Tensorflow学习:ResNet代码(详细剖析)-待补充,非最终版本
参考链接:
感谢此位博主的工作,本博主只做进一步的剖析,目的为掌握和具备二次开发能力。
http://blog.csdn.net/superman_xxx/article/details/65452735
先贴代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
""" Created on Thu Aug 17 16:24:55 2017 Project: Residual Neural Network E-mail: [email protected] Reference: 《Tensorflow实战》P143-P156 @author: DidiLv """
""" Typical use: from tensorflow.contrib.slim.nets import resnet_v2 ResNet-101 for image classification into 1000 classes: # inputs has shape [batch, 224, 224, 3] with slim.arg_scope(resnet_v2.resnet_arg_scope(is_training)): net, end_points = resnet_v2.resnet_v2_101(inputs, 1000) ResNet-101 for semantic segmentation into 21 classes: # inputs has shape [batch, 513, 513, 3] with slim.arg_scope(resnet_v2.resnet_arg_scope(is_training)): net, end_points = resnet_v2.resnet_v2_101(inputs, 21, global_pool=False, output_stride=16) """
import collections # 原生的collections库
import tensorflow as tf
slim = tf.contrib.slim # 使用方便的contrib.slim库来辅助创建ResNet
# 这里值得注意的是只有定义了类。其他的并没有定义,从空格发现。这也就是书中所说的“只包含数据结构,不包含具体方法”
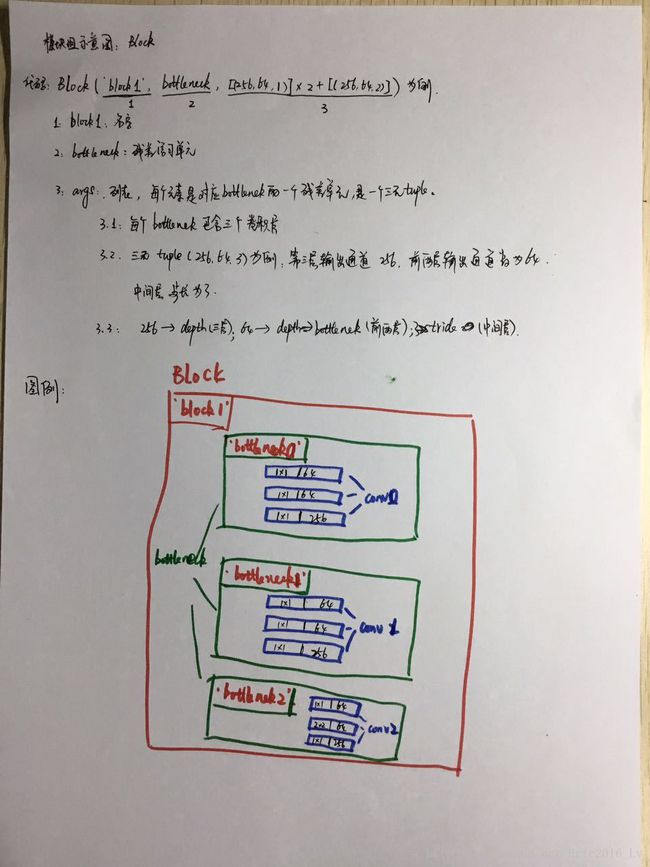
class Block(collections.namedtuple('Block', ['scope', 'unit_fn', 'args'])):
''' 使用collections.namedtuple设计ResNet基本模块组的name tuple,并用它创建Block的类 只包含数据结构,不包含具体方法。 定义一个典型的Block,需要输入三个参数: scope:Block的名称 unit_fn:ResNet V2中的残差学习单元 args:Block的args。 '''
#图片解释:图例1
########定义一个降采样的方法########
def subsample(inputs, factor, scope=None):
"""Subsamples the input along the spatial dimensions. Args: inputs: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels]. factor: The subsampling factor.(采样因子或采样率) scope: Optional variable_scope. Returns: output: 如果factor为1,则不做修改直接返回inputs;如果不为1,则使用 slim.max_pool2d最大池化来实现,通过1*1的池化尺寸,stride作步长,实 现降采样。 """
if factor == 1:
return inputs
else:
return slim.max_pool2d(inputs, [1, 1], stride=factor, scope=scope)
########创建卷积层########
def conv2d_same(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride, scope=None):
""" Args: inputs: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels]. num_outputs: An integer, the number of output filters. kernel_size: An int with the kernel_size of the filters. stride: An integer, the output stride. rate: An integer, rate for atrous convolution. scope: Scope. Returns: output: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels] with the convolution output. """
if stride == 1:
return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=1,
padding='SAME', scope=scope)
else:
pad_total = kernel_size - 1
pad_beg = pad_total // 2
pad_end = pad_total - pad_beg
inputs = tf.pad(inputs, # 对输入变量进行补零操作
[[0, 0], [pad_beg, pad_end], [pad_beg, pad_end], [0, 0]])
# 因为已经进行了zero padding,所以只需再使用一个padding模式为VALID的slim.conv2d创建这个卷积层
# 详细解释请见图二
return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding='VALID', scope=scope)
########定义堆叠Blocks的函数########
@slim.add_arg_scope
def stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks, outputs_collections=None):
""" Args: net: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height, width, channels].输入。 blocks: 是之前定义的Block的class的列表。 outputs_collections: 收集各个end_points的collections。 Returns: net: Output tensor """
# 使用两层循环,逐个Residual Unit地堆叠
for block in blocks: # 先使用两个tf.variable_scope将残差学习单元命名为block1/unit_1的形式
with tf.variable_scope(block.scope, 'block', [net]) as sc:
for i, unit in enumerate(block.args):
with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' % (i + 1), values=[net]):
# 在第2层循环中,我们拿到每个block中每个Residual Unit的args并展开为下面四个参数
unit_depth, unit_depth_bottleneck, unit_stride = unit
net = block.unit_fn(net, # 使用残差学习单元的生成函数顺序的创建并连接所有的残差学习单元
depth=unit_depth,
depth_bottleneck=unit_depth_bottleneck,
stride=unit_stride)
net = slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, sc.name, net) # 将输出net添加到collections中
return net # 当所有block中的所有Residual Unit都堆叠完成之后,再返回最后的net作为stack_blocks_dense
