线性表数据结构解读(二)链式存储结构LinkedList
在上一篇文章中,我们详细介绍了线性表数据结构的原理以及顺序存储结构,并结合ArrayList源码进行了分析,相关文章大家可以点击这里回看我的博客:线性表数据结构解读(一)顺序存储结构ArrayList
本篇文章,我将给大家继续解读线性表数据结构,这次我们来谈链式存储结构。
链式存储结构
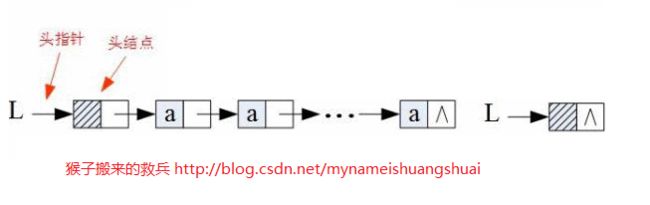
链式存储结构是用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素,这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的。 我们将数据元素和下一个元素位置的结构称为链表的节点。若第一个节点只表示整个链表的起始位置,而无任何信息,称其为头结点。对于最后一个结点,后面无任何元素,其表示元素位置的地址用“^”来表示,称其为尾结点,程序实现中用”null“表示。
链表中结点的表示必须要用到两个域,其中一个存放数组元素自身的信息ai,称其为数据域,另一个存放下一个元素的地址或位置,以保证链表的连续性,称其为指针。
链式存储结构的优缺点
优:删除和插入效率高
缺:查询效率低链表的分类
● 单链表
是由第一个元素到最后一个元素构成的一个链,其特点是从第一个元素(可能有头指针和头结点)到最后一个元素(结束标志位^)够成的一个链,成为单链表。我们通过第一个元素的指针可以顺序找到后面元素所在的位置,因此所有操作全部是从第一个元素(头指针或头结点)开始的。● 循环链表
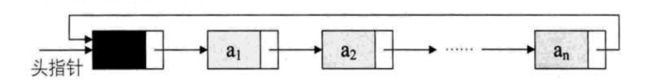
在单链表中,最后一个元素的存储区域是^,如果将它指向第一个元素(头结点)位置,就构成了循环链表。循环链表的特点是在所有元素之间构成的一个环,从任何一个元素出发,都可以查找其他所有元素,同时还充分利用了空间。
● 双向循环链表
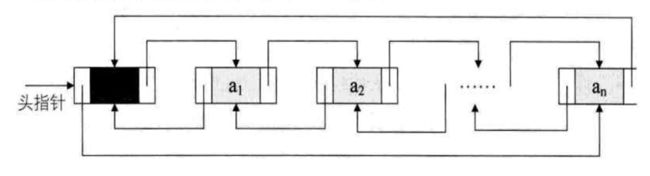
双向循环链表是单向循环链表的每个结点中,再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针域。也就是说,可以从任何一个元素出发,向两个方向分别查找相应的元素,可以提高操作效率。● 空的双向循环链表
在Java中,我们常见具有代表性的链式存储结构有很多,这里我们以LinkedList为例,进行分析,看看它内部是如何实现链式存储结构的,由于源码过长,这里我们重点分析增删改查和迭代器方法。
构造方法
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements
List<E>, Deque<E>, Queue<E>, Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
transient int size = 0;
transient Link<E> voidLink;// 头指针
private static final class Link<ET> {// 内部精简后的静态Link类,这个其实就是一个结点
ET data;
Link<ET> previous, next;// 双向链表
Link(ET o, Link<ET> p, Link<ET> n) {
data = o;
previous = p;
next = n;
}
}
/** * LinkedList无参构造 */
public LinkedList() {
// 实例化头指针
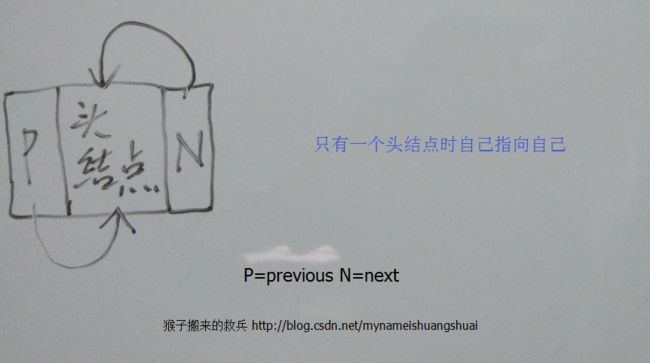
voidLink = new Link<E>(null, null, null);
// 分别让头指针的previous和next等于头指针
voidLink.previous = voidLink;
voidLink.next = voidLink;
}
/** * 接收一个Collection参数的LinkedList构造方法 */
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> collection) {
this();
addAll(collection);
}迭代器
// 作为一个List,LinkedList肯定也包含一个迭代器
private static final class LinkIterator<ET> implements ListIterator<ET> {
int pos, expectedModCount;
final LinkedList<ET> list;
// link表示当前正在遍历的指针,lastLink表示最后的节点
Link<ET> link, lastLink;
LinkIterator(LinkedList<ET> object, int location) {
list = object;
expectedModCount = list.modCount;
if (location >= 0 && location <= list.size) {
// pos ends up as -1 if list is empty, it ranges from -1 to
// list.size - 1
// if link == voidLink then pos must == -1
link = list.voidLink;
if (location < list.size / 2) {
for (pos = -1; pos + 1 < location; pos++) {
link = link.next;
}
} else {
for (pos = list.size; pos >= location; pos--) {
link = link.previous;
}
}
} else {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
// 在迭代器中的添加方法,单向链表
public void add(ET object) {
if (expectedModCount == list.modCount) {
Link<ET> next = link.next;// 拿到当前结点的下一个结点
Link<ET> newLink = new Link<ET>(object, link, next);// new一个新的Link
link.next = newLink;// 把当前结点的下一个结点指向newLink
next.previous = newLink;// 把先前结点的下一个结点的前驱指向newLink
link = newLink;// 最后把当前结点link变为newLink
lastLink = null;// 指向新结点后,把LastLink置空
pos++;
expectedModCount++;
list.size++;// 长度+1
list.modCount++;// 计量器+1
} else {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return link.next != list.voidLink;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return link != list.voidLink;
}
public ET next() {
if (expectedModCount == list.modCount) {
LinkedList.Link<ET> next = link.next;
if (next != list.voidLink) {
lastLink = link = next;
pos++;
return link.data;
}
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return pos + 1;
}
public ET previous() {
if (expectedModCount == list.modCount) {
if (link != list.voidLink) {
lastLink = link;
link = link.previous;
pos--;
return lastLink.data;
}
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public int previousIndex() {
return pos;
}
// 移除当前结点
public void remove() {
if (expectedModCount == list.modCount) {
if (lastLink != null) {
Link<ET> next = lastLink.next;
Link<ET> previous = lastLink.previous;
next.previous = previous;
previous.next = next;
if (lastLink == link) {
pos--;
}
link = previous;
lastLink = null;
expectedModCount++;
list.size--;
list.modCount++;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
} else {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 修改当前结点
