Spring Boot学习笔记:(二)常规属性配置
一、依赖注入
1 @Value
Spring Boot中,可使用@PropertySource指明属性文件所在的位置(默认为application.properties,不需要声明),通过@Value注入值。
(1)application.properties:
person.name=wgs
person.age=25(2)入口类:
package com.wgs;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
RestController
SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootdemoApplication {
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${person.name}")
private String age;
@RequestMapping(value = "/test1")
public String test1(){
return "person's name is:" + name + ",person's age is:" + age;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/")
public String index(){
return "Hello Spring Boot!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootdemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
(3)运行,访问http://localhost:8080/test1,结果如下:
person's name is:wgs ,person's age is:252 @Configuration和@PropertySource
当然如果属性过多时,用@Value一个一个注入会显得很繁琐,可以使用@ConfigurationProperties将properties属性和一个Bean关联起来。
注:在Spring Boot 1.5以上的版本,使用@Configuration和@PropertySource代替@ConfigurationProperties。下面来看看如何使用:
(1)在resources下建config文件夹,再建一个文件author.properties:
/config/author.properties
author.name=wgs
author.age=25(2)配置Bean:AuthorSettings.java
package com.wgs.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/** * @author GenshenWang.nomico * @date 2017/12/24. */
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:config/author.properties")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "author")
public class AuthorSettings {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
@PropertySource:指定properties文件的位置;
@ConfigurationProperties:通过prefix属性关联properties文件中的配置;
(注:在Spring Boot 1.5之前的版本可以使用
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "author", locations = "classpath:config/author.properties")
)
(3)Controller类:AuthorController.java
package com.wgs.controller;
import com.wgs.config.AuthorSettings;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/** * @author GenshenWang.nomico * @date 2017/12/24. */
@RestController
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AuthorSettings.class)
public class AuthorController {
@Autowired
AuthorSettings authorSettings;
@RequestMapping("/authorinfo")
public String index(){
return "Author name is : " + authorSettings.getName() + " , age is : " + authorSettings.getAge();
}
}
注:@EnableConfigurationProperties(AuthorSettings.class):当@EnableConfigurationProperties注解应用到程序中时,任何被ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean将自动被Environment属性配置。
(4)在main方法中启动后在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/authorinfo,即可看到输出信息:
Author name is : wgs , age is : 25二、Profile设置
Profile是Spring用来针对不同环境对不同的配置提供支持的。
(1)首先创建全局Profile配置文件,可多个,命名规则为:
application-{profile}.properties
如:在项目中创建两个Profile配置文件,设置不同的端口号,分别为:

application-dev.properties:设置开发环境下端口号为8888
server.port=8888application-prod.properties:设置开发环境下端口号为80
server.port=80(2)在application.properties中通过设置
spring.profile.active={profile}
来指定所需要的Profile。
如:
在application.properties中
指定生产环境下(profile = prod, port = 80):
spring.profiles.active=prod指定开发环境下(profile = dev,port= 8888):
spring.profiles.active=dev三、日志
Spring Boot内部日志系统使用的是Commons Logging,支持Java Util Logging、Log4j、Log4j2、Logback作为日志框架。
默认情况下使用Logback作为日志框架。
1 日志格式
启动Spring Boot,可以Spring Boot默认的日志输出格式:
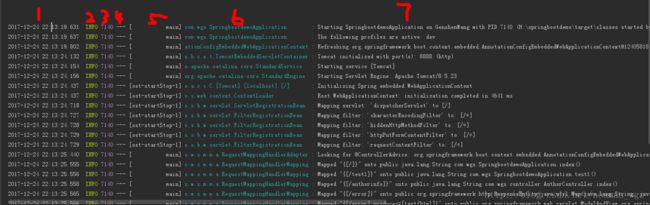
(1) 日期和时间,精确到毫秒,易于排序;
(2)日志级别:ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE, FATAL;
(3)Process ID;
(4)分隔符:区分实际日志信息开头;
(5)线程名:包括在方括号中;
(6)日志名:通常是源class的类名(缩写);
(7)日志信息。
2 配置日志级别
配置格式:
logging.level.包名 = 级别(ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE,FATAL)如:
logging.level.org.springframework.web = ERROR3 配置日志文件输出
logging.file = D:/mylog/log.log日志文件每到10M就会被轮换,和控制台一样,默认记录ERROR,WARN,INFO等级别。
四、Application属性文件
Spring Boot Application将会从以下位置(优先级从高到低)加载application.properties 和 application.yml :
- 当前应用程序运行目录下的/config子目录里;
- 当前应用程序运行目录;
- classpath下的/config包;
- classpath根路径
即src/main/resources/config下application.properties覆盖src/main/resources下application.properties中相同的属性。
此外,如果你在相同优先级位置同时有application.properties和application.yml,那么application.properties里的属性里面的属性就会覆盖application.yml。
属性占位符
当application.properties里的值被使用时,会被存在的Environment过滤,可以引用先前定义的值:
customer.name = WGS
customer.description=Merry Christmas to ${customer.name} !最近学车论文的事搞得一点学习的时间都木有,每次学习新技术都很兴奋,希望能够坚持下去。最后,今天是圣诞节。送给大家一颗圣诞树,Merry Christamas to U!
想见圣诞树戳我
2017/12/25 in NJ.
参考:
《SpringBoot实战》
http://tengj.top/2017/02/28/springboot2/

