android开发笔记之service(一)
前面的话
曾经去一个高大上的公司面试,面试官给我一支笔要我写一下service的生命周期。然后,我还真不会写,虽然说经常用service,但是还真说不清service的生命周期。然后就让人见笑了,最后自己也笑了。
今天,我们来详细的看看service的介绍
service简介
service的官方介绍:
A Service is an application component representing either an application’s desire to perform a longer-running operation while not interacting with the user or to supply functionality for other applications to use. Services can be started with Context.startService() and Context.bindService().
service是一个应用组件,主要设计是为了在后台进行一些长时间的操作。我们可以使用Context.startService() 和 Context.bindService()来启动service.
service,process与thread的关系:
A Service is not a separate process. The Service object itself does not imply it is running in its own process; unless otherwise specified, it runs in the same process as the application it is part of.
service不是一个单独的process. service与应用是在同一个process.A Service is not a thread. It is not a means itself to do work off of
the main thread (to avoid Application Not Responding errors).
service不是一个thread. 但是service与main thread是同一个thread.Thread 是程序执行的最小单元,它是分配CPU的基本单位。可以用 Thread 来执行一些异步的操作
Service 是android的一种机制,当它运行的时候如果是Local Service,那么对应的 Service 是运行在主进程的 main 线程上的。如:onCreate,onStart 这些函数在被系统调用的时候都是在主进程的 main 线程上运行的。如果是Remote Service,那么对应的 Service 则是运行在独立进程的 main 线程上。因此请不要把 Service 理解成线程,它跟线程半毛钱的关系都没有!
- 我们可以把Service 想象成一种消息服务,在任何有 Context 的地方调用 Context.startService、Context.stopService、 Context.bindService,Context.unbindService来控制它,也可以在 Service 里注册 BroadcastReceiver,在其他地方通过发送 broadcast 来控制它,但是这些都是 Thread 做不到的。
Service Lifecycle
Conte;xt.startService()启动服务, Context.stopService() or stopSelf()结束服务的生命周期
onCreate—–onStartCommand—– onStart—-(服务已经启动)—-(调用Context.stopService() or stopSelf()结束service)—-onDestroy
但是当service如果已经启动,我们再调用Conte;xt.startService()启动服务,则是再调用onStartCommand——onStart,而不再是调用onCreate方法。Context.bindService()启动服务,Context.unbindService结束服务的生命周期:
onCreate—–onBind—(服务已经启动)——-(Context.unbindService结束service)—– onUnbind—— onDestroy
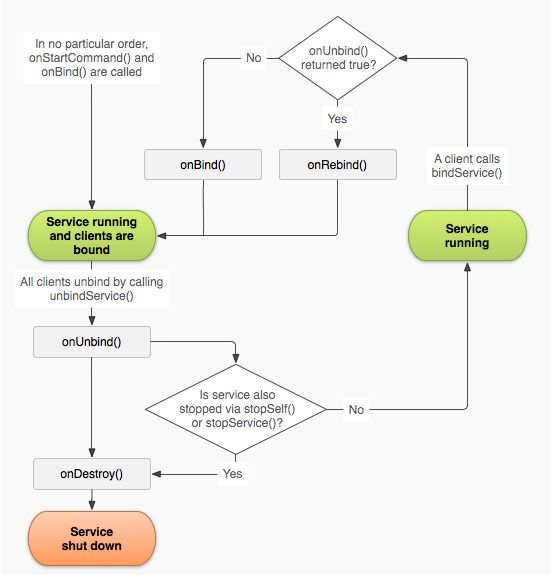
service生命周期的简图:
service 启动之后再bind的生命周期:
我们调用Conte;xt.startService()启动服务,再调用Context.bindService()绑定服务,然后再调用Context.unbindService解除绑定,再调用Context.stopService() 或者 stopSelf()结束服务。
onCreate—–>onStartCommand—–>onStart—–>onBind—–>onUnbind—–>onDestroy
常用service样例
自定义service
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.media.MediaPlayer;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class DemoService extends Service{
public static final String TAG ="DemoService";
public MediaPlayer mediaPlayer;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate");
if(mediaPlayer == null){
mediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(getApplicationContext(), R.raw.nx);
mediaPlayer.start();
}
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "onStartCommand");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
@Deprecated
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStart(intent, startId);
Log.i(TAG, "onStart");
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "onBind");
if(mediaPlayer == null){
mediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(getApplicationContext(), R.raw.nx);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "onUnbind");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onRebind(intent);
Log.i(TAG, "onRebind");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
Log.i(TAG, "onDestroy");
if(mediaPlayer != null){
mediaPlayer.stop();
mediaPlayer.release();
}
}
public class DemoServiceBinder extends Binder {
DemoService getService() {
return DemoService.this;
}
}
}在AndroidManifest.xml申明service
<service android:name=".DemoService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.DemoService" />
</intent-filter>
</service> 启动结束service
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class ServiceDemoMainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
//public static final String TAG = "ServiceDemoMainActivity";
public static final String TAG = "DemoService";
private Button myButton01;
private Button myButton02;
private Button myButton03;
private Button myButton04;
protected DemoService myService;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_service_demo_main);
init();
}
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
myButton01 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton01);
myButton01.setOnClickListener(this);
myButton02 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton02);
myButton02.setOnClickListener(this);
myButton03 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton03);
myButton03.setOnClickListener(this);
myButton04 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton04);
myButton04.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(ServiceDemoMainActivity.this, DemoService.class);
switch(view.getId()){
case R.id.myButton01:
startService(intent);
break;
case R.id.myButton02:
stopService(intent);
break;
case R.id.myButton03:
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.myButton04:
try {
unbindService(serviceConnection);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
Log.e(TAG,"e:"+e.toString());
}
break;
}
}
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.i(TAG, "service connect success");
myService = ((DemoService.DemoServiceBinder) service).getService();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.i(TAG, "service disconnected");
myService = null;
}
};
}参考资料
Android Service的生命周期
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/03/24/2979944.htmlActivity和Service的生命周期
http://www.cnblogs.com/andriod-html5/archive/2012/04/17/2539687.html