map/unordered_map原理和使用整理
1.结论
新版的hash_map都是unordered_map了,这里只说unordered_map和map.
运行效率方面:unordered_map最高,而map效率较低但 提供了稳定效率和有序的序列。
占用内存方面:map内存占用略低,unordered_map内存占用略高,而且是线性成比例的。
需要无序容器,快速查找删除,不担心略高的内存时用unordered_map;有序容器稳定查找删除效率,内存很在意时候用map。
2.原理
map的内部实现是二叉平衡树(红黑树);hash_map内部是一个hash_table一般是由一个大vector,vector元素节点可挂接链表来解决冲突,来实现.
hash_map
其插入过程是:
- 得到key
- 通过hash函数得到hash值
- 得到桶号(一般都为hash值对桶数求模)
- 存放key和value在桶内。
其取值过程是:
- 得到key
- 通过hash函数得到hash值
- 得到桶号(一般都为hash值对桶数求模)
- 比较桶的内部元素是否与key相等,若都不相等,则没有找到。
- 取出相等的记录的value。
hash_map中直接地址用hash函数生成,解决冲突,用比较函数解决。
3.内存占用测试
测试代码:
测试条件window下,VS2015 C++。string为key, int 为value。
1.UnorderMap:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#pragma comment(lib,"psapi.lib")
using namespace std;
using namespace stdext;
void showMemoryInfo(void)
{
HANDLE handle = GetCurrentProcess();
PROCESS_MEMORY_COUNTERS pmc;
GetProcessMemoryInfo(handle, &pmc, sizeof(pmc));
cout << "Memory Use:" << pmc.WorkingSetSize/1024.0f << "KB/" << pmc.PeakWorkingSetSize/1024.0f << "KB, Virtual Memory Use:" << pmc.PagefileUsage/1024.0f << "KB/" << pmc.PeakPagefileUsage/1024.0f << "KB" << endl;
}
//define the class
/*-------------------------------------------*/
/*函数类
*作为hash_map的hash函数
*string没有默认的hash函数
*/
class str_hash {
public:
size_t operator()(const string& str) const
{
unsigned long __h = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
__h = 5 * __h + str[i];
return size_t(__h);
}
};
/*-------------------------------------------*/
/*函数类
*作为hash_map的比较函数 )
*(查找的时候不同的key往往可能对用到相同的hash值
*/
class str_compare
{
public:
bool operator()(const string& str1, const string& str2)const
{
return str1 == str2;
}
};
struct CharLess : public binary_function
{
public:
result_type operator()(const first_argument_type& _Left, const second_argument_type& _Right) const
{
return(_Left.compare(_Right) < 0 ? true : false);
}
};
int main()
{
cout << "Test HashMap(unorder map) Memory Use Start..."<< endl;
// VC下自定义类型
unordered_map > CharHash;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
string key = to_string(i);
CharHash[key] = i;
}
cout << "Test HashMap(unorder map) Memory Use End." << endl;
showMemoryInfo();
while (1);
return 0;
}
2.map:
#include
#include 测试结果:
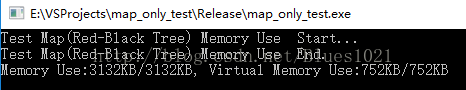
1000个元素:
map:
unorder_map:
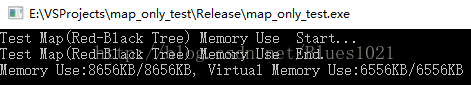
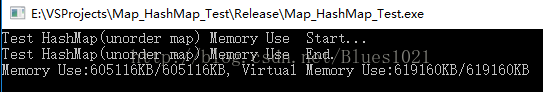
1000万个元素:
map:
unorder_map:
可以看到unordermap始终比map内存空间占用量大些,而且是线性成比例的。
4.性能特点
非频繁的查询用map比较稳定;频繁的查询用hash_map效率会高一些,c++11中的unordered_map查询效率会更高一些但是内存占用比hash_map稍微大点。unordered_map 就是 boost 里面的 hash_map 实现。
其实,stl::map对于与java中的TreeMap,而boost::unordered_map对应于java中的HashMap。
python中的map就是hashmap实现的,所以查询效率会比C++的map查询快。(java,python官方版的虚拟机都是用C语言实现的,所以内部的思想和方法都是通用的。)
若考虑有序,查询速度稳定,容器元素量少于1000,非频繁查询那么考虑使用map。
若非常高频查询(100个元素以上,unordered_map都会比map快),内部元素可非有序,数据大超过1k甚至几十万上百万时候就要考虑使用unordered_map(元素上千万上亿时4GB的内存就要担心内存不足了,需要数据库存储过程挪动到磁盘中)。
hash_map相比unordered_map就是千万级别以上内存占用少15MB,上亿时候内存占用少300MB,百万以下都是unordered_map占用内存少,
且unordered_map插入删除相比hash_map都快一倍,查找效率相比hash_map差不多,或者只快了一点约1/50到1/100。
综合非有序或者要求稳定用map,都应该使用unordered_map,set类型也是类似的。
