Linux 中断学习之小试牛刀篇
Linux中断内核编程
前言
在前面分析了中断的基本原理后,就可以写一个内核中断程序来体验以下,也可以借此程序继续深入来了解内核中断的执行过程
一.内核中断程序:
我们还是来看一看成程序:
在看程序之前,要熟悉如何进行模块编程,和了解module_pararm()的用法。如果不熟悉的话请大家看,module_param()的学习和Linux内核模块编程,在此不作解释。
1.程序interrupt.c
- 1 /*
- 2 *file name :interrupt.c
- 3 *atuthor : john
- 4 */
- 5 #include<linux/init.h>
- 6 #include<linux/module.h>
- 7 #include<linux/kernel.h>
- 8 #include<linux/interrupt.h>
- 9
- 10 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- 11 static int irq;
- 12 char *interface;
- 13 static irqreturn_t myirq_handler(int irq,void *dev);
- 14
- 15 static int __init myirq_init(void)
- 16 {
- 17 printk("the module is working!/n");
- 18 printk("the irq is ready for working!/n");
- 19 if(request_irq(irq,myirq_handler,IRQF_SHARED,interface,&irq)){
- 20 printk(KERN_ERR "%s interrrupt can't register %d IRQ /n",interface,irq);
- 21 return -EIO;
- 22 }
- 23 printk("%s request %d IRQ/n",interface,irq);
- 24 return 0;
- 25 }
- 26 static irqreturn_t myirq_handler(int irq,void *dev)
- 27 {
- 28 printk("%d IRQ is working/n",irq);
- 29 return IRQ_NONE;
- 30 }
- 31 static void __exit myirq_exit(void)
- 32 {
- 33 printk("the module is leaving!/n");
- 34 printk("the irq is bye bye!/n");
- 35 free_irq(irq,&irq);
- 36 printk("%s interrupt free %d IRQ/n",interface,irq);
- 37
- 38 }
- 39 module_init(myirq_init);
- 0 module_exit(myirq_exit);
- 41 module_param(interface,charp,0644);
- 42 module_param(irq,int,0644);
- 43
2.Makefile的编写
- 1 obj-m:=tiger.o
- 2
- 3 CURRENT_PATH:=$(shell pwd)
- 4 VERSION_NUM:=$(shell uname -r)
- 5 LINUX_PATH:=/usr/src/linux-headers-$(VERSION_NUM)
- 6
- 7
- 8 all :
- 9 make -C $(LINUX_PATH) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) modules
- 10 clean:
- 11 make -C $(LINUX_PATH) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) clean
(程序的调试,加载和运行,在此不进行说明)
3.首先我们来分析下内核加载模块
在内核加载模块中最重要的的action就是注册中断处理程序。很明显,这一动作是通过request_irq()函数来完成的。
int request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,unsigned long flags, const char *devname, void *dev_id)
A.先来分析形参:
第一个参数irq: 表示要分配的中断号。对于一些设备(系统时钟或键盘)它的值是预先固定的,而对于大多数设备来说,这个值是动态确定的。
第二个参数handler:表示要挂入到中断请求对列中的中断服务例程,这个中断服务函数的原型是static irqreturn_t handler(int , void *);
中断处理程序的前缀为static,因为它从来不会被别的文件中的代码直接调用。
第三个参数flags:为标志位。可以取IRQF_DISABLED、IRQF_SHARED和IRQF_SAMPLE_RANDOM之一。在本实例程序中取 IRQF_SHARED,该标志表示多个中断处理程序共享irq中断线。一般某个中断线上的中断服务程序在执行时会屏蔽请求该线的其他中断,如果取 IRQF_DISABLED标志,则在执行该中断服务程序时会屏蔽所有其他的中断。取IRQF_SAMPLE_RANDOM则表示设备可以被看做是事件随见的发生源。
以下是官方解释:
- /*
- * These flags used only by the kernel as part of the
- * irq handling routines.