# 创建ResNet通用的arg_scope,arg_scope用来定义某些函数的参数默认值
def resnet_arg_scope(is_training=True, # 训练标记 weight_decay=0.0001, # 权重衰减速率 batch_norm_decay=0.997, # BN的衰减速率 batch_norm_epsilon=1e-5, # BN的epsilon默认1e-5 batch_norm_scale=True): # BN的scale默认值
batch_norm_params = { # 定义batch normalization(标准化)的参数字典
'is_training': is_training,
'decay': batch_norm_decay,
'epsilon': batch_norm_epsilon,
'scale': batch_norm_scale,
'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
}
with slim.arg_scope( # 通过slim.arg_scope将[slim.conv2d]的几个默认参数设置好
[slim.conv2d],
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay), # 权重正则器设置为L2正则
weights_initializer=slim.variance_scaling_initializer(), # 权重初始化器
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, # 激活函数
normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm, # 标准化器设置为BN
normalizer_params=batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], **batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding='SAME') as arg_sc: # ResNet原论文是VALID模式,SAME模式可让特征对齐更简单
return arg_sc # 最后将基层嵌套的arg_scope作为结果返回
# 定义核心的bottleneck残差学习单元
@slim.add_arg_scope
def bottleneck(inputs, depth, depth_bottleneck, stride, outputs_collections=None, scope=None):
""" Args: inputs: A tensor of size [batch, height, width, channels]. depth、depth_bottleneck:、stride三个参数是前面blocks类中的args rate: An integer, rate for atrous convolution. outputs_collections: 是收集end_points的collection scope: 是这个unit的名称。 """
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'bottleneck_v2', [inputs]) as sc: # slim.utils.last_dimension获取输入的最后一个维度,即输出通道数。
depth_in = slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(), min_rank=4) # 可以限定最少为四个维度
# 使用slim.batch_norm对输入进行batch normalization,并使用relu函数进行预激活preactivate
preact = slim.batch_norm(inputs, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='preact')
if depth == depth_in:
shortcut = subsample(inputs, stride, 'shortcut')
# 如果残差单元的输入通道数和输出通道数一致,那么按步长对inputs进行降采样
else:
shortcut = slim.conv2d(preact, depth, [1, 1], stride=stride,
normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=None,
scope='shortcut')
# 如果不一样就按步长和1*1的卷积改变其通道数,使得输入、输出通道数一致
# 先是一个1*1尺寸,步长1,输出通道数为depth_bottleneck的卷积
residual = slim.conv2d(preact, depth_bottleneck, [1, 1], stride=1,
scope='conv1')
# 然后是3*3尺寸,步长为stride,输出通道数为depth_bottleneck的卷积
residual = conv2d_same(residual, depth_bottleneck, 3, stride,
scope='conv2')
# 最后是1*1卷积,步长1,输出通道数depth的卷积,得到最终的residual。最后一层没有正则项也没有激活函数
residual = slim.conv2d(residual, depth, [1, 1], stride=1,
normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=None,
scope='conv3')
output = shortcut + residual # 将降采样的结果和residual相加
return slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, # 将output添加进collection并返回output作为函数结果
sc.name,
output)
########定义生成resnet_v2的主函数########
def resnet_v2(inputs, # A tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].输入 blocks, # 定义好的Block类的列表 num_classes=None, # 最后输出的类数 global_pool=True, # 是否加上最后的一层全局平均池化 include_root_block=True, # 是否加上ResNet网络最前面通常使用的7*7卷积和最大池化 reuse=None, # 是否重用 scope=None): # 整个网络的名称
# 在函数体先定义好variable_scope和end_points_collection
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'resnet_v2', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:
end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points' # 定义end_points_collection
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, bottleneck,
stack_blocks_dense],
outputs_collections=end_points_collection): # 将三个参数的outputs_collections默认设置为end_points_collection
net = inputs
if include_root_block: # 根据标记值
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d],
activation_fn=None, normalizer_fn=None):
net = conv2d_same(net, 64, 7, stride=2, scope='conv1') # 创建resnet最前面的64输出通道的步长为2的7*7卷积
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool1') # 然后接最大池化
# 经历过两个步长为2的层图片缩为1/4
net = stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks) # 将残差学习模块组生成好
net = slim.batch_norm(net, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='postnorm')
