U16 转换成 Signed int
int CVNCClientDlg::U16Toint(char a, char b)
{
unsigned char x = a; // signed char convert to unsigned char
unsigned char y = b;
int output;
output = x * 256 + y;
return output;
}
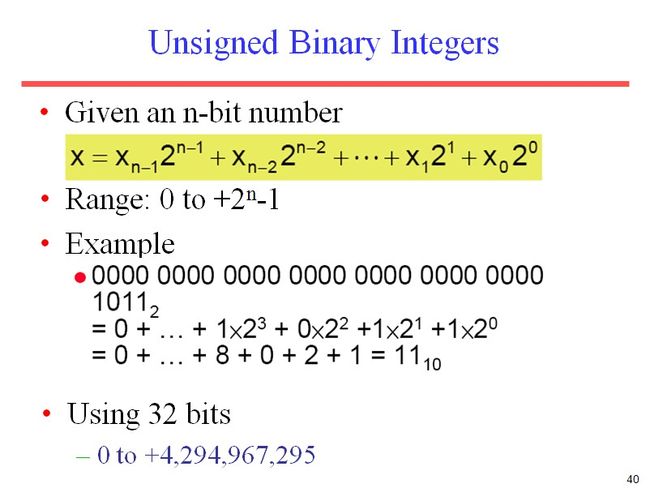
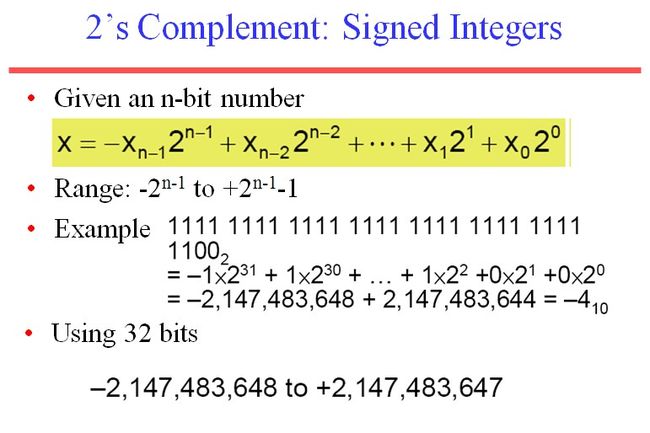
U16以为着用两个byte来表示一个数字,在这里用的是little endian字符序。
U在这里表示的是unsigned。 比如还有U8,U16,U32,S32。
所以U8表示用1个byte(8个bits)的无符号数表示一个数
S32表示用4个byte(32个bits)的有符号数表示一个数
在上面代码中 signed char 会强制转换成 unsigned char
乘上256是因为byte都是用16进制表示的。所以a比b所在的位数要乘上16*16.
普及背景知识:
为了叙述方便,下面先对本文中将要用到的两个术语做简单的定义。
1、MSB
MSB是Most Significant Bit/Byte的首字母缩写,通常译为最重要的位或者最
重要的字节。它通常用来表明在一个bit序列(如一个byte是8个bit组成的一个序
列)或者一个byte序列(如word是两个byte组成的一个序列)中对整个序列取值影
响最大的那个bit/byte。
2、LSB
LSB是Least Significant Bit/Byte的首字母缩写,通常译为最不重要的位或
者最不重要的字节。它通常用来表明在一个bit序列(如一个byte是8个bit组成的
一个序列)或者一个byte序列(如word是两个byte组成的一个序列)中对整个序
列取值影响最小的那个bit/byte。
三、各种endian
1、big-endian
A computer architecture in which, within a given multi-byte numeric
representation, the most significant byte has the lowest address (the
word is stored "big-end-first").