unordered_map 查找效率快五倍,插入更快,节省一定内存。如果没有必要排序的话,尽量使用 hash_map(unordered_map 就是 boost 里面的 hash_map 实现)。
python中的map就是hashmap实现的,所以查询效率会比C++的map查询快。(java,python官方版的虚拟机都是用C语言实现的,所以内部的思想和方法都是通用的。)
若考虑有序,查询速度稳定,容器元素量少于1000,非频繁查询那么考虑使用map。
若非常高频查询(100个元素以上,unordered_map都会比map快),内部元素可非有序,数据大超过1k甚至几十万上百万时候就要考虑使用unordered_map(元素上千万上亿时4GB的内存就要担心内存不足了,需要数据库存储过程挪动到磁盘中)。
hash_map相比unordered_map就是千万级别以上内存占用少15MB,上亿时候内存占用少300MB,百万以下都是unordered_map占用内存少,
且unordered_map插入删除相比hash_map都快一倍,查找效率相比hash_map差不多,或者只快了一点约1/50到1/100。
综合非有序或者要求稳定用map,都应该使用unordered_map,set类型也是类似的。
unordered_map 查找效率快五倍,插入更快,节省一定内存。如果没有必要排序的话,尽量使用 hash_map(unordered_map 就是 boost 里面的 hash_map 实现)。
5.使用unordered_map
unordered_map需要重载hash_value函数,并重载operator ==运算符。
详细参考见(感谢orzlzro写的这么好的文章):
详细参考见(感谢orzlzro写的这么好的文章):
http://blog.csdn.net/orzlzro/article/details/7099231
6.使用Hash_map需要注意的问题
/*
*
*\author peakflys
*\brief 演示hash_map键值更改造成的问题
*/
#include
#include
struct Unit
{
char name[32];
unsigned int score;
Unit( const char *_name, const unsigned int _score) : score(_score)
{
strncpy(name,_name,32);
}
};
int main()
{
typedef __gnu_cxx::hash_map< char*,Unit*> uHMap;
typedef uHMap::value_type hmType;
typedef uHMap::iterator hmIter;
uHMap hMap;
Unit *unit1 = new Unit("peak",100);
Unit *unit2 = new Unit("Joey",20);
Unit *unit3 = new Unit("Rachel",40);
Unit *unit4 = new Unit("Monica",90);
hMap[unit1->name] = unit1;
hMap[unit2->name] = unit2;
hMap.insert(hmType(unit3->name,unit3));
hMap.insert(hmType(unit4->name,unit4));
for(hmIter it=hMap.begin();it!=hMap.end();++it)
{
std::cout<first<<"\t"<second->score<//
正常操作
}
for(hmIter it=hMap.begin();it!=hMap.end();++it)
{
Unit *unit = it->second;
//hMap.erase(it++);
delete unit; // delete释放节点内存,但是hMap没有除去,造成hMap内部错乱,有可能宕机
}
hmIter it = hMap.begin();
strncpy(it->first,"cc",32); // 强行更改
for(hmIter it=hMap.begin();it!=hMap.end();++it)
{
std::cout<first<<"\t"<second->score<//
死循环,原因参加上面++操作说明
*\author peakflys
*\brief 演示hash_map键值更改造成的问题
*/
#include
#include
struct Unit
{
char name[32];
unsigned int score;
Unit( const char *_name, const unsigned int _score) : score(_score)
{
strncpy(name,_name,32);
}
};
int main()
{
typedef __gnu_cxx::hash_map< char*,Unit*> uHMap;
typedef uHMap::value_type hmType;
typedef uHMap::iterator hmIter;
uHMap hMap;
Unit *unit1 = new Unit("peak",100);
Unit *unit2 = new Unit("Joey",20);
Unit *unit3 = new Unit("Rachel",40);
Unit *unit4 = new Unit("Monica",90);
hMap[unit1->name] = unit1;
hMap[unit2->name] = unit2;
hMap.insert(hmType(unit3->name,unit3));
hMap.insert(hmType(unit4->name,unit4));
for(hmIter it=hMap.begin();it!=hMap.end();++it)
{
std::cout<
}
for(hmIter it=hMap.begin();it!=hMap.end();++it)
{
Unit *unit = it->second;
//hMap.erase(it++);
delete unit; // delete释放节点内存,但是hMap没有除去,造成hMap内部错乱,有可能宕机
}
hmIter it = hMap.begin();
strncpy(it->first,"cc",32); // 强行更改
for(hmIter it=hMap.begin();it!=hMap.end();++it)
{
std::cout<
/*operator++ 操作是从_M_cur开始,优先_M_cur->_M_next,为空时遍历vector直至找到一个_M_cur不为空的节点,遍历vector 时需要取它对应的桶位置(参砍上面hash_map取值过程),_M_bkt_num_key(key)中key的值是修改后的值,假如你改的键值,通过 此函数得到的桶位置在你当前元素之前,这样就造成了死循环.
