LevelDB : Skip List
引文
论文
http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/teaching/0506/Algorithms/skiplists.pdf
http://blog.nosqlfan.com/html/3041.html (翻译)
其他引文
http://www.csee.umbc.edu/courses/undergraduate/341/fall01/Lectures/SkipLists/skip_lists/skip_lists.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
http://mingxinglai.com/cn/2014/10/skip-list/
http://igoro.com/archive/skip-lists-are-fascinating/
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/uuQryy3 (作者对height的分析不错)
Skip List是对单向链表的扩展,使得其性能接近AVL和红黑树,同时实现起来更加简单。
Skip List被用来实现leveldb中的memtable,此外也被用来实现Redis中的sorted sets数据结构。
分析
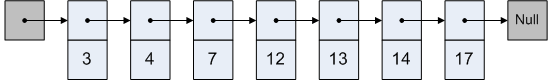
一个单向链表:
在单向链表中进行查找的时间复杂度是O(N)。此外,由于插入、删除操作首先都要使用查找操作,因此如何提高查找的性能成为关键问题。
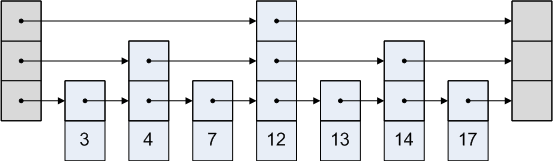
一种改善查找性能的方法,建立多级链表
那么查找7的过程是这样的(红色箭头):
从最高层链表(最稀疏的)开始,因为7小于12,所以进入下层链表继续查找,这样就不会在链表的后半部进行查找,所以查找范围减少了一半,过程类似折半查找。后续的查找过程类似,最后定位到7的位置。
所以,通过建立多级链表,可以提高查找性能。每层链表都是跳跃性前进的(skip),因此
称为 Skip List。Skip List通过在查找过程中“跳过”一些节点使得find,insert, remove的时间复杂度为O(lgN)。
概念梳理
We speak of a Skip List node having levels, one level per forward reference. The number of levels in a node is called the size of the node.
每个节点都在若干个level中出现,或者说节点有若干个level,而每个level是一个前进的指针。如果该节点有n个level,那么称该节点的size是n。
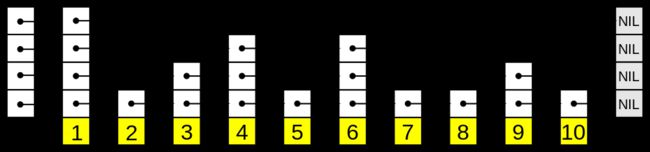
每级链表的跳跃距离
上面的skip list的最底层链表跳跃距离是1,第二次跳跃距离是2,最高层是4。这种跳跃策略是固定的。实际上,常用的跳跃策略是是基于概率的跳跃(probabilistically),像这样事儿的:
关于probabilistically策略,wikipedia是这样介绍的:
an element in layer i appears in layer i+1 with some fixed probability p (two commonly used values for p are 1/2 or 1/4). On average, each element appears in 1/(1-p) , and the tallest element (usually a special head element at the front of the skip list) in all the lists …(公式无法复制)
在第i层出现的元素出现在i+1层出现的概率是p(p通常是1/2或1/4)。平均下来,每个元素出现在1/(1-p)个链表中。
其中比较特殊的元素是head,它出现在所有list中,高度是 :
为什么要使用随机的level
原文解释在这里
大概是说,如果每层跳跃是2的i次方(i代表层数),那么find性能与二分查找类似,确实能达到O(lgN),但是insert和delete的性能却是O(N)。因为插入或删除时需要对节点进行必要的调整。
This data structure is looking pretty good, but there’s a serious problem with it for the insert and remove operations. The work required to reorganize the list after an insertion or deletion is in O(n) .
For example, suppose that the first element is removed in Figure 3. Since it is necessary to maintain the strict pattern of node sizes, values from 2 to the end must be moved toward the head and the end node must be removed. A similar situation occurs when a new element is added to the list. This is where the probabilistic approach of a true Skip List comes into play.
A Skip List is built with the same distribution of node sizes, but without the requirement for the rigid pattern of node sizes shown. It is no longer necessary to maintain the rigid pattern by moving values around after a remove or insert operation. Pugh shows that with high probability such a list still exhibits O(lgn) behavior. The probability that a given Skip List will perform badly is very small.
