SpringBoot系列:RabbitMq讲解与示例
RabbitMQ介绍
RabbitMQ是实现AMQP(高级消息队列协议)的消息中间件的一种,最初起源于金融系统,用于在分布式系统中存储转发消息,在易用性、扩展性、高可用性等方面表现不俗。RabbitMQ主要是为了实现系统之间的双向解耦而实现的。当生产者大量产生数据时,消费者无法快速消费,那么需要一个中间层。保存这个数据。
AMQP,即Advanced Message Queuing Protocol,高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计。消息中间件主要用于组件之间的解耦,消息的发送者无需知道消息使用者的存在,反之亦然。AMQP的主要特征是面向消息、队列、路由(包括点对点和发布/订阅)、可靠性、安全。
RabbitMQ是一个开源的AMQP实现,服务器端用Erlang语言编写,支持多种客户端,如:Python、Ruby、.NET、Java、JMS、C、PHP、ActionScript、XMPP、STOMP等,支持AJAX。用于在分布式系统中存储转发消息,在易用性、扩展性、高可用性等方面表现不俗。
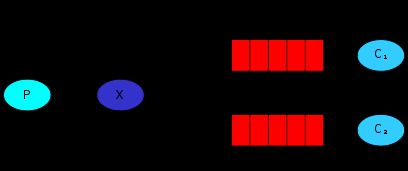
通常我们谈到队列服务, 会有三个概念: 发消息者、队列、收消息者,RabbitMQ 在这个基本概念之上, 多做了一层抽象, 在发消息者和 队列之间, 加入了交换器 (Exchange). 这样发消息者和队列就没有直接联系, 转而变成发消息者把消息给交换器, 交换器根据调度策略再把消息再给队列。
- 左侧 P 代表 生产者,也就是往 RabbitMQ 发消息的程序。
- 中间即是 RabbitMQ,其中包括了 交换机 和 队列。
- 右侧 C 代表 消费者,也就是往 RabbitMQ 拿消息的程序。
那么,其中比较重要的概念有 4 个,分别为:虚拟主机,交换机,队列,和绑定。
- 虚拟主机:一个虚拟主机持有一组交换机、队列和绑定。为什么需要多个虚拟主机呢?很简单,RabbitMQ当中,用户只能在虚拟主机的粒度进行权限控制。 因此,如果需要禁止A组访问B组的交换机/队列/绑定,必须为A和B分别创建一个虚拟主机。每一个RabbitMQ服务器都有一个默认的虚拟主机“/”。
- 交换机:Exchange 用于转发消息,但是它不会做存储 ,如果没有 Queue bind 到 Exchange 的话,它会直接丢弃掉 Producer 发送过来的消息。
这里有一个比较重要的概念:路由键 。消息到交换机的时候,交互机会转发到对应的队列中,那么究竟转发到哪个队列,就要根据该路由键。 - 绑定:也就是交换机需要和队列相绑定,这其中如上图所示,是多对多的关系。
四种交换机(Exchange)
交换机的功能主要是接收消息并且转发到绑定的队列,交换机不存储消息,在启用ack模式后,交换机找不到队列会返回错误。交换机有四种类型:Direct, topic, Headers and Fanout
- Direct:direct 类型的行为是"先匹配, 再投送". 即在绑定时设定一个 routing_key, 消息的routing_key 匹配时, 才会被交换器投送到绑定的队列中去.
