android开发笔记之remote service 的aidl详解
写在前面的话:
关于remote service中使用aidl来实现跨进程,多线程通信,我是参考了三篇文章,大概把这个弄明白了。
(1)android 官方关于aidl的说明文档
docs/guide/components/aidl.html
(2)Android学习笔记23服务Service之AIDL和远程服务实现进程通信以及进程间传递自定义类型参数
http://blog.csdn.net/honeybaby201314/article/details/19989455
(3) Android AIDL使用详解
http://blog.csdn.net/stonecao/article/details/6425019
aidl的官方描述:
AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language) is similar to other IDLs you might have worked with. It allows you to define the programming interface that both the client and service agree upon in order to communicate with each other using interprocess communication (IPC).
AIDL(android接口定义语言)与IDLs类似,他主要是定义客户端与服务器统一的编程接口以便让客户端与服务器端跨进程通信(IPC)。
什么地方使用aidl:
Note: Using AIDL is necessary only if you allow clients from different applications to access your service for IPC and want to handle multithreading in your service. If you do not need to perform concurrent IPC across different applications, you should create your interface by implementing a Binder or, if you want to perform IPC, but do not need to handle multithreading, implement your interface using a Messenger.
如果clients要从不同应用跨进程访问service,在service中处理多线程操作。我们才会使用AIDL。如果不需要跨进程,我们可以创建实现Binder的接口,如果我们需要跨进程通信,但是不需要处理多线程操作,那么,我们可以使用Messager.
如何使用aidl:
To create a bounded service using AIDL, follow these steps:
1. Create the .aidl file
This file defines the programming interface with method signatures.
2. Implement the interface
The Android SDK tools generate an interface in the Java programming language, based on your .aidl file. This interface has an inner abstract class named Stub that extends Binder and implements methods from your AIDL interface. You must extend the Stub class and implement the methods.
3. Expose the interface to clients
Implement a Service and override onBind() to return your implementation of the Stub class.
aidl使用的详细步骤
我以官方文档和另外一个样例,写了一个Demo来说明如何实现aidl的
使用。
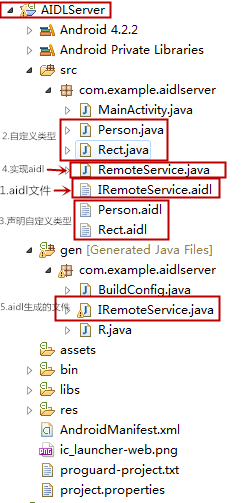
(1)服务端
创建aidl文件(IRemoteService.aidl):
package com.example.aidlserver;
import com.example.aidlserver.Rect;
import com.example.aidlserver.Person;
interface IRemoteService {
int getPid();
void onRemoteServiceDo();
void onProcessRect(in com.example.aidlserver.Rect rect);
com.example.aidlserver.Rect getRect();
Person getPerson();
void savePerson(in Person person);
}我们定义 6个接口,其中getPid(),onRemoteServiceDo()处理基本的数据类型,onProcessRect和getRect方法处理自定义的数据类型Rect,getPerson和savePerson方法处理自定义数据类型Person.
编写Aidl文件时,需要注意的地方:
- 接口名和aidl文件名相同
- 接口和方法前不用加访问权限修饰符public,private,protected等,也不能用final,static
- Aidl默认支持的类型包话java基本类型(int、long、boolean)和(String、List、Map、CharSequence),使用这些类型时不需要import声明。对于List和Map中的元素类型必须是Aidl支持的类型。如果使用自定义类型作为参数或返回值,自定义类型必须实现Parcelable接口
- 自定义类型和AIDL生成的其它接口类型在aidl描述文件中,应该显式import,即便在该类和定义的包在同一个包中
- 在aidl文件中所有非Java基本类型参数必须加上in、out、inout标记,以指明参数是输入参数、输出参数还是输入输出参数
- Java原始类型默认的标记为in,不能为其它标记
aidl中自定义数据类型
我们的样例中,aidl中使用了二个自定义的数据类型(Rect,Person)。使用自定义的类,我们必须让此类实现Parcelable接口,重写describeContents和writeToParcel方法,并且要定义一个Parcelable.Creator 类型的变量CREATOR。
- 类Rect
package com.example.aidlserver;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Rect implements Parcelable{
public int left;
public int top;
public int right;
public int bottom;
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Rect> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Rect>() {
@Override
public Rect createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Rect(source);
}
@Override
public Rect[] newArray(int size) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Rect[size];
}
};
public Rect() {
}
public Rect(int left,int top,int right,int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
private Rect(Parcel in) {
readFromParcel(in);
}
private void readFromParcel(Parcel in) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
left = in.readInt();
top = in.readInt();
right = in.readInt();
bottom = in.readInt();
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
out.writeInt(left);
out.writeInt(top);
out.writeInt(right);
out.writeInt(bottom);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.toString()
+"--left:"+left
+"--top:"+top
+"--right:"+right
+"--bottom:"+bottom;
}
}- 类Person
package com.example.aidlserver;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Person implements Parcelable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int arg1) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
