iOS 数据持久化/沙盒/归档解档/缓存(内存缓存、磁盘缓存)
文章目录
- iOS 数据持久化
- plist文件
- 沙盒
- 归档解档
- 缓存
- NSCache
- NSURLCache
iOS 数据持久化
- iOS的几种数据持久化方案
- plist文(
property list file:属性列表) - 沙盒
- NSKeyedArchiver(归档)
- SQLite
- CoreData
plist文件
plist文件中只能存储NSString、NSArray、NSDictionary、NSData、NSNumber、NSDate数据类型plist文件一般用来存储用户登录、注册信息,程序的设置信息、配置信息等这些小数据。NSString、NSArray、NSDictionary、NSData这些类都提供writeToFile方法,实现将当前对象数据直接写入文件,但是只有NSArray、NSDictionary会写出plist文件,生成的plist文件是xml格式。
//创建一个数组根据路径生成一个`plist`文件,及写入数
NSArray * arry = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"name", @1,@{@"gae":@18},nil];
BOOL flag = [arry writeToFile:@"/Users/xxx/Desktop/test.plist" atomically:YES];
//根据`plist`文件创建一个数组,获得数据
NSArray * arr = [[NSArray alloc]initWithContentsOfFile:@"/Users/xxx/Desktop/test.plist"];
、
沙盒
沙盒:也叫沙箱,英文standby, 每个iOS应用程序都会为自己创建一个文件系统目录(文件夹),是一个独立,封闭,安全的空间 ;通过重定向技术,把程序生成和修改的文件定向到自身文件夹中,在沙盒机制下,每个程序之间的文件夹不能互相访问。iOS系统为了保证系统安全,采用了这种机制。注意:
1: 每一个应用程序都会拥有一个应用程序沙盒
2: 应用程序沙盒就是一个系统目录
3: 所有的非代码文件都保存在这个地方比如图片, 声音, 属性列表(plist), sqlite数据库和文本文件等.
4.独立: 不可能出现两个程序公用同一个沙盒
5.封闭 : 每一个沙盒 都只能他自己的应用去使用(很少的有和其他的app交互的,iOS8部分开放访问也允许了用的并不多,应用程序向外请求或者接收数据都需要经过权限认证)
6.安全 :沙盒有被删除的时效- 获取沙盒根目录:
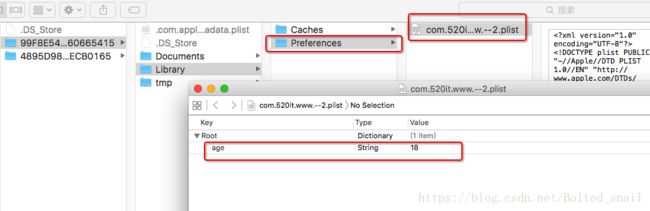
NSHomeDirectory(),通过路径前往文件夹可以看到下图结构:

- 沙盒结构:沙盒包含
Documents、Library、tmp三个文件夹,其中Library里面又包含应用程序包、Caches、preferences两个文件夹。
应用程序包:这里面存放的是应用程序的源文件,包括资源文件和可执行文件。Documents:一般需要持久的数据都放在此目录中,可以在当中添加子文件夹,iTunes备份和恢复的时候,会包括此目录。应该将所有的应用程序数据文件写入到这个目录下。这个目录用于存储用户数据或其它应该定期备份的信息。Library/Caches::存放缓存文件,iTunes不会备份此目录,此目录下文件不会在应用退出删除。- .