Most processors, including the IBM 370 family, the PDP-10, the
Motorola microprocessor families, and most of the various RISC designs
current in mid-1993, are big-endian. [From: Free On-Line Dictionary Of
Computing or Jargon File]
big-endian:计算机体系结构中一种描述多字节存储顺序的术语,在这种机制
中最重要字节(MSB)存放在最低端的地址上。采用这种机制的处理器有IBM3700系
列、PDP-10、Mortolora微处理器系列和绝大多数的RISC处理器。
+----------+
| 0x34 |<-- 0x00000021
+----------+
| 0x12 |<-- 0x00000020
+----------+
图1:双字节数0x1234以big-endian的方式存在起始地址0x00000020中
在Big-Endian中,对于bit序列中的序号编排方式如下(以双字节数0x8B8A为
例):
bit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
+----------------------------------------+
val | 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 | 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 |
+----------------------------------------+
^ 0x8B 0x8A ^
MSB LSB
图2:Big-Endian的bit序列编码方式
注1:通常在TCP/IP协议栈所说的网络序(Network Order)就是遵循Big-Endian
规则。在TCP/IP网络通信中,通信双方把消息按照如图2的方式进行编码,然后按
从MSB(Bit0)到LSB的顺序在网络上传送。
2、little-endian
A computer architecture in which, within a given
16- or 32-bit word,bytes at lower addresses have lower significance (the
word is stored "little-end-first"). The PDP-11 and VAX families of
computers and Intel microprocessors and a lot of communications and
networking hardware are little-endian.
The term is sometimes used to describe the ordering of units other
than bytes; most often, bits within a byte. [From: Free On-Line Dictionary
Of Computing or Jargon File]
little-endian:计算机体系结构中一种描述多字节存储顺序的术语,在这种机
制中最不重要字节(LSB)存放在最低端的地址上。采用这种机制的处理器有PDP-11、
VAX、Intel系列微处理器和一些网络通信设备。该术语除了描述多字节存储顺序外
还常常用来描述一个字节中各个比特的排放次序。
+----------+
| 0x12 |<-- 0x00000021
+----------+
| 0x34 |<-- 0x00000020
+----------+
图3:双字节数0x1234以little-endian的方式存在起始地址0x00000020中
在Little-Endian中,对于bit序列中的序号编排和Big-Endian刚好相反,其方
式如下(以双字节数0x8B8A为例):
bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
+-----------------------------------------+
val | 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 | 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 |
+-----------------------------------------+
^ 0x8B 0x8A ^
MSB LSB
图4:Little-Endian的bit序列编码方式
注2:通常我们说的主机序(Host Order)就是遵循Little-Endian规则。所以
当两台主机之间要通过TCP/IP协议进行通信的时候就需要调用相应的函数进行主机
序(Little-Endian)和网络序(Big-Endian)的转换。
注3:正因为这两种机制对于同一bit序列的序号编排方式恰恰相反,所以《现
代英汉词典》中对MSB的翻译为"最高有效位"欠妥,故本文定义为"最重要的bit
/byte"。
3、middle-endian:
Neither big-endian nor little-endian. Used of
perverse byte orders such as 3-4-1-2 or 2-1-4-3, occasionally found in
the packed decimal formats of some minicomputer manufacturers.[From:
Free On-Line Dictionary Of Computing or Jargon File]
middle-endian:除了big-endian和little-endian之外的多字节存储顺序就是
middle-endian,比如以4个字节为例:象以3-4-1-2或者2-1-4-3这样的顺序存储的
就是middle-endian。这种存储顺序偶尔会在一些小型机体系中的十进制数的压缩格
式中出现。
四、收尾
要详细解释这两种编码顺序已经超出本文所涉及的内容,如果你有兴趣的话可
以参考上面提及的Danny Cohen的论文("On Holy Wars and a Plea for Peace"),
该论文详细的描述了这两种编码顺序的历史、所基于的数学理论和各自拥护者争论
的焦点等知识,绝对可以大饱你打破沙锅问到底的内心需要。
五、References & WebLinks
1. Free On-Line Dictionary Of Computing
[http://foldoc.doc.ic.ac.uk/foldoc/index.html]
2. Jargon File [http://info.astrian.net/jargon/]
3. Gulliver's Travels《格利佛游记》
[http://www.jaffebros.com/lee/gulliver/]
4. On Holy Wars and a Plea for Peace
[http://khavrinen.lcs.mit.edu/wollman/ien-137.txt]