? 0 : sy; canvas.saveLayer(scrollX, scrollY, scrollX + mRight - mLeft, scrollY + mBottom - mTop, mLayerPaint, Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG | Canvas.CLIP_TO_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG); } } if (!layerRendered) { if (!hasDisplayList) { // Fast path for layouts with no backgrounds if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) == PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK; dispatchDraw(canvas); } else { draw(canvas); } } else { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK; ((HardwareCanvas) canvas).drawDisplayList(displayList, null, flags); } } } else if (cache != null) { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK; Paint cachePaint; if (layerType == LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { cachePaint = parent.mCachePaint; if (cachePaint == null) { cachePaint = new Paint(); cachePaint.setDither(false); parent.mCachePaint = cachePaint; } if (alpha < 1) { cachePaint.setAlpha((int) (alpha * 255)); parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_ALPHA_LOWER_THAN_ONE; } else if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_ALPHA_LOWER_THAN_ONE) != 0) { cachePaint.setAlpha(255); parent.mGroupFlags &= ~ViewGroup.FLAG_ALPHA_LOWER_THAN_ONE; } } else { cachePaint = mLayerPaint; cachePaint.setAlpha((int) (alpha * 255)); } canvas.drawBitmap(cache, 0.0f, 0.0f, cachePaint); } if (restoreTo >= 0) { canvas.restoreToCount(restoreTo); } if (a != null && !more) { if (!hardwareAccelerated && !a.getFillAfter()) { onSetAlpha(255); } parent.finishAnimatingView(this, a); } if (more && hardwareAccelerated) { if (a.hasAlpha() && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_ALPHA_SET) == PFLAG_ALPHA_SET) { // alpha animations should cause the child to recreate its display list invalidate(true); } } mRecreateDisplayList = false; return more; }
现在讲二个案例
仿网易新网客户端左侧滑动效果:
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.example.myscrollerdemo.CustomLinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#ffff00" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="200px" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="阿里巴巴" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="腾讯" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="百度" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="网易" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="搜狐" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="新浪" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="340" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="恒生电子" android:textColor="#000000" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="海康威视" android:textColor="#000000" /> </LinearLayout> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:text="内容" android:gravity="center" android:background="#ffffff" android:textColor="#ff999999" android:textSize="30sp" /> </com.example.myscrollerdemo.CustomLinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>效果:
现在只要把左侧的菜单离左边-200px就行,它就完全隐藏了
自定义的LinearLayout:
package com.example.myscrollerdemo; import android.content.Context; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.widget.LinearLayout; import android.widget.Scroller; /** * Created by admin on 2016/6/12. */ public class CustomLinearLayout extends LinearLayout { private static final String TAG = "CustomLinearLayout"; private Scroller mScroller; public CustomLinearLayout(Context context) { this(context,null); } public CustomLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);//设置水平方向 mScroller = new Scroller(getContext()); } float downX = 0; @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()){ case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: downX = event.getX(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: float moveX = event.getX(); int distance = (int) (downX-moveX); int scrollX = getScrollX(); int startX = scrollX+distance; if(startX<=-200){ startX = -200; } else if(startX>=0){ startX = 0; } mScroller.startScroll(startX,0,distance,0,5000); downX = moveX; invalidate(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: break; } return true; } @Override public void computeScroll() { if(mScroller.computeScrollOffset()){ scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(),0); invalidate(); } } }效果:
突然发现上面有一个bug,手指往右边滑动的时候,抬起后左侧的菜单还会慢慢的滑几下,是因为computeScroll()方法中调用了invalidate(),把这行代码删除就好了!现在发现还有问题就是手指在竖直方向滑动,它也会动一点点,请看效果图:
解决方案就是横向移动的距离大于竖直方向的距离才让它滑动
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
downX = event.getX();
downY = event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
float moveX = event.getX();
float moveY = event.getY();
if(Math.abs(moveY-downY)<Math.abs(moveX-downX)){
int distance = (int) (downX-moveX);
int scrollX = getScrollX();
int startX = scrollX+distance;
Log.e(TAG,"startX="+startX);
if(startX<-200){
startX = -200;
} else if(startX>0){
startX = 0;
}
mScroller.startScroll(startX,0,distance,0,5000);
downX = moveX;
invalidate();
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
}
return true;
}
效果:
ok,这个问题已解决,现在还有一个地方需要优化就是当手指滑动到一半抬起的时候需要回弹,这个逻辑重要在UP的时候判断它是向左还是向右滑动,
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
int currX = mScroller.getCurrX();
if(currX<=-200/2){//打开
mScroller.startScroll(-200,0,Math.abs(currX),0,8000);
invalidate();
}else{//关闭
mScroller.startScroll(0,0,Math.abs(200+currX),0,8000);
invalidate();
}
break;
效果图:
ok,回弹效果实现了,