- *
- * IRQF_DISABLED - keep irqs disabled when calling the action handler
- * IRQF_SAMPLE_RANDOM - irq is used to feed the random generator
- * IRQF_SHARED - allow sharing the irq among several devices
- * IRQF_PROBE_SHARED - set by callers when they expect sharing mismatches to occur
- * IRQF_TIMER - Flag to mark this interrupt as timer interrupt
- * IRQF_PERCPU - Interrupt is per cpu
- * IRQF_NOBALANCING - Flag to exclude this interrupt from irq balancing
- * IRQF_IRQPOLL - Interrupt is used for polling (only the interrupt that is
- * registered first in an shared interrupt is considered for
- * performance reasons)
- */
- #define IRQF_DISABLED 0x00000020
- #define IRQF_SAMPLE_RANDOM 0x00000040
- #define IRQF_SHARED 0x00000080
- #define IRQF_PROBE_SHARED 0x00000100
- #define IRQF_TIMER 0x00000200
- #define IRQF_PERCPU 0x00000400
- #define IRQF_NOBALANCING 0x00000800
- #define IRQF_IRQPOLL 0x00001000
第四个参数devname:是请求中断的设备的名称。当你加载模块成功后可以在/proc/interrupts中查看到具体设备的名称,与此同时也可以看到这个设备对应的中断号以及请求次数。
第五个参数dev_id:为一个指针型变量。注意该参数为void型,也就是说通过强制转换可以转换为任意类型。dev_id主要用于共享中断线,对每个注册的中断处理程序来说,( Dev_id must be globally unique. Normally the address of the device data structure is used as the cookie.)dev_id参数必须唯一(指向任一设备结构的指针就可以满足此要求,选择设备结构因为它是唯一的,而且中断处理程序可能会用到它)如果无需共享中断线,则将该参数赋值为NULL。
B:函数返回值
requset_irq()函数成功执行后返回0。如果返回非0值,就表示错误发生。此时,指定的中断处理程序不会被注册。
这里面有几个疑问:
为什么要注册中断函数
共享中断线的概念,参数dev_id的作用是什么
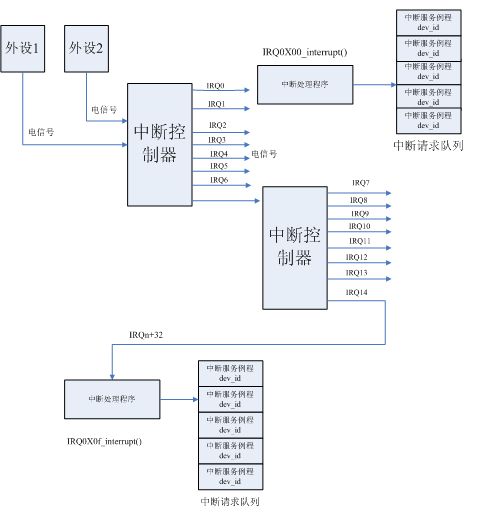
看一个图进行说明:
1>由图可知:有16个中断线。要使用中断线,就要进行中断线的申请 ,也常把申请一条中断线称为申请一个中断号,这就 与request_irq()函数中的第一个形参irq有关系 。
2>Linux有256个中断向量,而外部中中断向量只有16个(32~47)。由于硬件上的限制,很多外部设备不得不共享中断线。
(例如:一些PC机所用的网卡和图形卡可以把它们分配到一条中断线上)
让每个中断源独自占用一条中断线是不实现的。
3>共享中断线的话虽然解决了中断资源的问题,但是,此时引出了另一个问题(任何事物都有其两面性),此时仅仅用中断描述符并不能提供中断产生的所有信息。为了解决这个问题,内核必须对中断线给出近一步的描述,所以在Linux设计中,为每个中断请求IRQ设置了一个专用队列(中断请求队列)。
4>中断服例程序和中断处理程序的区别:
a.中断服务例程(interrupt service routine):
Linux中,15条中断线对应15个中断处理程序,依次命名是IRQ0x00_interrupt(),IRQ0x01_interrupt()..... IRQ0X1f_interrupt().