*/
}
return 0;
}
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20384806-id-3055333.html
http://blog.csdn.net/whizchen/article/details/9286557
http://blog.csdn.net/gamecreating/article/details/7698719
http://www.cppblog.com/peakflys/archive/2012/07/24/184855.aspx
}
return 0;
}
7.VC下参考实例
#include "stdafx.h"
// 存放过程:key->hash函数->hash值对桶数求模得到桶号(桶有值则解决冲突),存放key和value在桶内
// 取回过程:key->hash函数->hash值对桶数求模得到桶号(桶有值则解决冲突),比较桶内的key是否相等,
// 若不相等则返回空迭代器,否则返回迭代器。
// 1.hash_map为下面类型的key定义了hash寻址函数(用于从key到hash值)和哈希比较函数(用于解决冲突)。
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
//struct hash
// 内建的类型直接 hash_map mymap;像普通map一样使用即可。
// 2.自定义hash函数和比较函数
//在声明自己的哈希函数时要注意以下几点:
//使用struct,然后重载operator().
//返回是size_t
//参数是你要hash的key的类型。
//函数是const类型的。
// 定义自己的比较函数:
//使用struct,然后重载operator().
//返回是bool
//参数是你要hash的key的类型的两个常量参数,用于比较。
//函数是const类型的。
// 自定义hash函数和比较函数的使用:
// hash_map hmap;
// 3.hash_map使用的常用函数
//hash_map的函数和map的函数差不多。具体函数的参数和解释,请参看:STL 编程手册:Hash_map,这里主要介绍几个常用函数。
//
//hash_map(size_type n) 如果讲究效率,这个参数是必须要设置的。n 主要用来设置hash_map 容器中hash桶的个数。
//桶个数越多,hash函数发生冲突的概率就越小,重新申请内存的概率就越小。n越大,效率越高,但是内存消耗也越大。
//
//const_iterator find(const key_type& k) const. 用查找,输入为键值,返回为迭代器。
//
//data_type& operator[](const key_type& k) . 这是我最常用的一个函数。因为其特别方便,可像使用数组一样使用。
//不过需要注意的是,当你使用[key ]操作符时,如果容器中没有key元素,这就相当于自动增加了一个key元素。
//因此当你只是想知道容器中是否有key元素时,你可以使用find。如果你希望插入该元素时,你可以直接使用[]操作符。
//
//insert 函数。在容器中不包含key值时,insert函数和[]操作符的功能差不多。但是当容器中元素越来越多,
//每个桶中的元素会增加,为了保证效率,hash_map会自动申请更大的内存,以生成更多的桶。因此在insert以后,
//以前的iterator有可能是不可用的。
//
//erase 函数。在insert的过程中,当每个桶的元素太多时,hash_map可能会自动扩充容器的内存。
//但在sgi stl中是erase并不自动回收内存。因此你调用erase后,其他元素的iterator还是可用的。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace stdext;
//define the class
/*-------------------------------------------*/
/*函数类
*作为hash_map的hash函数
*string没有默认的hash函数
*/
class str_hash{
public:
size_t operator()(const string& str) const
{
unsigned long __h = 0;
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < str.size() ; i ++)
__h = 5*__h + str[i];
return size_t(__h);
}
};
/*-------------------------------------------*/
/*函数类
*作为hash_map的比较函数 )
*(查找的时候不同的key往往可能对用到相同的hash值
*/
class str_compare
{
public:
bool operator()(const string& str1,const string& str2)const
{return str1==str2;}
};
struct CharLess : public binary_function
{
public:
result_type operator()(const first_argument_type& _Left, const second_argument_type& _Right) const
{
return(strcmp(_Left, _Right) < 0 ? true : false);
}
};
int main()
{
// 内建类型
hash_map myHashMap;
myHashMap[0] = "JesseCen";
myHashMap[1] = "OZZ";
hash_map::iterator itrHash = myHashMap.find(0);
if(itrHash != myHashMap.end())
{
cout<<"My Name is:"<second.c_str()< > CharHash;
CharHash["a"] = 123;
CharHash["b"] = 456;
hash_map >::iterator itrChar = CharHash.find("b");
if( itrChar != CharHash.end())
{
cout<<"The find number is:"<< itrChar->second< http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20384806-id-3055333.html
http://blog.csdn.net/whizchen/article/details/9286557
http://blog.csdn.net/gamecreating/article/details/7698719
http://www.cppblog.com/peakflys/archive/2012/07/24/184855.aspx