spring boot 实例演示+深度剖析
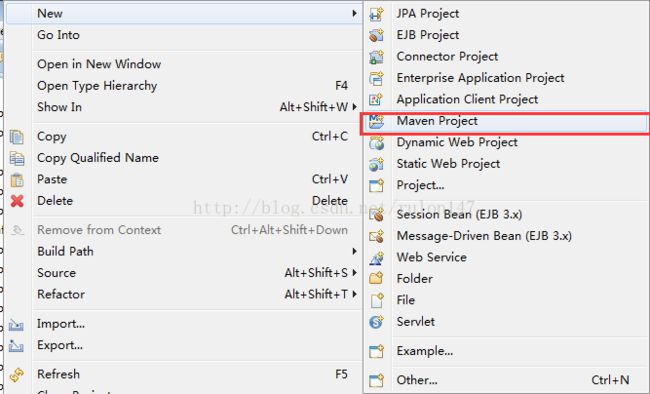
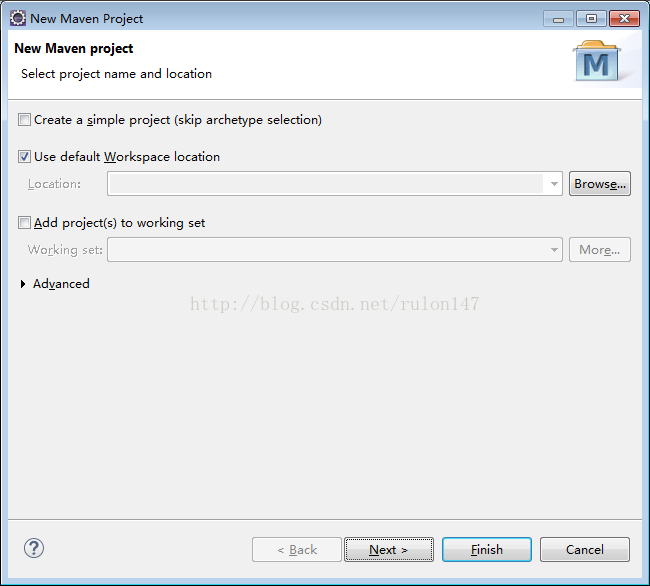
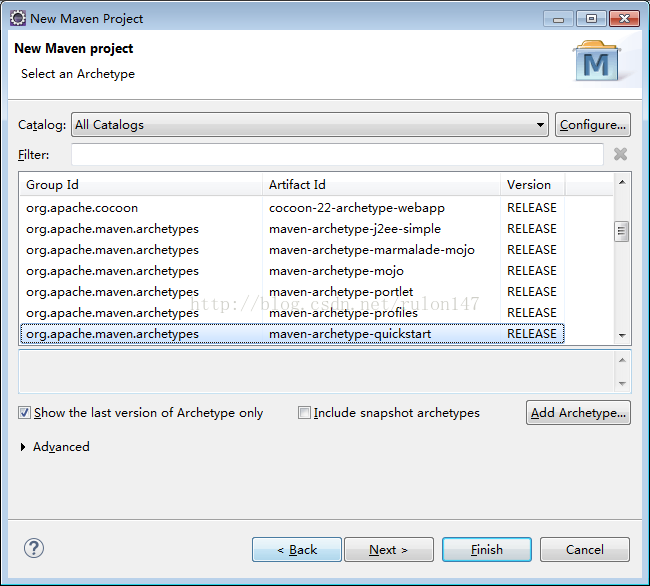
一、先上实例
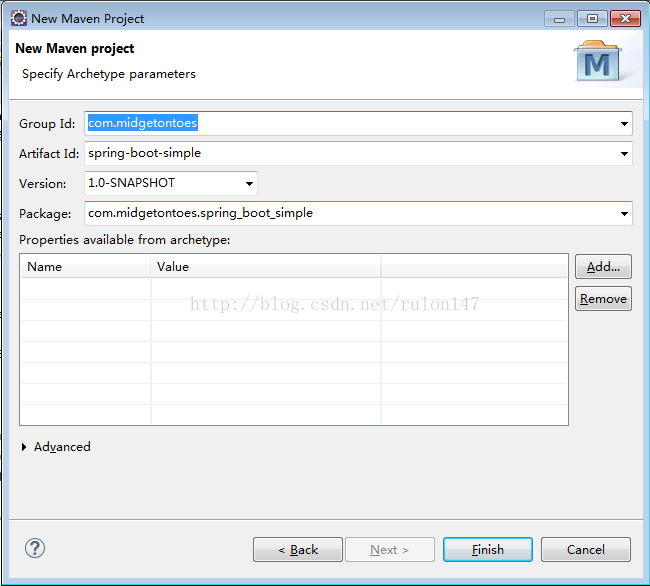
4.0.0
com.midgetontoes
spring-boot-simple
1.0-SNAPSHOT
UTF-8
1.1.4.RELEASE
junit
junit
3.8.1
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
${spring.boot.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
${spring.boot.version}
repackage
7、创建Application.java
package com.midgetontoes.spring_boot_simple;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class Application {
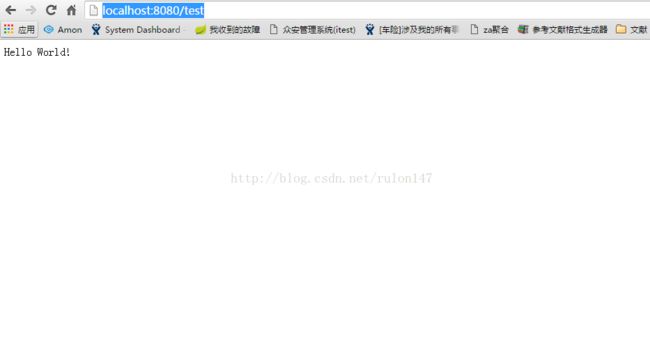
@RequestMapping("/test")
String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v1.1.4.RELEASE)
2016-12-22 17:33:22.843 INFO 3100 --- [ main] c.m.spring_boot_simple.Application : Starting Application on LY-201604240839 with PID 3100 (D:\workspace-castle\spring-boot-simple\target\classes started by Administrator in D:\workspace-castle\spring-boot-simple)
2016-12-22 17:33:22.887 INFO 3100 --- [ main] ationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext@530612ba: startup date [Thu Dec 22 17:33:22 CST 2016]; root of context hierarchy
2016-12-22 17:33:23.350 INFO 3100 --- [ main] o.s.b.f.s.DefaultListableBeanFactory : Overriding bean definition for bean 'beanNameViewResolver': replacing [Root bean: class [null]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=false; autowireMode=3; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration; factoryMethodName=beanNameViewResolver; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=(inferred); defined in class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/web/ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration.class]] with [Root bean: class [null]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=false; autowireMode=3; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter; factoryMethodName=beanNameViewResolver; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=(inferred); defined in class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/web/WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter.class]]
2016-12-22 17:33:24.398 INFO 3100 --- [ main] .t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory : Server initialized with port: 8080
2016-12-22 17:33:24.628 INFO 3100 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service Tomcat
2016-12-22 17:33:24.630 INFO 3100 --- [ main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet Engine: Apache Tomcat/7.0.54
