【机器学习算法-python实现】决策树-Decision tree(1) 信息熵划分数据集
1.背景
决策书算法是一种逼近离散数值的分类算法,思路比较简单,而且准确率较高。国际权威的学术组织,数据挖掘国际会议ICDM (the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining)在2006年12月评选出了数据挖掘领域的十大经典算法中,C4.5算法排名第一。C4.5算法是机器学习算法中的一种分类决策树算法,其核心算法是ID3算法。
算法的主要思想就是将数据集按照特征对目标指数的影响由高到低排列。行成一个二叉树序列,进行分类,如下图所示。
现在的问题关键就是,当我们有很多特征值时,哪些特征值作为父类写在二叉树的上面的节点,哪下写在下面。我们可以直观的看出上面的特征值节点应该是对目标指数影响较大的一些特征值。那么如何来比较哪些特征值对目标指数影响较大呢。这里引出一个概念,就是信息熵。
信息理论的鼻祖之一Claude E. Shannon把信息(熵)定义为离散随机事件的出现概率。说白了就是信息熵的值越大就表明这个信息集越混乱。
信息熵的计算公式,(建议去wiki学习一下)
这里我们通过计算目标指数的熵和特征值得熵的差,也就是熵的增益来确定哪些特征值对于目标指数的影响最大。
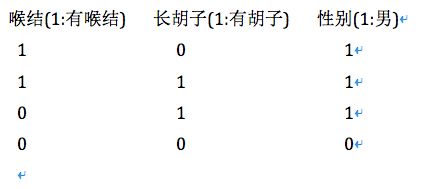
2.数据集
3.代码
(1)第一部分-计算熵
函数主要是找出有几种目标指数,根据他们出现的频率计算其信息熵。
- def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
- numEntries=len(dataSet)
- labelCounts={}
- for featVec in dataSet:
- currentLabel=featVec[-1]
- if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
- labelCounts[currentLabel]=0
- labelCounts[currentLabel]+=1
- shannonEnt=0.0
- for key in labelCounts:
- prob =float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
- shannonEnt-=prob*math.log(prob,2)
- return shannonEnt
(2)第二部分-分割数据
因为要每个特征值都计算相应的信息熵,所以要对数据集分割,将所计算的特征值单独拿出来。
- def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
- retDataSet = []
- for featVec in dataSet:
- if featVec[axis] == value:
- reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #chop out axis used for splitting
- reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
- retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
- return retDataSet
(3)第三部分-找出信息熵增益最大的特征值
- def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
- numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels
- baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
- bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
- for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features
- featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature
- uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values
- newEntropy = 0.0
- for value in uniqueVals:
- subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
- prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
- newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
- infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy
- if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far
- bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best
- bestFeature = i
- return bestFeature #returns an integer
4.代码下载
结果是输出0,也就是是否有喉结对性别影响最大。
下载地址(ShannonEnt)