中断处理程序相当于某个中断向量的总处理程序。
eg:IRQ0X05_interupt()是5号中断(向量为37)的总处理程序。
b.中断服务例程是针对一个具体设备的中断。
5>.注册中断服务例程:
在IDT表完成初始化时,每个中断服务队列还为空。此时即使打开中断且某个外设的中断真的发生了,也得不到实际的服务。因为CPU虽然通过中断门进入了某个中断向量的总处理程序。但是,具体的中断服务例程还没有挂入中断请求队列。所以,在设备驱动程序的初始化阶段,必须通过request_irq()函数将响应的中断服务例程挂入中断请求队列,也就是进行注册。
6>分析一下中断服务程序,即request_irq()函数中第二个参数所对应的函数
static irqreturn_t myirq_handler(int irq,void *dev_id)
{
printk("ISR is Working/n");
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
中断服务例程的形参:
a.int irq :中断号。
b.void *dev_id :与request_irq()的参数dev_id一致,可以根据这个设备id号得到相应设备的数据结构,进而得到相应设备的信息和相关数据。
c.返回值:中断程序的返回值是一个特殊类型 rqreturn_t。但是中断程序的返回值却只有两个值IRQ_NONE和IRQ_HANDLED。
IRQ_NONE:中断程序接收到中断信号后发现这并不是注册时指定的中断原发出的中断信号。
IRQ_HANDLED:接收到了准确的中断信号,并且作了相应正确的处理。
一般中断处理程序要做什么service,主要取决于产生的设备和该设备为什么要发送中断。
John哥说明:
1.当一个给定的中断处理程序正在执行时,这条中断线上的其它中断都会被屏蔽。but,所有其他中断线上的中断都是打开的。因此这些不同中断线上的其他中断都能被处理。
2.request_irq()函数可能会睡眠,所以,不能在中断上下文或其它不允许阻塞的代码中调用该函数。
4.在深入分析request_irq()函数之前,先来看几个重要的数据结构。
A.irqaction的数据结构(用irqaction结构体来描述一个具体的中断服务例程)
- 113struct irqaction {
- 114 irq_handler_t handler;
- 115 unsigned long flags;
- 116 const char *name;
- 117 void *dev_id;
- 118 struct irqaction *next;
- 119 int irq;
- 120 struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
- 121 irq_handler_t thread_fn;
- 122 struct task_struct *thread;
- 123 unsigned long thread_flags;
- 124};
- 125
1>handler:指向具体的一个中断服务例程。
2>flags:表示中断标志位,对应于request_irq()函数中所传递的第三个参数,可取IRQF_DISABLED、IRQF_SAMPLE_RANDOM和IRQF_SHARED其中之一。
3>name:请求中断的设备名称,对应request_irq()函数中所传递的第四个参数
4>dev_id:共享中断时有用。对应于request_irq()函数中所传递的第五个参数,可取任意值,但必须唯一能够代表发出中断请求的设备,通常取描述该设备的结构体。
5>strct irqaction *next:指向irqaction描述符的下一个元素。用一条链表将共享同一条中断线上的中断服务例程链接起来。
6>irq:所申请的中断号
7>dir:指向proc/irq/NN/name entry
8>thread_fn:指向具体的一个线程化的中断。
9>thread:指向线程中断的指针。
10>thread_flags:线程中断的标志。
B.irq_desc的数据结构体
每个中断向量都有它自己的irq_desc 描述符。即用irq_desc来描述中断向量。所有的这些中断描述符组织在一起就形成了irq_desc irq_desc[NR_IRQS]数组
- 175struct irq_desc {
- 176 unsigned int irq;
- 177 struct timer_rand_state *timer_rand_state;
- 178 unsigned int *kstat_irqs;
- 179#ifdef CONFIG_INTR_REMAP
- 180 struct irq_2_iommu *irq_2_iommu;
- 181#endif
- 182 irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq;
- 183 struct irq_chip *chip;
- 184 struct msi_desc *msi_desc;
- 185 void *handler_data;
- 186 void *chip_data;
- 187 struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */
- 188 unsigned int status; /* IRQ status */
- 189
- 190 unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */
- 191 unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */
- 192 unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */
- 193 unsigned long last_unhandled; /* Aging timer for unhandled count */
- 194 unsigned int irqs_unhandled;
- 195 raw_spinlock_t lock;
- 196#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
- 197 cpumask_var_t affinity;
- 198 const struct cpumask *affinity_hint;
- 199 unsigned int node;
- 200#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
- 201 cpumask_var_t pending_mask;
- 202#endif
- 203#endif
- 204 atomic_t threads_active;
- 205 wait_queue_head_t wait_for_threads;
- 206#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
- 207 struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
- 208#endif
- 209 const char *name;
- 210} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
- 211
- 212extern void arch_init_copy_chip_data(struct irq_desc *old_desc,
- 213 struct irq_desc *desc, int node);