- Topic:按规则转发消息(最灵活)
- Headers:设置header attribute参数类型的交换机
- Fanout:转发消息到所有绑定队列
下面我们将在Spring Boot框架中,先整合RabbitMq,分别对四种交换机进行讲解。
搭建Spring Boot工程
JDK版本1.8或以上,ide工具没有要求,这里使用了eclipse,选择新建工程,选择Spring Starter Project。
然后设置项目名和包名,进行下一步。
接着选择Spring Boot版本,选择合适的版本即可,这里我勾选了2.1.3,但是在下载jar包出现了问题,后在pom文件中更改为了2.1.1。然后添加web和RabbitMq即可。
下面给出项目包结构和核心配置文件,主要配置RabbitMq服务器的连接,在项目启动时要确保RabbitMq服务器已经正常启动。
下面给出pom文件,这里额外引入了swagger,方便对接口进行测试,还引入了devtools热部署插件,这个可以按需添加或删除。
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.1.RELEASE
com.yanger
mq
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
mq
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
2.7.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
${swagger.version}
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
${swagger.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
true
其中在common包下,是swagger的配置文件。
package com.yanger.rabbitmq.common;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
/**
* @description Swagger插件
* @author 杨号
* @date 2018年9月14日
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()).select()
// 当前包路径
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.yanger"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
// 页面标题
.title("yblog Swagger2 API接口").description("yblog API接口文档")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://github.com/imyanger")
// 创建人
.contact(new Contact("yanger", "https://github.com/imyanger/", "[email protected]")).version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
这样我们的SpringBoot + RabbitMq环境就已经搭建完毕了,下面我们来具体探讨4中交换机策略。
1.Direct Exchange
Direct Exchange是RabbitMQ默认的交换机模式,也是最简单的模式,根据key全文匹配去寻找队列。
定义队列及路由匹配规则,分别为direct_queue_1和direct_queue_2
定义消费者,也就是消息接收者,我们这里发送者和接收在一个项目中,而实际生产中,可能不在一个项目中,但是效果都是一样的。@RabbitListener声明监听,并设置queues属性表明监听的队列。
然后是生产者,也就是消息发送者,这里发送消息的路由和队列的规则完全匹配,也为direct_queue_1和direct_queue_2
最后是测试类,我们创建了Controller进行接口调用,项目启动后,因为是get请求,可以浏览器地址栏调用,也可以使用swagger工具。
然后启动项目,在http://localhost:19031/swagger-ui.html下,我们已经可以看到该接口了。输入参数进行测试,后面的测试也是相同,将不在累述。
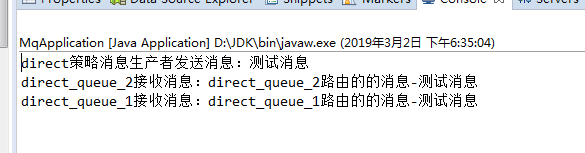
我们可以看到控制台的输出,和direct交换机策略介绍的一样,direct_queue_1接收接受了指向direct_queue_1路由的的消息,direct_queue_2接收接受了指向direct_queue_2路由的的消息。
2.Topic Exchange
按规则转发消息(最灵活) 转发消息主要是根据通配符。 在这种交换机下,队列和交换机的绑定会定义一种路由模式,那么,通配符就要在这种路由模式和路由键之间匹配后交换机才能转发消息。
路由键必须是一串字符,用句号(.) 隔开,路由模式必须包含一个 星号(*),主要用于匹配路由键指定位置的一个单词, 井号(#)就表示相当于一个或者多个单词。
下面是配置文件,队列1.2.3绑定了topic交换机,且路由规则分别定义为routingkey.#、#.topic和#。
package com.yanger.rabbitmq.topic;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TopicConfig {
/*
按规则转发消息(最灵活) 转发消息主要是根据通配符。 在这种交换机下,队列和交换机的绑定会定义一种路由模式,那么,通配符就要在这种路由模式和路由键之间匹配后交换机才能转发消息。
路由键必须是一串字符,用句号(.) 隔开,
路由模式必须包含一个 星号(*),主要用于匹配路由键指定位置的一个单词, 井号(#)就表示相当于一个或者多个单词
*/
public static final String QUEUE1 = "topic_queue_1";
public static final String QUEUE2 = "topic_queue_2";
public static final String QUEUE3 = "topic_queue_3";
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new Queue(QUEUE1);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new Queue(QUEUE2);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue3() {
return new Queue(QUEUE3);
}
// topic策略的交换机
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("topic");
}
// 绑定topicQueue1到topic交换机上,并指定路由匹配规则为routingkey.#,即路由以routingkey.开头的消息都将被topicQueue1接收
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding1(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("routingkey.#");