Library/preferences:存放应用程序的偏好设置文件,iTunes会备份此目录, 应用程序重新启动不会丢弃数据,不应该直接创建偏好设置文件,而是应该使用NSUserDefaults类来取得和设置应用程序的偏好,里面有个plist文件以键值对的形式保存信息。 tmp:这个目录用于存放临时文件,当iOS设备重启时,文件会被自动清除。
- 获取相应的路径
//获取沙盒根目录
NSLog(@"standby:%@", NSHomeDirectory());
//获取Documents目录
NSArray * paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory,NSUserDomainMask,YES);
NSLog(@"Documents:%@",paths.firstObject);
//获取Library目录
NSArray * paths2 = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSLibraryDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSLog(@"Library:%@",paths2.firstObject);
//获取Library/Caches目录
NSArray * paths3 = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSLog(@"Caches:%@",paths3.firstObject);
//Library/preferences,偏好设置保存值
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setValue:@"18" forKey:@"age"];
NSLog(@"preferences:%@",[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] valueForKey:@"age"]);
//需要注意的是如果程序意外退出,NSUserDefaultsstandardUserDefaults数据不会被系统写入到该文件,所以,要使用[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults]synchronize] 直接同步到文件里,来避免数据的丢失。
//获取tmp路径
NSLog(@"tmp:%@",NSTemporaryDirectory());
//储存文件
归档解档
- OC中的归档就是将对象写入到文件中,尤其是自定义对象只能通过归档的方式进行本地化存储。
NSObject没有遵循- 归档就需要实现
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder方法。
*解档就需要实现- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder方法。 - 归档调用
NSKeyedArchiver的工厂方法archiveRootObject: toFile:方法。 - 解档调用
NSKeyedUnarchiver的工厂方法unarchiveObjectWithFile:。 - 如果需要归档的类是某个自定义类的子类时,就需要在归档和解档之前先实现父类的归档和解档方法。即
[super encodeWithCoder:aCoder]和[super initWithCoder:aDecoder]方法; - 示例:
//自定义Person实现归档解档
//.h文件
#import
@interface Person : NSObject
/**名字*/
@property(nonatomic,copy) NSString * name;
/**年龄*/
@property(nonatomic,assign) int age;
/**性别*/
@property(nonatomic,copy) NSString * sex ;
@end
//.m文件
#import "Person.h"
@implementation Person
//归档要实现的协议方法
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder{
[aCoder encodeObject:_name forKey:@"name"];
[aCoder encodeInt:_age forKey:@"age"];
[aCoder encodeObject:_sex forKey:@"sex"];
}
//解档要实现的协议方法
-(instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder{
if (self = [super init]) {
_name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
_age = [aDecoder decodeIntForKey:@"age"];
_sex = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"sex"];
}
return self;
}
@end
//在ViewController中实现Person的归档解档
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "Person.h"
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
Person * p =[[Person alloc]init];
p.name = @"娟娟";
p.age = 18;
p.sex = @"女";
//归档
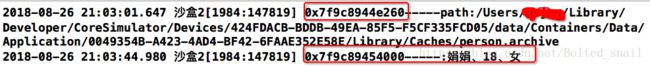
NSString * path = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES).firstObject stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.archive"];
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:p toFile:path];
NSLog(@"%p-----path:%@",p,path);
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
//解档
NSString * path = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES).firstObject stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.archive"];
Person * p = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:path];
NSLog(@"%p-----:%@、%d、%@",p,p.name,p.age,p.sex);
}
@end
- 结果可见虽然对象不再是保存的那个对象了,但是内容还是保存的对象的内容。
缓存
NSCache
-
iOS缓存分为内存缓存和磁盘缓存,内存即手机的运行内存(RAM),磁盘即手机的sd卡, 磁盘缓存上面已经讲过就是在
Library/Caches目录下缓存文件。 -
NSCache是一个类似于集合的容器,即内存缓存。用来临时存储短时间使用但创建昂贵的对象。重用这些对象可以优化性能,因为它们的值不需要重新计算。另外一方面,这些对象对于程序来说不是紧要的,在内存紧张时会被丢弃。如果对象被丢弃了,则下次使用时需要重新计算。NSCache对象是一个可变集合,用于存储键值对,类似于NSMutableDictionary对象。 -
NSCache类包含各种自动驱逐策略,可确保缓存不会占用太多的系统内存。如果其他应用程序需要内存,则这些策略会从缓存中删除一些项目,从而最大限度地减少内存占用。 -
NSCache是线程安全的,你可以从不同的线程添加,删除和查询缓存中的项目,而无需自己锁定缓存。 -