- 214extern void arch_free_chip_data(struct irq_desc *old_desc, struct irq_desc *desc);
- 215
- 216#ifndef CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ
- 217extern struct irq_desc irq_desc[NR_IRQS];
1>irq:表示这个描述符所对应的中断号。
2>handle_irq:指向该IRQ线的公共服务程序(即该IRQ所对应的中断处理程序。
3>chip:它是一个struct irq_chip类型的指针,是中断控制器的描述符 。在2.6以前的版本中它是hw_irq_controller。
4>handler_data:是handler_irq的参数。
5>chip_data:是指向irq_chip的指针。
6>atcion:一个struct irqaction类型的指针,它指向一个单链表。该链表是由该中断线上所有中断服务例程链接起来的。
7>status:表示中断线当前的状态。
8>depth:中断线被激活时,值为0;当值为正数时,表示被禁止的次数。
9>irq_count:表示该中断线上发生中断的次数
10>irqs_unhandled:该IRQ线上未处理中断发生的次数
11>name:申请中断设备的名字。
C.struct irq_chip结构体:
struct irq_chip是一个中断控制器的描述符。Linux支持N种可编程中断控制器PIC(中断控制器),通常不同的体系结构就有一套自己的中断处理方式。内核为了统一的处理中断,提供了底层的中断处理抽象接口,对于每个平台都需要实现底层的接口函数。这样对于上层的中断通用处理程序就无需任何改动。
struct irq_chip的具体代码如下:
- 111struct irq_chip {
- 112 const char *name;
- 113 unsigned int (*startup)(unsigned int irq);
- 114 void (*shutdown)(unsigned int irq);
- 115 void (*enable)(unsigned int irq);
- 116 void (*disable)(unsigned int irq);
- 117
- 118 void (*ack)(unsigned int irq);
- 119 void (*mask)(unsigned int irq);
- 120 void (*mask_ack)(unsigned int irq);
- 121 void (*unmask)(unsigned int irq);
- 122 void (*eoi)(unsigned int irq);
- 123
- 124 void (*end)(unsigned int irq);
- 125 int (*set_affinity)(unsigned int irq,
- 126 const struct cpumask *dest);
- 127 int (*retrigger)(unsigned int irq);
- 128 int (*set_type)(unsigned int irq, unsigned int flow_type);
- 129 int (*set_wake)(unsigned int irq, unsigned int on);
- 130
- 131 void (*bus_lock)(unsigned int irq);
- 132 void (*bus_sync_unlock)(unsigned int irq);
- 133
- 134 /* Currently used only by UML, might disappear one day.*/
- 135#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_RELEASE_METHOD
- 136 void (*release)(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id);
- 137#endif
- 138 /*
- 139 * For compatibility, ->typename is copied into ->name.
- 140 * Will disappear.
- 141 */
- 142 const char *typename;
- 143};
- 144
name:中断控制器的名字;
Startup:启动中断线;
Shutdown:关闭中断线;
Enable:允许中断;
Disable:禁止中断;
分析了struct irq_desc,struct irq_chip和irqaction的数据结构之后我们来看看他们之间的关系。
现在深入分析request_irq()内部是如何实现的。
- 135request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags,
- 136 const char *name, void *dev)
- 137{
- 138 return request_threaded_irq(irq, handler, NULL, flags, name, dev);
- 139}
- 140
可以看到request_irq()函数里面有封装了request_threaded_irq(irq, handler, NULL, flags, name, dev)函数。
先看一下官方的解释
- 1006/**
- 1007 * request_threaded_irq - allocate an interrupt line
- 1008 * @irq: Interrupt line to allocate
- 1009 * @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
- 1010 * Primary handler for threaded interrupts
- 1011 * If NULL and thread_fn != NULL the default
- 1012 * primary handler is installed
- 1013 * @thread_fn: Function called from the irq handler thread
- 1014 * If NULL, no irq thread is created
- 1015 * @irqflags: Interrupt type flags
- 1016 * @devname: An ascii name for the claiming device
- 1017 * @dev_id: A cookie passed back to the handler function
- 1018 *
- 1019 * This call allocates interrupt resources and enables the
- 1020 * interrupt line and IRQ handling. From the point this
- 1021 * call is made your handler function may be invoked. Since
- 1022 * your handler function must clear any interrupt the board
- 1023 * raises, you must take care both to initialise your hardware
- 1024 * and to set up the interrupt handler in the right order.
