java的多线程与并发的学习
记录学习的多线程与并发
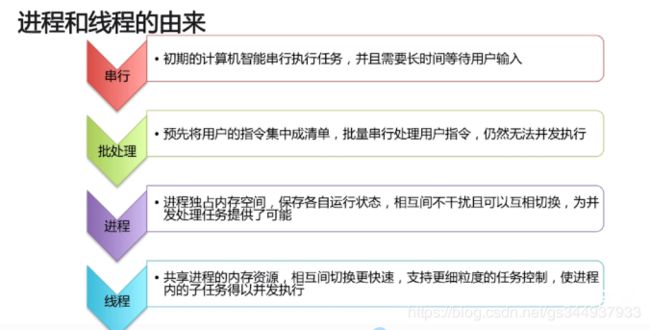
什么是进程与线程?及二者的关系
普通操作系统中的进程与线程
java 的进程与线程
基础知识
// (1)通过 FutureTask 实现 callable 接口
class MyCallable implements Callable {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception{
String value="test";
System.out.println("Ready to work");
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);
System.out.println("task done");
return value;
}
}
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask task = new FutureTask(new MyCallable());
new Thread(task).start();
if(!task.isDone()){
System.out.println("task has not finished, please wait!");
}
System.out.println("task return: " + task.get());
}
}
//运行后的结果:(其中有5秒的停顿)
task has not finished, please wait!
Ready to work
task done
task return: test
//(2)使用线程池来实现 callable 接口
public class ThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future future = newCachedThreadPool.submit(new MyCallable());
if(!future.isDone()){
System.out.println("task has not finished, please wait!");
}
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
newCachedThreadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
//运行结果:(有停顿)
task has not finished, please wait!
Ready to work
task done
test
// 代码 notify 和 notifyall 的区别,注意让出cpu使用权,同时释放锁。
public class NotificationDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
final NotificationDemo test = new NotificationDemo();
Runnable waitTask = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
try {
test.shouldGo();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " finished Execution");
}
};
Runnable notifyTask = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
test.go();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " finished Execution");
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(waitTask, "WT1"); //will wait
Thread t2 = new Thread(waitTask, "WT2"); //will wait
Thread t3 = new Thread(waitTask, "WT3"); //will wait
Thread t4 = new Thread(notifyTask,"NT1"); //will notify
//starting all waiting thread
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
//pause to ensure all waiting thread started successfully
Thread.sleep(200);
//starting notifying thread
t4.start();
}
/*
* wait and notify can only be called from synchronized method or bock
*/
private synchronized void shouldGo() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()
+ " is going to wait on this object");
wait(); //release lock and reacquires on wakeup
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is woken up");
}
/*
* both shouldGo() and go() are locked on current object referenced by "this" keyword
*/
private synchronized void go() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()
+ " is going to notify all or one thread waiting on this object");
//notify(); // only one out of three waiting thread WT1, WT2,WT3 will woke up
notifyAll(); // all waiting thread WT1, WT2,WT3 will woke up
}
}
// 运行结果:
Thread[WT1,5,main] is going to wait on this object
Thread[WT2,5,main] is going to wait on this object
Thread[WT3,5,main] is going to wait on this object
Thread[NT1,5,main] is going to notify all or one thread waiting on this object
Thread[WT3,5,main] is woken up
Thread[WT2,5,main] is woken up
WT3 finished Execution
Thread[WT1,5,main] is woken up
WT1 finished Execution
WT2 finished Execution
NT1 finished Execution
// 中断线程 interrupt 的使用。
public class InterruptDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable interruptTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
try {
//在正常运行任务时,经常检查本线程的中断标志位,如果被设置了中断标志就自行停止线程
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
Thread.sleep(100); // 休眠100ms
i++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " (" + Thread.currentThread().getState() + ") loop " + i);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//在调用阻塞方法时正确处理InterruptedException异常。(例如,catch异常后就结束线程。)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " (" + Thread.currentThread().getState() + ") catch InterruptedException.");
}
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(interruptTask, "t1");
System.out.println(t1.getName() +" ("+t1.getState()+") is new.");
t1.start(); // 启动“线程t1”
System.out.println(t1.getName() +" ("+t1.getState()+") is started.");
// 主线程休眠300ms,然后主线程给t1发“中断”指令。
Thread.sleep(300);
t1.interrupt();
System.out.println(t1.getName() +" ("+t1.getState()+") is interrupted.");
// 主线程休眠300ms,然后查看t1的状态。
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println(t1.getName() +" ("+t1.getState()+") is interrupted now.");
}
}
//程序运行结果:
t1 (NEW) is new.
t1 (RUNNABLE) is started.
t1 (RUNNABLE) loop 1
t1 (RUNNABLE) loop 2
t1 (TIMED_WAITING) is interrupted.
t1 (RUNNABLE) catch InterruptedException.
t1 (TERMINATED) is interrupted now.
这个还有几个知识点,只是简单的列出来,就不一一举例了:
| 1 | 线程中strat和run方法的区别 | strat()函数,进入native层创建一个线程,并且这个线程会调用java层的run方法 |
| 2 | thread 和 runnable 的区别 | thread 是类,只能单继承,runnable是接口。 线程启动的方式,只有一种,就是 thread.start()。 |
| 3 | notify 和 notifyall 的区别 | |
| 4 | yield函数 | 当前线程调用 Thread.yield()函数时,会给线程调度器一个当前线程愿意让出CPU使用的暗示,但是线程调度器可能会忽略这个暗示。 |
| 5 | interrupt函数 | 需要配合使用。 |
synchronized关键字
见:java的Synchronized关键字的学习
线程池
见:java线程池的学习