2016-12-22 17:33:24.739 INFO 3100 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2016-12-22 17:33:24.740 INFO 3100 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1856 ms
2016-12-22 17:33:25.313 INFO 3100 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.s.b.c.e.ServletRegistrationBean : Mapping servlet: 'dispatcherServlet' to [/]
2016-12-22 17:33:25.316 INFO 3100 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.s.b.c.embedded.FilterRegistrationBean : Mapping filter: 'hiddenHttpMethodFilter' to: [/*]
2016-12-22 17:33:25.479 INFO 3100 --- [ main] o.s.w.s.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping : Mapped URL path [/**/favicon.ico] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
2016-12-22 17:33:25.658 INFO 3100 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/test],methods=[],params=[],headers=[],consumes=[],produces=[],custom=[]}" onto java.lang.String com.midgetontoes.spring_boot_simple.Application.home()
2016-12-22 17:33:25.661 INFO 3100 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/error],methods=[],params=[],headers=[],consumes=[],produces=[],custom=[]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity> org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.BasicErrorController.error(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest)
2016-12-22 17:33:25.662 INFO 3100 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/error],methods=[],params=[],headers=[],consumes=[],produces=[text/html],custom=[]}" onto public org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.BasicErrorController.errorHtml(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest)
2016-12-22 17:33:25.685 INFO 3100 --- [ main] o.s.w.s.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping : Mapped URL path [/webjars/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
2016-12-22 17:33:25.686 INFO 3100 --- [ main] o.s.w.s.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping : Mapped URL path [/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
2016-12-22 17:33:25.856 INFO 3100 --- [ main] o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup
2016-12-22 17:33:25.950 INFO 3100 --- [ main] s.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080/http
2016-12-22 17:33:25.951 INFO 3100 --- [ main] c.m.spring_boot_simple.Application : Started Application in 3.532 seconds (JVM running for 3.947)
二、关于spring boot 详细介绍
简介
从 Spring Boot 项目名称中的 Boot 可以看出来,Spring Boot 的作用在于创建和启动新的基于 Spring 框架的项目。它的目的是帮助开发人员很容易的创建出独立运行和产品级别的基于 Spring 框架的应用。Spring Boot 会选择最适合的 Spring 子项目和第三方开源库进行整合。大部分 Spring Boot 应用只需要非常少的配置就可以快速运行起来。