确定Max Level
The level of the header node is the maximum allowed level in the SkipList and is chosen at construction. Pugh shows that the maximum level should be chosen as log1pn . Thus, for p=12 , the maximum level for a SkipList of up to 65,536 elements should be chosen no smaller than lg265536=16 .
对于 p=12 , 有65536个元素的SkipList,MaxLevel应该小于 lg265536=16
随机生成节点的level
节点的level是根据概率p随机生成的。伪代码如下所示:
int generateNodeLevel(double p, int maxLevel)
{
int level = 1;
while (drand48() < p)
level++;
return (level > maxLevel) ? maxLevel : level;
}那么find的平均比对次数为: 1+log1pnp+11−p
具体来说,对于含有n=65536个元素的skiplist来说, p=14 ,则平均比较次数为34.3; p=12 , 则平均比较次数为35。
对于一个sorted list来说,平均查找次数是 n2=32768
可以看到,skip list的查找性能有多大的提升。
这篇文章指出:
MaxHeight 为SkipList的关键参数,与性能直接相关。
程序中修改MaxHeight时,在数值变小时,性能上有明显下降,但当数值增大时,甚至增大到10000时,和默认的 MaxHeight= 12相比仍旧无明显差异,内存使用上也是如此。
kBranching及 (rnd_.Next() % kBranching。 这使得上层节点的数量约为下层的1/4。那么,当设定MaxHeight=12时,根节点为1时,约可均匀容纳Key的数量为4^11= 4194304(约为400W)。
当单独增大MaxHeight时,并不会使得SkipList的层级提升。MaxHeight=12为经验值,在百万数据规模时,尤为适用。
LevelDB中的Skip List
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000003051117
源码位置: db/skiplist.h db/skiplist.c
MaxLevel
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 };可以看到,初始时,MaxLevel定义为12,但是Insert操作有可能会修改它。
节点定义
// Implementation details follow
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
Key const key; // 保存的key
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return reinterpret_cast(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
}
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].Release_Store(x);
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return reinterpret_cast(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
}
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
port::AtomicPointer next_[1]; // 数组的长度就是该节点的高度,next_[0]是最底层的链表
};
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList::Node*
SkipList::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned(
sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - 1));
return new (mem) Node(key);
} 创建节点时使用Arena分派空间。Arena是LevelDB中的内存池。next_[1]使用了弹性指针,可以根据Node的高度不同,申请不同的空间。
目前还不清楚弹性指针相对于指针变量的优势是什么? 个人觉得如果需要将变长数据拷贝到结构体中(深拷贝),使用弹性指针更方便。对比如下:
struct Foo {
int key;
char val[1];
};
struct Foo2 {
int key;
char* val;
};在堆上分派Foo对象可以这么写,其中val部分可以是变长的。通过对比可以看出弹性指针在申请和释放时都要简便。
const char* name = "hongjin";
Foo *f = malloc(sizeof(Foo) - 1 + strlen(name));
free(f);const char* name = "hongjin";
Foo2 *f = malloc(sizeof(Foo2));
f->val = malloc(strlen(name));
free(f->val);
free(f);随机生成高度
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
} (rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == 0) 这句为真的概率为 1/kBranching,因为kBranching=4,所以上面提到的概率p=1/4.
查找操作
返回第一个大于或等于该节点的位置。
其中prev数组记录了在每一层中的前驱节点。
prev数组的作用应该是方便后续的插入过程。这与单链表中的插入是一个道理。
// Return the earliest node that comes at or after key.
// Return NULL if there is no such node.
//
// If prev is non-NULL, fills prev[level] with pointer to previous
// node at "level" for every level in [0..max_height_-1].