}
// 绑定topicQueue2到topic交换机上,并指定路由匹配规则为#.topic,即路由以.topic结尾的消息都将被topicQueue2接收
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("#.topic");
}
// 绑定topicQueue3到topic交换机上,并指定路由匹配规则为路由#,即任意路由消息都将被topicQueue3接收
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding3(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue3()).to(topicExchange()).with("#");
}
}
下面是消费者,主要是对规则及接收的消息进行打印输出。
生产者,向topic交换机上路由routingkey.all、all.topic、all.all发送消息。
进行测试,最终结果,可以发现绑定#规则的队列接收了该交换机上所有路由的消息,routingkey.#则接收该交换机上routingkey.开头的,#.topic则接收所有.topic结尾的。可以将all换成一个或多个字符,测试结果是一样的。
3. Headers Exchange
设置header attribute参数类型的交换机,相较于 direct 和 topic 固定地使用 routing_key , headers 则是一个自定义匹配规则的类型. 在队列与交换器绑定时, 会设定一组键值对规则, 消息中也包括一组键值对( headers 属性), 当这些键值对有一对, 或全部匹配时, 消息被投送到对应队列。
header策略配置文件,将headers_queue_1和headers_queue_2分别绑定到headers交换机上,并指定匹配规则,whereAll要求header中属性全部都匹配,而whereAny允许有任意一个属性匹配即可。
package com.yanger.rabbitmq.headers;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.HeadersExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class HeadersConfig {
/**
headers是一个自定义匹配规则的类型,在队列与交换器绑定时,会设定一组键值对规则,
消息中也包括一组键值对( headers 属性), 当这些键值对有一对, 或全部匹配时, 消息被投送到对应队列
*/
public static final String QUEUE1 = "headers_queue_1";
public static final String QUEUE2 = "headers_queue_2";
@Bean
public Queue headersQueue1() {
return new Queue(QUEUE1);
}
@Bean
public Queue headersQueue2() {
return new Queue(QUEUE2);
}
// headers策略的交换机
@Bean
public HeadersExchange headersExchange(){
return new HeadersExchange("headers");
}
// 绑定headersQueue1到headers交换机上,并指定当type和key全匹配
@Bean
public Binding headersBinding1(){
Map allMap = new HashMap<>();
allMap.put("type", "headers");
allMap.put("key", "1234");
return BindingBuilder.bind(headersQueue1()).to(headersExchange()).whereAll(allMap).match();
}
// 绑定headersQueue2到headers交换机上,并指定当type和key任意匹配一个
@Bean
public Binding headersBinding2(){
Map allMap = new HashMap<>();
allMap.put("type", "headers");
allMap.put("key", "1234");
return BindingBuilder.bind(headersQueue2()).to(headersExchange()).whereAny(allMap).match();
}
}
消息费,依旧输出接收的消息。
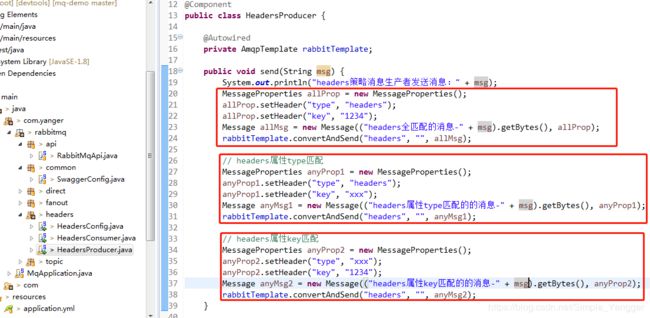
生产者,分别headers属性全匹配、headers属性type匹配、headers属性key匹配。
进行测试,结果如下。全匹配的只能接收headers属性全匹配的消息,而任意匹配的则最低只需要满足header属性中任意一个即可,当然满足多个也能接收,所以同样也接收到了全匹配发出的消息。
4. Fanout Exchange
转发消息到所有绑定队列,消息广播的模式,不管路由键或者是路由模式,会把消息发给绑定给它的全部队列,如果配置了routing_key会被忽略。
配置文件,fanou策略的交换机,只需要绑定队列到fanout交换机上,不需要指定路由规则。
package com.yanger.rabbitmq.fanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
/*
转发消息到所有绑定队列,消息广播的模式,不管路由键或者是路由模式,
会把消息发给绑定给它的全部队列,如果配置了routing_key会被忽略。
*/
public static final String QUEUE1 = "fanout_queue_1";
public static final String QUEUE2 = "fanout_queue_2";
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1() {
return new Queue(QUEUE1);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2() {
return new Queue(QUEUE2);
}
// fanout策略的交换机
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("fanout");
}
// 绑定fanoutQueue2到fanout交换机上,不需要指定路由
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
// 绑定fanoutQueue3到fanout交换机上,不需要指定路由
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding3(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
消费者。
生产者,可以看到并没有指定消息发送的路由,只指定了交换机。
测试结果,可以看到fanout交换机上队列fanout_queue_1和fanout_queue_2都收到了消息。
源码地址:https://github.com/imyanger/mq-demo