Spring Boot 包含的特性如下:
- 创建可以独立运行的 Spring 应用。
- 直接嵌入 Tomcat 或 Jetty 服务器,不需要部署 WAR 文件。
- 提供推荐的基础 POM 文件来简化 Apache Maven 配置。
- 尽可能的根据项目依赖来自动配置 Spring 框架。
- 提供可以直接在生产环境中使用的功能,如性能指标、应用信息和应用健康检查。
- 没有代码生成,也没有 XML 配置文件。
Spring Boot 推荐的基础 POM 文件
上一节的代码清单 1 中给出的“org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web”是 Spring Boot 所提供的推荐的基础 POM 文件之一,用来提供创建基于 Spring MVC 的 Web 应用所需的第三方库依赖。除了这个 POM 文件之外,Spring Boot 还提供了其他类似的 POM 文件。所有这些基础 POM 依赖都在“org.springframework.boot”组中。一些重要 POM 文件的具体说明见表 1。
表 1. Spring Boot 推荐的基础 POM 文件
名称 说明
spring-boot-starter 核心 POM,包含自动配置支持、日志库和对 YAML 配置文件的支持。
spring-boot-starter-amqp 通过 spring-rabbit 支持 AMQP。
spring-boot-starter-aop 包含 spring-aop 和 AspectJ 来支持面向切面编程(AOP)。
spring-boot-starter-batch 支持 Spring Batch,包含 HSQLDB。
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa 包含 spring-data-jpa、spring-orm 和 Hibernate 来支持 JPA。
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb 包含 spring-data-mongodb 来支持 MongoDB。
spring-boot-starter-data-rest 通过 spring-data-rest-webmvc 支持以 REST 方式暴露 Spring Data 仓库。
spring-boot-starter-jdbc 支持使用 JDBC 访问数据库。
spring-boot-starter-security 包含 spring-security。
spring-boot-starter-test 包含常用的测试所需的依赖,如 JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito 和 spring-test 等。
spring-boot-starter-velocity 支持使用 Velocity 作为模板引擎。
spring-boot-starter-web 支持 Web 应用开发,包含 Tomcat 和 spring-mvc。
spring-boot-starter-websocket 支持使用 Tomcat 开发 WebSocket 应用。
spring-boot-starter-ws 支持 Spring Web Services。
spring-boot-starter-actuator 添加适用于生产环境的功能,如性能指标和监测等功能。
spring-boot-starter-remote-shell 添加远程 SSH 支持。
spring-boot-starter-jetty 使用 Jetty 而不是默认的 Tomcat 作为应用服务器。
spring-boot-starter-log4j 添加 Log4j 的支持。
spring-boot-starter-logging 使用 Spring Boot 默认的日志框架 Logback。
spring-boot-starter-tomcat 使用 Spring Boot 默认的 Tomcat 作为应用服务器。所有这些 POM 依赖的好处在于为开发 Spring 应用提供了一个良好的基础。Spring Boot 所选择的第三方库是经过考虑的,是比较适合产品开发的选择。但是 Spring Boot 也提供了不同的选项,比如日志框架可以用 Logback 或 Log4j,应用服务器可以用 Tomcat 或 Jetty。
自动配置
Spring Boot 对于开发人员最大的好处在于可以对 Spring 应用进行自动配置。Spring Boot 会根据应用中声明的第三方依赖来自动配置 Spring 框架,而不需要进行显式的声明。比如当声明了对 HSQLDB 的依赖时,Spring Boot 会自动配置成使用 HSQLDB 进行数据库操作。
Spring Boot 推荐采用基于 Java 注解的配置方式,而不是传统的 XML。只需要在主配置 Java 类上添加“@EnableAutoConfiguration”注解就可以启用自动配置。Spring Boot 的自动配置功能是没有侵入性的,只是作为一种基本的默认实现。开发人员可以通过定义其他 bean 来替代自动配置所提供的功能。比如当应用中定义了自己的数据源 bean 时,自动配置所提供的 HSQLDB 就不会生效。这给予了开发人员很大的灵活性。既可以快速的创建一个可以立即运行的原型应用,又可以不断的修改和调整以适应应用开发在不同阶段的需要。可能在应用最开始的时候,嵌入式的内存数据库(如 HSQLDB)就足够了,在后期则需要换成 MySQL 等数据库。Spring Boot 使得这样的切换变得很简单。