public void set(ET object) {
if (expectedModCount == list.modCount) {
if (lastLink != null) {
lastLink.data = object;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
} else {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}添加方法
/** * 添加方法,在指定位置进行添加 * @param location the index at which to insert. * @param object the object to add. * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * if {@code location < 0 || location > size()} */
@Override
public void add(int location, E object) {
if (location >= 0 && location <= size) {// 在链表的中间添加
Link<E> link = voidLink;
// 为了提高效率,采用二分法的思想,需要判断前半段和后半段进行插入
if (location < (size / 2)) {// 表示在前半段
for (int i = 0; i <= location; i++) {
link = link.next;
}
} else {// 表示在后半段
for (int i = size; i > location; i--) {
link = link.previous;
}
}
// 将当前结点的前一结点赋值给previous
Link<E> previous = link.previous;
// 初始化先创建结点newLink,其数据域是object,前面的结点是previous,后面的结点是link
Link<E> newLink = new Link<E>(object, previous, link);
// 让previous.next指向新节点
previous.next = newLink;
// 同时让link.previous指向新节点
link.previous = newLink;
size++;// 长度+1
modCount++;// 计量器+1
} else {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
/** * 将元素(E)添加到LinkedList中 * @param object the object to add. * @return always true */
@Override
public boolean add(E object) {
return addLastImpl(object);
}
/** * 在最猴添加元素的方法 */
private boolean addLastImpl(E object) {
// 将头结点的previous,其实就是头结点自己,赋值给oldLast
Link<E> oldLast = voidLink.previous;
// 新建一个要插入的新节点,其数据域是object,previous结点是oldLast,next结点是voidLink
Link<E> newLink = new Link<E>(object, oldLast, voidLink);
// 让头指针的前面previous指向新建结点
voidLink.previous = newLink;
// 让oldLast.next指向新建结点
oldLast.next = newLink;
size++;// 长度+1
modCount++;// 计量器+1
return true;
}为了方便大家理解,下面我将画图来解释下插入结点的实现机制
删除方法
/** * Removes the object at the specified location from this {@code LinkedList}. * @param location the index of the object to remove * @return the removed object * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * if {@code location < 0 || location >= size()} */
@Override
public E remove(int location) {
// 先判断location >= 0 && location < size
if (location >= 0 && location < size) {
Link<E> link = voidLink;
// 采用二分法的思想,先找前半段
if (location < (size / 2)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= location; i++) {
link = link.next;
}
} else {// 再找后半段
for (int i = size; i > location; i--) {
link = link.previous;
}
}
Link<E> previous = link.previous;
Link<E> next = link.next;
previous.next = next;// 待删除结点的前一结点的后指针指向待删除结点的后一个结点
next.previous = previous;// 待删除结点的后一结点的前指针指向待删除结点的前一个结点
size--;// 长度-1
modCount++;// 计量器+1
// 返回移除结点的内容
return link.data;
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}获取方法
@Override
public E get(int location) {
// 先判断location >= 0 && location < size
if (location >= 0 && location < size) {
Link<E> link = voidLink;
// 采用二分法的思想,先找前半段
if (location < (size / 2)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= location; i++) {
link = link.next;
}
} else {// 再找后半段
for (int i = size; i > location; i--) {
link = link.previous;
}
}
return link.data;// 返回结点内容
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}修改方法
/** * Replaces the element at the specified location in this {@code LinkedList} * with the specified object. * * @param location * the index at which to put the specified object. * @param object * the object to add. * @return the previous element at the index. * @throws ClassCastException * if the class of an object is inappropriate for this list. * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if an object cannot be added to this list. * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * if {@code location < 0 || location >= size()} */
@Override
public E set(int location, E object) {
// 先判断location >= 0 && location < size
if (location >= 0 && location < size) {
Link<E> link = voidLink;
// 采用二分法的思想,先找前半段
if (location < (size / 2)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= location; i++) {
link = link.next;
}
} else {// 再找后半段
for (int i = size; i > location; i--) {
link = link.previous;
}
}
// 做数据修改
E result = link.data;
link.data = object;
return result;
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}上一篇文章:线性表数据结构解读(一)顺序存储结构ArrayList