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList::Node* SkipList::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
const {
Node* x = head_; // x指向head
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1; // 获得当前的高度,从最顶层level开始查找
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) { // 要查找的值在前node后面,则继续在该层进行查找
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else { // 要查找的值小于或等于当前node,则继续该该层进行查找
if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x; // 记录在该层的前驱
if (level == 0) { // 所有层次的链表均遍历完,返回该位置。有可能是找到了,也有可能是第一个大于该值的位置
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--; // 转到下一层链表
}
}
}
} 还有一个判断是否包含某个元素的接口:
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList::Contains(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, NULL);
if (x != NULL && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} 其中Equal调用的是创建SkipList传入的比较器
bool Equal(const Key& a, const Key& b) const { return (compare_(a, b) == 0); }插入操作
插入过程与单链表冲插入过程一样,需要得到前驱节点。而前驱节点的信息是在查找过程中确定的,保存在了prev数组中。
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev); // 进行查找
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key)); // 不允许插入重复数据
int height = RandomHeight(); // 生成随机的高度height
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) { // 如果height大于最大高度,将增加层次中的前驱设为head
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
//fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height);
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height)); // 更新当前高度max_height_
}
x = NewNode(key, height); // 生成一个新节点
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { // 插入该节点
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
} 可供单独测试的代码
C++
下面的代码是从LevelDB中抽离出来的,去掉了内存池arena的使用,去掉了并发控制、内存屏障等,存在的问题是动态申请的堆资源没有释放。不过不影响理解skiplist。
$ g++ -Wall -O2 skiplist_test.cc -o test// skiplist_test.cc
#include "skiplist.h"
#include list(cmp);
std::set<int> s;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Key key = random() % N;
if(s.insert(key).second)
list.Insert(key);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (list.Contains(i)) {
//ASSERT_EQ(keys.count(i), 1);
printf("Contains %d\n", i);
} else {
//ASSERT_EQ(keys.count(i), 0);
printf("Not contains %d\n", i);
}
}
} // skiplist.h
#ifndef STORAGE_JINGER_SKIPLIST_H_
#define STORAGE_JINGER_SKIPLIST_H_
#include ::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
Key const key;
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
//return reinterpret_cast(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
return reinterpret_cast(next_[n]);
}
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
//next_[n].Release_Store(x);
next_[n] = reinterpret_cast<void*>(x);
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
//Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
// assert(n >= 0);
// return reinterpret_cast(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
//}
//void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
// assert(n >= 0);
// next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
//}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
//port::AtomicPointer next_[1];
void* next_[1];
};
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList::Node*
SkipList::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
//char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned(
// sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - 1));
//return new (mem) Node(key);
//
char* new_mem = new char[sizeof(Node) + sizeof(void*) * (height - 1)];
return new (new_mem) Node(key); // 使用自己分配的内存空间上调用构造函数,没有考虑资源的释放,资源泄露
//return static_cast(malloc(sizeof(Node) + sizeof(void*) * (height - 1))); // 没有调用构造函数,malloc只分配空间,不会调用构造函数。而new会调用构造函数
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline SkipList::Iterator::Iterator(const SkipList* list) {
list_ = list;
node_ = NULL;
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline bool SkipList::Iterator::Valid() const {
return node_ != NULL;
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline const Key& SkipList::Iterator::key() const {
assert(Valid());
return node_->key;
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList::Iterator::Next() {
assert(Valid());
node_ = node_->Next(0);
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList::Iterator::Prev() {
// Instead of using explicit "prev" links, we just search for the
// last node that falls before key.
assert(Valid());
node_ = list_->FindLessThan(node_->key);
if (node_ == list_->head_) {
node_ = NULL;
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList::Iterator::Seek(const Key& target) {
node_ = list_->FindGreaterOrEqual(target, NULL);
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList::Iterator::SeekToFirst() {
node_ = list_->head_->Next(0);
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList::Iterator::SeekToLast() {
node_ = list_->FindLast();
if (node_ == list_->head_) {
node_ = NULL;
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
//while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((random() % kBranching) == 0)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList::KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const {
// NULL n is considered infinite
return (n != NULL) && (compare_(n->key, key) < 0);
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList::Node* SkipList::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x;
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList::Node*
SkipList::FindLessThan(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
assert(x == head_ || compare_(x->key, key) < 0);
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == NULL || compare_(next->key, key) >= 0) {
if (level == 0) {
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
} else {
x = next;
}
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList::Node* SkipList::FindLast()
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == NULL) {
if (level == 0) {
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
} else {
x = next;
}
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList::SkipList(Comparator cmp)
: compare_(cmp),
head_(NewNode(0 /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
max_height_(1) {
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, NULL);
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key));
int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height);
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
//max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast(height));
max_height_ = height;
}
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
//x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
//prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
x->SetNext(i, prev[i]->Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList::Contains(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, NULL);
if (x != NULL && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
} // namespace jinger
#endif // STORAGE_JINGER_SKIPLIST_H_ c
c语言版本大体上是对c++版本的“翻译”
$gcc skiplist.c -o sl// skiplist.c
#include