外部化的配置
在应用中管理配置并不是一个容易的任务,尤其是在应用需要部署到多个环境中时。通常会需要为每个环境提供一个对应的属性文件,用来配置各自的数据库连接信息、服务器信息和第三方服务账号等。通常的应用部署会包含开发、测试和生产等若干个环境。不同的环境之间的配置存在覆盖关系。测试环境中的配置会覆盖开发环境,而生产环境中的配置会覆盖测试环境。Spring 框架本身提供了多种的方式来管理配置属性文件。Spring 3.1 之前可以使用 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer。Spring 3.1 引入了新的环境(Environment)和概要信息(Profile)API,是一种更加灵活的处理不同环境和配置文件的方式。不过 Spring 这些配置管理方式的问题在于选择太多,让开发人员无所适从。Spring Boot 提供了一种统一的方式来管理应用的配置,允许开发人员使用属性文件、YAML 文件、环境变量和命令行参数来定义优先级不同的配置值。
Spring Boot 所提供的配置优先级顺序比较复杂。按照优先级从高到低的顺序,具体的列表如下所示。
- 命令行参数。
- 通过 System.getProperties() 获取的 Java 系统参数。
- 操作系统环境变量。
- 从 java:comp/env 得到的 JNDI 属性。
- 通过 RandomValuePropertySource 生成的“random.*”属性。
- 应用 Jar 文件之外的属性文件。
- 应用 Jar 文件内部的属性文件。
- 在应用配置 Java 类(包含“@Configuration”注解的 Java 类)中通过“@PropertySource”注解声明的属性文件。
- 通过“SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties”声明的默认属性。
Spring Boot 的这个配置优先级看似复杂,其实是很合理的。比如命令行参数的优先级被设置为最高。这样的好处是可以在测试或生产环境中快速地修改配置参数值,而不需要重新打包和部署应用。
SpringApplication 类默认会把以“--”开头的命令行参数转化成应用中可以使用的配置参数,如 “--name=Alex” 会设置配置参数 “name” 的值为 “Alex”。如果不需要这个功能,可以通过 “SpringApplication.setAddCommandLineProperties(false)” 禁用解析命令行参数。
RandomValuePropertySource 可以用来生成测试所需要的各种不同类型的随机值,从而免去了在代码中生成的麻烦。RandomValuePropertySource 可以生成数字和字符串。数字的类型包含 int 和 long,可以限定数字的大小范围。以“random.”作为前缀的配置属性名称由 RandomValuePropertySource 来生成,如代码清单 3 所示。
清单 3. 使用 RandomValuePropertySource 生成的配置属性
user.id=${random.value}
user.count=${random.int}
user.max=${random.long}
user.number=${random.int(100)}
user.range=${random.int[100, 1000]}属性文件
属性文件是最常见的管理配置属性的方式。Spring Boot 提供的 SpringApplication 类会搜索并加载 application.properties 文件来获取配置属性值。SpringApplication 类会在下面位置搜索该文件。
- 当前目录的“/config”子目录。
- 当前目录。
- classpath 中的“/config”包。
- classpath
上面的顺序也表示了该位置上包含的属性文件的优先级。优先级按照从高到低的顺序排列。可以通过“spring.config.name”配置属性来指定不同的属性文件名称。也可以通过“spring.config.location”来添加额外的属性文件的搜索路径。如果应用中包含多个 profile,可以为每个 profile 定义各自的属性文件,按照“application-{profile}”来命名。
对于配置属性,可以在代码中通过“@Value”来使用,如代码清单 4 所示。
清单 4. 通过“@Value”来使用配置属性
@RestController
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class Application {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@RequestMapping("/")
String home() {
return String.format("Hello %s!", name);
}
}在代码清单 4 中,变量 name 的值来自配置属性中的“name”属性。
YAML
相对于属性文件来说,YAML 是一个更好的配置文件格式。YAML 在 Ruby on Rails 中得到了很好的应用。SpringApplication 类也提供了对 YAML 配置文件的支持,只需要添加对 SnakeYAML 的依赖即可。代码清单 5 给出了 application.yml 文件的示例。
清单 5. 使用 YAML 表示的配置属性
spring:
profiles: development
db:
url: jdbc:hsqldb:file:testdb
username: sa
password:
---
spring:
profiles: test
db:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/test
username: test
password: test代码清单 5 中的 YAML 文件同时给出了 development 和 test 两个不同的 profile 的配置信息,这也是 YAML 文件相对于属性文件的优势之一。除了使用“@Value”注解绑定配置属性值之外,还可以使用更加灵活的方式。代码清单 6 给出的是使用代码清单 5 中的 YAML 文件的 Java 类。通过“@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="db")”注解,配置属性中以“db”为前缀的属性值会被自动绑定到 Java 类中同名的域上,如 url 域的值会对应属性“db.url”的值。只需要在应用的配置类中添加“@EnableConfigurationProperties”注解就可以启用该自动绑定功能。
清单 6. 使用 YAML 文件的 Java 类
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="db")
public class DBSettings {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
}开发 Web 应用
Spring Boot 非常适合于开发基于 Spring MVC 的 Web 应用。通过内嵌的 Tomcat 或 Jetty 服务器,可以简化对 Web 应用的部署。Spring Boot 通过自动配置功能对 Spring MVC 应用做了一些基本的配置,使其更加适合一般 Web 应用的开发要求。
HttpMessageConverter
Spring MVC 中使用 HttpMessageConverter 接口来在 HTTP 请求和响应之间进行消息格式的转换。默认情况下已经通过 Jackson 支持 JSON 和通过 JAXB 支持 XML 格式。可以通过创建自定义 HttpMessageConverters 的方式来添加其他的消息格式转换实现。
静态文件
默认情况下,Spring Boot 可以对 “/static”、“/public”、“/resources” 或 “/META-INF/resources” 目录下的静态文件提供支持。同时 Spring Boot 还支持 Webjars。路径“/webjars/**”下的内容会由 webjar 格式的 Jar 包来提供。
生产环境运维支持
与开发和测试环境不同的是,当应用部署到生产环境时,需要各种运维相关的功能的支持,包括性能指标、运行信息和应用管理等。所有这些功能都有很多技术和开源库可以实现。Spring Boot 对这些运维相关的功能进行了整合,形成了一个功能完备和可定制的功能集,称之为 Actuator。只需要在 POM 文件中增加对 “org.springframe.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator” 的依赖就可以添加 Actuator。Actuator 在添加之后,会自动暴露一些 HTTP 服务来提供这些信息。这些 HTTP 服务的说明如表 2。
表 2. Spring Boot Actuator 所提供的 HTTP 服务
名称 说明 是否包含敏感信息
autoconfig 显示 Spring Boot 自动配置的信息。 是
beans 显示应用中包含的 Spring bean 的信息。 是
configprops 显示应用中的配置参数的实际值。 是
dump 生成一个 thread dump。 是
env 显示从 ConfigurableEnvironment 得到的环境配置信息。 是
health 显示应用的健康状态信息。 否
info 显示应用的基本信息。 否
metrics 显示应用的性能指标。 是
mappings 显示 Spring MVC 应用中通过“
@RequestMapping”添加的路径映射。 是
shutdown 关闭应用。 是
trace 显示应用相关的跟踪(trace)信息。 是对于表 2中的每个服务,通过访问名称对应的 URL 就可以获取到相关的信息。如访问“/info”就可以获取到 info 服务对应的信息。服务是否包含敏感信息说明了该服务暴露出来的信息是否包含一些比较敏感的信息,从而确定是否需要添加相应的访问控制,而不是对所有人都公开。所有的这些服务都是可以配置的,比如通过改变名称来改变相应的 URL。下面对几个重要的服务进行介绍。
health 服务
Spring Boot 默认提供了对应用本身、关系数据库连接、MongoDB、Redis 和 Rabbit MQ 的健康状态的检测功能。当应用中添加了 DataSource 类型的 bean 时,Spring Boot 会自动在 health 服务中暴露数据库连接的信息。应用也可以提供自己的健康状态信息,如代码清单 7 所示。
清单 7. 自定义 health 服务
@Component
public class AppHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Override
public Health health() {
return Health.up().build();
}
}应用只需要实现 org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator 接口,并返回一个 org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health 对象,就可以通过 health 服务来获取所暴露的信息。如代码清单 8 所示。