- 1025 *
- 1026 * If you want to set up a threaded irq handler for your device
- 1027 * then you need to supply @handler and @thread_fn. @handler ist
- 1028 * still called in hard interrupt context and has to check
- 1029 * whether the interrupt originates from the device. If yes it
- 1030 * needs to disable the interrupt on the device and return
- 1031 * IRQ_WAKE_THREAD which will wake up the handler thread and run
- 1032 * @thread_fn. This split handler design is necessary to support
- 1033 * shared interrupts.
- 1034 *
- 1035 * Dev_id must be globally unique. Normally the address of the
- 1036 * device data structure is used as the cookie. Since the handler
- 1037 * receives this value it makes sense to use it.
- 1038 *
- 1039 * If your interrupt is shared you must pass a non NULL dev_id
- 1040 * as this is required when freeing the interrupt.
- 1041 *
- 1042 * Flags:
- 1043 *
- 1044 * IRQF_SHARED Interrupt is shared
- 1045 * IRQF_SAMPLE_RANDOM The interrupt can be used for entropy
- 1046 * IRQF_TRIGGER_* Specify active edge(s) or level
- 1047 *
- 1048 */
5.首先分析request_threaded_irq()函数中的各个形参
1>:irq:表示申请的中断号。
2>:handler:表示中断服务例程
3.> thread_fn:中断线程化,此处传递的是NULL。NULL表示没有中断线程化。
此参数是最新版本中才出现的。为什么要提出中断线程化?
在 Linux 中,中断具有最高的优先级。不论在任何时刻,只要产生中断事件,内核将立即执行相应的中断
处理程序,等到所有挂起的中断和软中断处理完毕后才能执行正常的任务,因此有可能造成实时任务得不
到及时的处理。中断线程化之后,中断将作为内核线程运行而且被赋予不同的实时优先级,实时任务可以
有比中断线程更高的优先级。这样,具有最高优先级的实时任务就能得到优先处理,即使在严重负载下仍
有实时性保证。but,并不是所有的中断都可以被线程化,比如时钟中断,主要用来维护系统时间以及定时器
等,其中定时器是操作系统的脉搏,一旦被线程化,就有可能被挂起,这样后果将不堪设想,所以不应当
被线程化。
4>.irqflags:表示中断标志位。
5>.devname:表示请求中断的设备的名称。
6>.dev_id:对应于request_irq()函数中所传递的第五个参数,可取任意值,但必须唯一能够代表发出中断请求的设备,通常取描述该设备的结构体。共享中断时所用。
现在继续迭代深入request_threaded_irq()内部是如何实现的。
- 1049int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
- 1050 irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,
- 1051 const char *devname, void *dev_id)
- 1052{
- 1053 struct irqaction *action;
- 1054 struct irq_desc *desc;
- 1055 int retval;
- 1056
- 1057 /*
- 1058 * Sanity-check: shared interrupts must pass in a real dev-ID,
- 1059 * otherwise we'll have trouble later trying to figure out
- 1060 * which interrupt is which (messes up the interrupt freeing
- 1061 * logic etc).
- 1062 */
- 1063 if ((irqflags & IRQF_SHARED) && !dev_id)
- 1064 return -EINVAL;
- 1065
- 1066 desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
- 1067 if (!desc)
- 1068 return -EINVAL;
- 1069
- 1070 if (desc->status & IRQ_NOREQUEST)
- 1071 return -EINVAL;
- 1072
- 1073 if (!handler) {
- 1074 if (!thread_fn)
- 1075 return -EINVAL;
- 1076 handler = irq_default_primary_handler;
- 1077 }
- 1078
- 1079 action = kzalloc(sizeof(struct irqaction), GFP_KERNEL);
- 1080 if (!action)
- 1081 return -ENOMEM;
- 1082
- 1083 action->handler = handler;
- 1084 action->thread_fn = thread_fn;
- 1085 action->flags = irqflags;
- 1086 action->name = devname;
- 1087 action->dev_id = dev_id;
- 1088
- 1089 chip_bus_lock(irq, desc);
- 1090 retval = __setup_irq(irq, desc, action);
- 1091 chip_bus_sync_unlock(irq, desc);
- 1092
- 1093 if (retval)
- 1094 kfree(action);
- 1095
- 1096#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SHIRQ
- 1097 if (!retval && (irqflags & IRQF_SHARED)) {
- 1098 /*
- 1099 * It's a shared IRQ -- the driver ought to be prepared for it
- 1100 * to happen immediately, so let's make sure....
