Java Gradle项目中的资源正确获取
-
- 引言
- 两个getResource方法
- 小结
引言
一个Java Gradle项目会涉及到资源的访问. 一般情况下会将当前项目所需的资源文件全部放置于resources文件夹下, 无论是main文件下的source code 还是test文件夹下的test code. 都或多或少的涉及到获取resources文件夹下的资源. 本文主要目的就是详细的总结一下如何获取resources文件夹下的资源.
两个getResource方法
来看一个简单的Java Gradle项目(称呼其为simpleresource)的项目结构
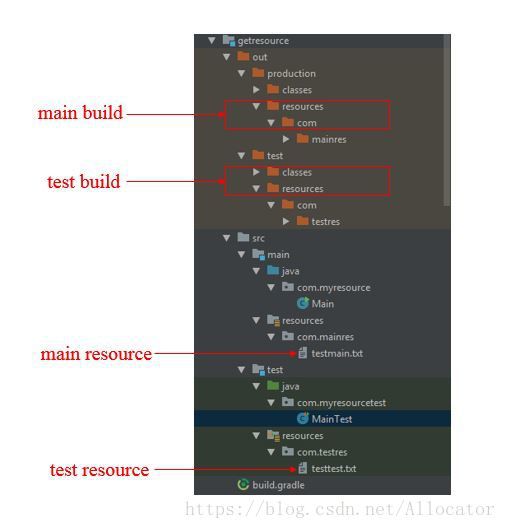
首先这个project执行build之后会在根目录下创建一个out目录, 这个目录存放所有的编译结果(class文件以及资源文件). 如上图所示production文件夹对应的是source code而test文件夹对应的是test code.
所有的资源都会存储在resources文件夹内部. 当程序运行时获取的资源就是这个resources文件夹下的资源.
我们使用最多的获取资源的方法有两个
Class.getResource 和
ClassLoader.getResource 但是这两个方法传递参数与结果不同, 下面详细分析一下这两个方法参数以及返回值.
先看
ClassLoader 中的
getResource 方法. 只需要获取类加载器对象即可(获取方式不再赘述). 先看这个方法的API文档相关的描述:
Finds the resource with the given name. A resource is some data (images, audio, text, etc) that can be accessed by class code in a way that is independent of the location of the code.
The name of a resource is a '/'-separated path name that identifies the resource.
This method will first search the parent class loader for the resource; if the parent is null the path of the class loader built-in to the virtual machine is searched. That failing, this method will invoke findResource(String) to find the resource.从这个描述中可以得知提供资源的路径(我理解的是相对路径), 正常情况下该方法会返回资源完整的URL. 传递的参数有一个重要的注意事项, 就是传递的参数不能够以/ 开始, 这也是我为什么称呼这个参数为资源的相路径. 举个例子
URL test = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/");运行上述代码返回的结果是:
参考simpleresource的项目结构, 正确获取
com.mainres 下的文件的正确做法是:
String name = "com/mainres/testmain.txt";
URL test = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(name);结果为:
如果在表示资源路径的字符串中加上
/ 那么获取到的URL依然为null
String name = "/com/mainres/testmain.txt";
URL test = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(name);宗上所述, 使用类加载器获取资源的方式传递的参数为资源相对路径(相对于resources文件夹的路径), 既然是相对路径自然参数 不能够以
/ 开始.
有一个问题需要注意, 当传递参数为空字符串的时候, 得到路径其实是classes文件夹的绝对路径, 但当传递一个正确的资源路径相对字符串时, 得到路径却是resources文件夹下的资源路径.
String name = "";
URL test = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(name);我的理解是本质上是通过此方法获取的其实类加载器加载的class字节码目录, 所以使用空字符串会看到实际输出的是classes文件夹绝对路径, 当传递正确的资源路径的时候, 代码层面做转换, 转而获取与classes文件夹同级的resources文件夹下的资源.
再看
Class 中的
getResurce 方法
由于这个方法传递参数是否是以
/ 开头会产生不同的结果, 且使用这个方法也比较容易和
ClassLoader 中的
getResource 方法搞混淆, 所以本文多次强调传递的参数是否以
/ 开始.
首先看传递参数为
"" 和
/ 的两种情况得到的结果:
使用空字符串:
String name = "";
URL test = this.getClass().getResource(name);运行结果:
使用
/
String name = "/";
URL test = this.getClass().getResource(name);运行结果为:
最大的区别是使用空字符串
"" 获取的路径是相对于包的目录, 而使用
/ 获取的路径是类加载器加载class文件的目录, 这个和
ClassLoader 的
getResource 方法传递
"" 字符串的结果是一样的. 所以如果要正确的获取到资源文件, 那么使用
Class 的
getResource 方法如下:
String name = "/com/mainres/testmain.txt";
URL test = this.getClass().getResource(name);运行结果:
所以综上所述, 一个简单的防止两个方法传递参数搞混淆的记忆方式就是使用
Class 的
getResource 方法需要加
/ 而使用
ClassLoader 的
getResource 方法不要加
/.
其实参考
Class 类中的
getResource 方法:
public java.net.URL getResource(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(name);
}
return cl.getResource(name);
}本质上讲它也是调用ClassLoader 中的getResource 方法. 其中resolveName 这个方法对传递的参数做了转换.
private String resolveName(String name) {
if (name == null) {
return name;
}
if (!name.startsWith("/")) {
Class c = this;
while (c.isArray()) {
c = c.getComponentType();
}
String baseName = c.getName();
int index = baseName.lastIndexOf('.');
if (index != -1) {
name = baseName.substring(0, index).replace('.', '/')
+"/"+name;
}
} else {
name = name.substring(1);
}
return name;
}当传递的参数带有/ 时候, resolveName 会将/ 去除后的字符串返回, 最后调用ClassLoader 中的 getResource 方法.
小结
本文对比了一下Class 和 ClassLoader 中的getResource 方法的差异,如果单纯从资源的获取角度来看最终调用的都是ClassLoader 中的getResource 方法. 简单记忆即是使用Class 的getResource 方法资源路径需要加/ 而使用ClassLoader 中的getResource 方法则不需要加/.