NSCache的key只是做强引用,不需要实现NScopying协议。 -
NSCache的API:
//名称
@property (copy) NSString *name;
//代理
@property (nullable, assign) id delegate;
//通过key在缓存中取值
- (nullable ObjectType)objectForKey:(KeyType)key;
//在缓存中设置指定键名对应的值。
- (void)setObject:(ObjectType)obj forKey:(KeyType)key; // 0 cost
//在缓存中设置指定键名对应的值,并且指定该键值对的成本。成本`cost`用于计算记录在缓存中所有对象的总成本。当出现内存警告,或者超出缓存的成本上限时,缓存会开启一个回收过程,删除部分元素。
- (void)setObject:(ObjectType)obj forKey:(KeyType)key cost:(NSUInteger)g;
//删除缓存中指定键名的对象。
- (void)removeObjectForKey:(KeyType)key;
//删除缓存中的所有对象。
- (void)removeAllObjects;
//缓存空间的最大成本,超出上限会自动回收对象。默认值是0没有限制。
@property NSUInteger totalCostLimit; // limits are imprecise/not strict
//能够缓存对象的最大数量,默认值也是0(默认没有限制)。
@property NSUInteger countLimit; // limits are imprecise/not strict
//标示是否回收废弃的内容,默认值是YES(自动回收)
@property BOOL evictsObjectsWithDiscardedContent;
@end
@protocol NSCacheDelegate
@optional
//缓存将要删除对象时调用,不能在此方法中修改缓存。仅仅用于后台的打印,以便于程序员的测试。
- (void)cache:(NSCache *)cache willEvictObject:(id)obj;
- 示例
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
// 缓存的容器
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSCache *myCache;
@end
@implementation ViewController
-(NSCache *)myCache
{
if (_myCache == nil) {
_myCache = [[NSCache alloc] init];
/** NSCache类以下几个属性用于限制成本
NSUInteger totalCostLimit "成本" 限制,默认是0(没有限制)
NSUInteger countLimit 数量的限制 默认是0 (没有限制)
// 设置缓存的对象,同时指定限制成本
-(void)setObject:(id) obj forKey:(id) key cost:(NSUInteger) g
*/
// 设置数量限额。一旦超出限额,会自动删除之前添加的东西
_myCache.countLimit = 30; // 设置了存放对象的最大数量
_myCache.delegate = self;
}
return _myCache;
}
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
for (int i =0 ; i< 100; i++) {
// 向缓存中添加对象
NSString *str = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"hello - %d", i];
[self.myCache setObject:str forKey:@(i)]; // @(i) 相当于 [NSNumber numberWith......]
}
for (int i=0 ; i< 100; i++) {
NSLog(@"%@", [self.myCache objectForKey:@(i)]);
}
}
// NSCache的代理方法只有一个
// 告诉即将要被删除的对象
-(void)cache:(NSCache *)cache willEvictObject:(id)obj
{
// 此代理方法主要用于程序员的测试
NSLog(@"要删除的对象obj-------------%@", obj);
}
@end
NSURLCache
NSURLCache为你的应用的URL请求提供了内存中以及磁盘上的综合缓存机制。- 网络缓存减少了需要向服务器发送请求的次数,同时也提升了离线或在低速网络中使用应用的体验。当一个请求完成下载来自服务器的响应,一个缓存的响应将在本地保存。下一次同一个请求再发起时,本地保存的回应就会马上返回,不需要连接服务器。
NSURLCache会自动且透明地返回回应。需要说明的是NSURLCache与NSCache毫无关系。 - 使用
- 设置缓存策略:
NSURLRequest有个cachePolicy属性,它根据以下常量指定了请求的缓存行为:
NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy:对特定的 URL 请求使用网络协议中实现的缓存逻辑。这是默认的策略。
NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData:数据需要从原始地址加载。不使用现有缓存。
NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData:不仅忽略本地缓存,同时也忽略代理服务器或其他中间介质目前已有的、协议允许的缓存。
NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataElseLoad:无论缓存是否过期,先使用本地缓存数据。如果缓存中没有请求所对应的数据,那么从原始地址加载数据。
NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataDontLoad:无论缓存是否过期,先使用本地缓存数据。如果缓存中没有请求所对应的数据,那么放弃从原始地址加载数据,请求视为失败(即:“离线”模式)。
NSURLRequestReloadRevalidatingCacheData:从原始地址确认缓存数据的合法性后,缓存数据就可以使用,否则从原始地址加载。 - 在发送请求之前设置一下缓存大小:
默认情况下,内存是4M,4* 1024 * 1024;硬盘为20M,20 * 1024 * 1024
[[NSURLCache sharedURLCache] setMemoryCapacity:4*1024*1024]。//设置内存缓存
[[NSURLCache sharedURLCache] setDiskCapacity:20*1024*1024]。//设置沙盒缓存
也可以自己初始化缓存对象
NSURLCache *URLCache = [[NSURLCache alloc] initWithMemoryCapacity:4*1024*1024 diskCapacity:20*1024*1024 diskPath:path];
[NSURLCache setSharedURLCache:URLCache]; - 控制需不需要缓存:
NSURLConnectionDataDelegate代理方法中,下面的方法用来指定此次请求需不需要缓存,同时也可以在返回之前,修改response里面的数据:
- (NSCachedURLResponse *)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection willCacheResponse:(NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponse
- 要点:
UIWebView的的NSURLRequest请求,以及自己用NSURLConnection发送的请求,NSURLCache都会拦截并存储。NSURLCache只对异步请求有效。NSURLCache的缓存包括内存缓存和磁盘缓存,iOS4.x系统只有内存缓存,iOS5.x及以上两者都有,但仅支持HTTP,HTTPS在iOS6中增加了支持。磁盘缓存有默认的缓存路径,也可以自己指定路径。- 当系统存储空间不足时,当前的请求不会被缓存,包括之前的磁盘缓存也可能被系统清除掉。
- 如果有使用
NSURLCache,在应用收到内存警告时,应该清空缓存:removeAllCachedResponses。
NSURLCache相关API:
功能方法:
//返回对应的NSURLRequest缓存的response,如果没有则返回nil。
- (NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponseForRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request;
//为特定的NSURLRequest指定缓存对象,并存储。
- (void)storeCachedResponse:(NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponse forRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request;
//移除特定NSURLRequest的cache。
- (void)removeCachedResponseForRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request;
//移除所有的cache。
- (void)removeAllCachedResponses;
属性:
//设置的内存缓存大小
@property NSUInteger memoryCapacity;
//设置的沙盒缓存大小
@property NSUInteger diskCapacity;
//当前用的内存缓存大小
@property (readonly) NSUInteger currentMemoryUsage;
//当前用的沙盒缓存大小
@property (readonly) NSUInteger currentDiskUsage;
NSCachedURLResponse对象:包装了一下系统缓存机制的对象,保持了缓存对象的个性和特性。
//NSURLCacheStoragePolicy 缓存策略有三种
enum
{
NSURLCacheStorageAllowed,
NSURLCacheStorageAllowedInMemoryOnly,
NSURLCacheStorageNotAllowed,
};
// 构造方法
- (id)initWithResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response data:(NSData *)data;
- (id)initWithResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response data:(NSData *)data userInfo:(NSDictionary *)userInfo storagePolicy:(NSURLCacheStoragePolicy)storagePolicy;
//相关API
- (NSURLResponse *)response;
- (NSData *)data;
- (NSDictionary *)userInfo;
- (NSURLCacheStoragePolicy)storagePolicy;
- 自定义
NSURLCache
1.重写cachedResponseForRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request,这个会在请求发送前会被调用,从中我们可以判定是否针对此NSURLRequest返回本地数据。如果本地没有缓存就调用下面这条语句:return [super cachedResponseForRequest:request];
2.重写storeCachedResponse:(NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponse forRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request,我们可以对某一个请求做我们自己的数据保存机制,如果使用系统默认的数据保存机制,则调用[super storeCachedResponse:cachedResponse forRequest:request]; - 简单示例
- (NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponseForRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request{
//获取URL整体路径
NSString *urlStringMD5 = [self md5:request.URL.absoluteString];
//获取缓存文件存储地址
NSString *filePath = [[self getDocumentPath] stringByAppendingPathComponent:urlStringMD5];
//如果缓存存在,则返回缓存数据,否则使用系统默认处理
if ([[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:filePath]) {
//获取缓存文件路径
NSData *fileData = [[NSData alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
//根据URL路径,获取媒体类型
NSString *memiType = [self mimeTypeForPath:request.URL.absoluteString];
//合成NSCachedURLResponse对象,返回
NSURLResponse *response = [[NSURLResponse alloc] initWithURL:[request URL]
MIMEType:memiType
expectedContentLength:[fileData length]
textEncodingName:nil];
NSCachedURLResponse *cachedResponse = [[NSCachedURLResponse alloc] initWithResponse:response data:fileData];
return cachedResponse;
}else{
return [super cachedResponseForRequest:request];
}
}
- (void)storeCachedResponse:(NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponse forRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request{
//将服务器返回数据缓存起来
NSString *urlStringMD5 = [self md5:request.URL.absoluteString];
NSString *filePath = [[self getDocumentPath] stringByAppendingPathComponent:urlStringMD5];
[cachedResponse.data writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES];
}
- 参考文档:
NSCache
NSCache
NSURLCache
聊聊NSCache
NSCache和NSURLCache、网络缓存优化
南峰子的技术博客
NSHipster 关注被忽略的 Objective-C、Swift 和 Cocoa 特性。每周更新。
iOS网络请求缓存:NSURLCache详解
和你聊聊加密那些事儿