if global_pool: # 根据标记添加全局平均池化层
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], name='pool5', keep_dims=True) # tf.reduce_mean实现全局平均池化效率比avg_pool高
if num_classes is not None: # 是否有通道数
net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, # 无激活函数和正则项
normalizer_fn=None, scope='logits') # 添加一个输出通道num_classes的1*1的卷积
end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection) # 将collection转化为python的dict
if num_classes is not None:
end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net, scope='predictions') # 输出网络结果
return net, end_points
#------------------------------ResNet的生成函数定义好了----------------------------------------
def resnet_v2_50(inputs, # 图像尺寸缩小了32倍 num_classes=None, global_pool=True, reuse=None, # 是否重用 scope='resnet_v2_50'):
blocks = [
Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
# Args::
# 'block1':Block名称(或scope)
# bottleneck:ResNet V2残差学习单元
# [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]:Block的Args,Args是一个列表。其中每个元素都对应一个bottleneck
# 前两个元素都是(256, 64, 1),最后一个是(256, 64, 2)。每个元素
# 都是一个三元tuple,即(depth,depth_bottleneck,stride)。
# (256, 64, 3)代表构建的bottleneck残差学习单元(每个残差学习单元包含三个卷积层)中,第三层输出通道数
# depth为256,前两层输出通道数depth_bottleneck为64,且中间那层步长3。这个残差学习单元结构为:
# [(1*1/s1,64),(3*3/s2,64),(1*1/s1,256)]
Block(
'block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block(
'block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 5 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block(
'block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
def resnet_v2_101(inputs, # unit提升的主要场所是block3 num_classes=None, global_pool=True, reuse=None, scope='resnet_v2_101'):
"""ResNet-101 model of [1]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""
blocks = [
Block(
'block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block(
'block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block(
'block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 22 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block(
'block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
def resnet_v2_152(inputs, # unit提升的主要场所是block3 num_classes=None, global_pool=True, reuse=None, scope='resnet_v2_152'):
"""ResNet-152 model of [1]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""
blocks = [
Block(
'block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block(
'block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 7 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block(
'block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block(
'block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
def resnet_v2_200(inputs, # unit提升的主要场所是block2 num_classes=None, global_pool=True, reuse=None, scope='resnet_v2_200'):
"""ResNet-200 model of [2]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""
blocks = [
Block(
'block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),
Block(
'block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 23 + [(512, 128, 2)]),
Block(
'block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),
Block(
'block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]
return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,
include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
#-------------------评测函数---------------------------------
# 测试152层深的ResNet的forward性能
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print ('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print ('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
batch_size = 32
height, width = 224, 224
inputs = tf.random_uniform((batch_size, height, width, 3))
with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=False)): # is_training设置为false
net, end_points = resnet_v2_152(inputs, 1000)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
num_batches=100
time_tensorflow_run(sess, net, "Forward")
# forward计算耗时相比VGGNet和Inception V3大概只增加了50%,是一个实用的卷积神经网络。