清单 8. health 服务返回的结果
{"status":"UP","app":{"status":"UP"},"db":{"status":"UP","database":"HSQL Database Engine","hello":1}}info 服务
info 服务所暴露的信息是完全由应用来确定的。应用中任何以“info.”开头的配置参数会被自动的由 info 服务来暴露。只需要往 application.properties 中添加以“info.”开头的参数即可,如代码清单 9 所示。
清单 9. 添加 info 服务所需配置参数的属性文件
info.app_name=My First Spring Boot Application
info.app_version=1.0.0当访问“/info”时,访问的 JSON 数据如代码清单 10 所示。
清单 10. Info 服务返回的结果
{"app_name":"My First Spring Boot Application","app_version":"1.0.0"}metrics 服务
当访问 metrics 服务时,可以看到 Spring Boot 通过 SystemPublicMetrics 默认提供的一些系统的性能参数值,包括内存、CPU、Java 类加载和线程等的基本信息。应用可以记录其他所需要的信息。Spring Boot 默认提供了两种类型的性能指标记录方式:gauge 和 counter。gauge 用来记录单个绝对数值,counter 用来记录增量或减量值。比如在一个 Web 应用中,可以用 counter 来记录当前在线的用户数量。当用户登录时,把 counter 的值加 1;当用户退出时,把 counter 的值减 1。代码清单 11 给出了一个示例。
清单 11. 自定义的 metrics 服务
@RestController
public class GreetingsController {
@Autowired
private CounterService counterService;
@RequestMapping("/greet")
public String greet() {
counterService.increment("myapp.greet.count");
return "Hello!";
}
}在代码清单 11 中添加了对 Spring Boot 提供的 CounterService 的依赖。当 greet 方法被调用时,会把名称为“myapp.greet.count”的计数器的值加 1。也就是当用户每次访问“/greet”时,该计算器就会被加 1。除了 CounterService 之外,还可以使用 GaugeService 来记录绝对值。
使用 JMX 进行管理
添加 Actuator 后所暴露的 HTTP 服务只能提供只读的信息。如果需要对应用在运行时进行管理,则需要用到 JMX。Spring Boot 默认提供了 JMX 管理的支持。只需要通过 JDK 自带的 JConsole 连接到应用的 JMX 服务器,就可以看到在域“org.springframework.boot”中 mbean。可以通过 Spring 提供的 @ManagedResource、@ManagedAttribute 和 @ManagedOperation 注解来创建应用自己的 mbean。
使用 Spring Boot CLI
Spring Boot 提供了命令行工具来运行 Groovy 文件。命令行工具的安装非常简单,只需要下载之后解压缩即可。下载地址见参考资源。解压之后可以运行 spring 命令来使用该工具。通过 Groovy 开发的应用与使用 Java 并没有差别,只不过使用 Groovy 简化的语法可以使得代码更加简单。代码清单 12 给出了与代码清单 2 功能相同的 Groovy 实现。
清单 12. 使用 Groovy 的示例应用
@RestController
class WebApplication {
@RequestMapping("/")
String home() {
"Hello World!"
}
}只需要使用“spring run app.groovy”就可以运行该应用。还可以使用 Groovy 提供的 DSL 支持来简化应用,如代码清单 13 所示。
清单 13. 使用 Groovy DSL 简化应用
@RestController
class WebApplication {
@Autowired
Service service
@RequestMapping("/")
String home() {
service.greet()
}
}
class Service {
String message
String greet() {
message
}
}
beans {
service(Service) {
message = "Another Hello"
}
}结束语
对于广大使用 Spring 框架的开发人员来说,Spring Boot 无疑是一个非常实用的工具。本文详细介绍了如何通过 Spring Boot 快速创建 Spring 应用以及它所提供的自动配置和外部化配置的能力,同时还介绍了 Spring Boot 内建的 Actuator 提供的可以在生产环境中直接使用的性能指标、运行信息和应用管理等功能,最后介绍了 Spring Boot 命令行工具的使用。通过基于依赖的自动配置功能,使得 Spring 应用的配置变得非常简单。在依赖的管理上也变得更加简单,不需要开发人员自己来进行整合。Actuator 所提供的功能非常实用,对于在生产环境下对应用的监控和管理是大有好处的。Spring Boot 应该成为每个使用 Spring 框架的开发人员使用的工具。