- 1101 * We disable the irq to make sure that a 'real' IRQ doesn't
- 1102 * run in parallel with our fake.
- 1103 */
- 1104 unsigned long flags;
- 1105
- 1106 disable_irq(irq);
- 1107 local_irq_save(flags);
- 1108
- 1109 handler(irq, dev_id);
- 1110
- 1111 local_irq_restore(flags);
- 1112 enable_irq(irq);
- 1113 }
- 1114#endif
- 1115 return retval;
- 1116}
程序的第一行和第二行分别定义了:
(1) struct irqaction *action;
(2)2struct irq_desc *desc;
两个指针action和desc,它们分别指向了结构体irqaction和 irq_desc。
(3) if ((irqflags & IRQF_SHARED) && !dev_id)
return -EINVAL;
作用是:判断中断标志位,如果是共享中断的话就必须要有一个唯一的dev_id,否则返回一个错误。
(4) desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
irq_to_desc(irq):根据中断号irq在 irq_desc[NR_IRQS]数组中返回一个具体的irq_desc。即根据irq找到它的中断处理程序。
(5) if (!desc)
return -EINVAL;
当返回一个空值时返回一个错误。说明申请中断号失败。
(6)if (desc->status & IRQ_NOREQUEST)
return -EINVAL;
判断中断线的状态,若为IRQ_NOREQUEST时(IRQ_NOREQUEST表示 IRQ 不能被申请)
(7) if (!handler) {
if (!thread_fn)
return -EINVAL;
handler = irq_default_primary_handler;
}
判断中断服务例程是否为空,如果handler为空,则判断线程中断服务例程,若线程中断服务例程也为空,则返回一个错误值。否则中断服务例程指向:rq_default_primary_handler。
(8)
1079 action = kzalloc(sizeof(struct irqaction), GFP_KERNEL);
1080 if (!action)
1081 return -ENOMEM;
1082
1083 action->handler = handler;
1084 action->thread_fn = thread_fn;
1085 action->flags = irqflags;
1086 action->name = devname;
1087 action->dev_id = dev_id;
从1079~1087:根据requst_irq()函数中传递的参数生成一个irqaction.
1097 if (!retval && (irqflags & IRQF_SHARED)) {
1098 /*
1099 * It's a shared IRQ -- the driver ought to be prepared for it
1100 * to happen immediately, so let's make sure....
1101 * We disable the irq to make sure that a 'real' IRQ doesn't
1102 * run in parallel with our fake.
1103 */
1104 unsigned long flags;
1105
1106 disable_irq(irq);
1107 local_irq_save(flags);
1108
1109 handler(irq, dev_id);
1110
1111 local_irq_restore(flags);
1112 enable_irq(irq);
1113 }
1097~1113:如果为共享中断的话,在执行中断服务例程之前,要先把这条中断线上的中断屏蔽,让后在执行,执行完之后打开中断。
6.有注册中断服务函数,那必然有相应的释放中断函数。
可以调用void free_irq(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id)来释放我们申请的中断线。
函数形参:
1>unsigned int riq:表示申请的中断号与request_irq()函数中的第一个形参对应。
2>void *dev_id:与request_irq()函数中的最后一个形参含义和用法相同,在此不再说明。
函数功能:
如果指定的中断线不是共享的,那么,该函数删除处理程序的同时将禁用这条中断线。如果中断线是共享的,则仅删除dev_id所对应的处理程序,而这条中断线本省只有在删除了最后一个处理程序时才会被禁止。
切记:This function must not be called from interrupt context
freee_irq()函数不能在中断上下文中被调用。
3>深入分析下free_irq()函数内部是如何实现的
- 993void free_irq(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id)
- 994{
- 995 struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
- 996
- 997 if (!desc)
- 998 return;
- 999
- 1000 chip_bus_lock(irq, desc);
- 1001 kfree(__free_irq(irq, dev_id));
- 1002 chip_bus_sync_unlock(irq, desc);
- 1003}
可以看到free_irq()函数了封装了_free_irq(irq,dev_id)函数。
free_irq()调用_free_irq()把每一个具体的中断服务例程()释放。