dest.writeInt(id);
dest.writeString(name);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Person> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Person>() {
@Override
public Person createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Person(source.readInt(), source.readString());
}
@Override
public Person[] newArray(int size) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Person[size];
}
};
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.toString()
+"--id:"+id
+"--name:"+name;
}
}声明自定义的数据类型
我们在自定义的数据类型所在包下创建一个aidl文件对自定义类型进行声明,文件的名称与自定义类型同名。例如,Person.aidl声明Person类,Rect.aidl声明Rect类。
- Person.aidl
package com.example.aidlserver;
parcelable Person;- Rect.aidl
package com.example.aidlserver;
parcelable Rect;实现aidl的接口
我们使用RemoteService.java来实现aidl接口:
package com.example.aidlserver;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.os.Process;
import com.example.aidlserver.Rect;
public class RemoteService extends Service{
private final static String TAG ="RemoteService";
private Rect rect = new Rect(0, 0, 100, 100);
private Person person = new Person(1,"name_01");
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mBinder;
}
private final IRemoteService.Stub mBinder = new IRemoteService.Stub() {
public int getPid(){
return Process.myPid();
}
@Override
public void onRemoteServiceDo() throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "RemoteService---onRemoteServiceDo()");
}
@Override
public Rect getRect() throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return rect;
}
@Override
public void onProcessRect(Rect rect)
throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
RemoteService.this.rect.left = rect.left;
RemoteService.this.rect.top = rect.top;
RemoteService.this.rect.right = rect.right;
RemoteService.this.rect.bottom = rect.bottom;
Log.i(TAG, "onProcessRect--:"+RemoteService.this.rect);
}
@Override
public Person getPerson() throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return person;
}
@Override
public void savePerson(Person person) throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
person.setId(2);
person.setName("name_02");
Log.i(TAG,"savePerson:"+person);
}
};
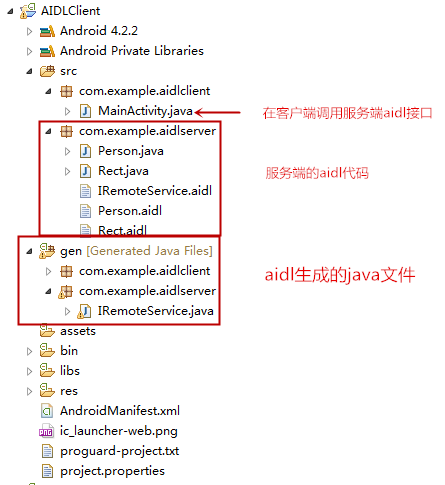
}(2)客户端
1. 将服务端的aidl文件复制到客户端
主要包括aidl文件,自定义的数据类型的java文件。(IRemoteService.aidl,Person.aidl,Rect.aidl,Person.java,Rect.java)
2.在客户端调用aidl接口
MainActivity.java
package com.example.aidlclient;
import com.example.aidlserver.IRemoteService;
import com.example.aidlserver.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Process;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private final static String TAG ="MainActivity";
private Button button;
private IRemoteService mIRemoteService;
private Intent intent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
intent = new Intent("com.android.ACTION.RemoteService");
//startService(intent);
bindService(intent, mConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(view == button){
try {
Log.i(TAG, "Process.myPid():"+Process.myPid());
Log.i(TAG, "mIRemoteService.getPid():"+mIRemoteService.getPid());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
mIRemoteService.onRemoteServiceDo();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Log.i(TAG, "mIRemoteService.getRect():"+mIRemoteService.getRect());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
mIRemoteService.onProcessRect(new Rect(0,0,200,200));
} catch (RemoteException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Log.i(TAG, "mIRemoteService.getPerson():"+mIRemoteService.getPerson());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
mIRemoteService.savePerson(mIRemoteService.getPerson());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
//stopService(intent);
unbindService(mConnection);
}
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
// Called when the connection with the service is established
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
// Following the example above for an AIDL interface,
// this gets an instance of the IRemoteInterface, which we can use to call on the service
mIRemoteService = IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
// Called when the connection with the service disconnects unexpectedly
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
Log.e(TAG, "Service has unexpectedly disconnected");
mIRemoteService = null;
}
};
}代码下载
这是我的源码