【iOS】MVC设计模式
MVC
前言
如何设计一个程序的结构,这是一门专门的学问,叫做"架构模式"(architectural pattern),属于编程的方法论。MVC 模式就是架构模式的一种。
它是Apple 官方推荐的 App 开发架构,也是一般开发者最先遇到、最经典的架构。
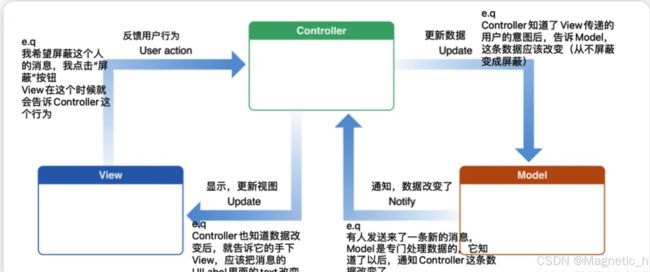
MVC各层
controller层
Controller / ViewController / VC(控制器)负责协调Model 和 View,处理大部分逻辑
它将数据从Model 层传送到View 层并展示出来,同时将View 层的交互传到Model 层以改变数据。**大部分的逻辑操作(点击Button就是一种逻辑)都应该交由VC完成。
model层
Model(模型)负责处理数据,以及处理部分的业务逻辑
通俗来说,就是你的程序是什么,就是你的程序将要实现的功能,或者是它所能干的事情。也就是微信消息列表里的人名字,信息内容,头像,是否屏蔽该人的消息等等数据,可以认为,Model 里面装满了这个程序的各种数据,它负责处理数据、以及处理部分的业务逻辑。
view层
V:View(视图)负责数据的展示和事件捕捉
通俗来说,在屏幕上你所看到的,比如一个UITableView,TableView 里面有UILabel,UIImageView,你在屏幕上看到的组件,都可以归类为View。
总结
总的来说,MVC模式就是将一个程序分为了三个部分,model负责处理数据,view负责处理视图,controller负责处理逻辑。但是model、view和controller之间并不是一一对应的关系。
⚠️Model 和 View 是相互独立的
胖model和瘦model
胖Model对应的是瘦的VC(Skinny Controller),在Model 中 对数据进行处理 ,让Controller可以直接使用经过处理后的数据。
瘦Model对应的是胖的VC(Fat Controller),Model中的数据 不进行任何处理或修改 ,原封不动的把服务器返回内容发送给Controller。
流程
用户点击view—>视图响应事件—>通过代理传递事件到controller—>发起网络请求更新model—>model处理完数据—>代理或通知给controller—>改变视图样式—>完成
优缺点
优点
通过controller控制全局,同时将view和model的变化分开,对于复杂的项目结构,有了明确的组织方式
缺点
大量逻辑代码放进controller,导致controller越来越臃肿,后期维护成本高
实例
LoginModel
@property(nonatomic, retain)NSMutableArray *accountArray;
@property(nonatomic, retain)NSMutableArray *passwordArray;
- (void)initLoginModel;#import "LoginModel.h"
@implementation LoginModel
- (void)initLoginModel {
self.accountArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
self.passwordArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
[self.accountArray addObject:@"111"];
[self.passwordArray addObject:@"111"];
}
@end
LoginView
@interface LoginView : UIView
@property(retain, nonatomic)UITextField *textfield1;
@property(retain, nonatomic)UITextField *textfield2;
@property(nonatomic, strong)UIButton *loginBtn;
@property(nonatomic, strong)UIButton *registerBtn;
- (void)initView;
@end#import "LoginView.h"
@implementation LoginView
- (void)initView {
self.textfield1 = [[UITextField alloc] init];
self.textfield1.frame = CGRectMake(20, 30, 280, 40);
self.textfield1.placeholder = @"请输入账号";
self.textfield1.borderStyle = UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect;
[self.textfield1 becomeFirstResponder];
[self addSubview:self.textfield1];
self.textfield2 = [[UITextField alloc] init];
self.textfield2.frame = CGRectMake(20, 80, 280, 40);
self.textfield2.placeholder = @"请输入密码";
self.textfield2.borderStyle = UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect;
[self.textfield2 becomeFirstResponder];
[self addSubview:self.textfield2];
self.loginBtn = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeRoundedRect];
self.frame = CGRectMake(120, 130, 80, 40);
[_loginBtn setTitle:@"登录" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
self.loginBtn.tintColor = [UIColor blackColor];
self.loginBtn.titleLabel.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:20];
[self addSubview:self.loginBtn];
self.registerBtn = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeRoundedRect];
self.registerBtn.frame = CGRectMake(120, 180, 80, 40);
[self.registerBtn setTitle:@"注册" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
[self addSubview:self.registerBtn];
}
@end
LoginViewController
@interface LoginViewController : UIViewController
@property (nonatomic, strong)LoginView *loginView;
@property (nonatomic, strong)LoginModel *loginModel;
@property (retain, nonatomic)UIAlertController *alert;
@end#import "LoginViewController.h"
@interface LoginViewController ()
@end
@implementation LoginViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
self.loginModel = [[LoginModel alloc] init];
[self.loginModel initLoginModel];
self.loginView = [[LoginView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.frame];
[self.loginView initView];
[self.view addSubview:self.loginView];
[self.loginView.loginBtn addTarget:self action:@selector(login) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
}
- (void)login {
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _loginModel.accountArray.count; i ++) {
if ([_loginModel.accountArray[i] isEqualToString:_loginView.textfield1.text] && [_loginModel.passwordArray[i] isEqualToString:_loginView.textfield2.text]) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 1) {
self.alert = [UIAlertController alertControllerWithTitle:@"提示" message:@"登陆成功" preferredStyle:UIAlertControllerStyleAlert];
UIAlertAction *confirmAction = [UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:@"确认" style:UIAlertActionStyleDefault handler:^(UIAlertAction * _Nonnull action) {
}];
[self.alert addAction:confirmAction];
[self presentViewController:self.alert animated:YES completion:nil];
} else {
self.alert = [UIAlertController alertControllerWithTitle:@"提示" message:@"用户名或密码错误" preferredStyle:UIAlertControllerStyleAlert];
UIAlertAction *confirmAction = [UIAlertAction actionWithTitle:@"确认" style:UIAlertActionStyleDefault handler:^(UIAlertAction * _Nonnull action) {
}];
[self.alert addAction:confirmAction];
[self presentViewController:self.alert animated:YES completion:nil];
}
}
@end