MyBatisPlus + SpringBoot + Thymeleaf 完成简单的入门案例【上】
这篇文章主要用于学习SpringBoot以及整合MyBatisPlus和前端框架LayUI,使用的都是最新的版本:
SpringBoot2.1.0 , MyBatisPlus3.0.6 , LayUI2.4.5 ,MySQL5.5.15, 以及SpringBoot默认支持的模板引擎Thymeleaf3.0.4,使用以上技术,了解SpringBoot怎么集成以上框架技术,怎么完成XML配置的替换等…
本来是做一个RBAC权限管理系统的,但是这样做的话,这个博客会很臃肿,后面把它改了,重点还是介绍SpringBoot的相关知识。以及各个技术的集成,先简单的入门,后面再统一完成项目说明,就不在做技术知识点讲解了
文章目录
- SpringBoot简介
- 使用IDEA工具快速构建SpringBoot入门案例
- 在数据库中创建两张表,用于测试
- 使用MybatisPlus 的代码生成器获取所需文件
- SpringBoot启动类
- 集成配置MyBatisPlus以及数据源
- SpringBoot核心配置文件
- 整合测试
- MyBatisPlus 封装的CRUD接口
- Mapper CRUD 接口
- Service CRUD 接口
- 条件构造器
- 使用SpringBootTest熟悉一下MyBatisPlus提供的CRUD接口
- 接下来我们测试几个常见的方法
- Thymeleaf模板引擎简单入门
- 1. 语法
- 2. 表达式
SpringBoot简介
Spring由于其繁琐的配置,一度被人认为“配置地狱”,各种XML、Annotation配置,让人眼花缭乱,而且如果出错了也很难找出原因。Spring Boot更多的是采用Java Config的方式,对Spring进行配置。
Spring Boot可以轻松创建独立的,生产级的基于Spring的应用程序,您可以直接“运行”启动服务,而不用再去配置Tomcat启动。包括静态资源处理,视图解析器,注解扫描等…
- SpringBoot特征
- 创建独立的Spring应用程序
- 直接嵌入Tomcat,Jetty或Undertow(无需部署WAR文件)
- 提供简洁的“入门”依赖项以简化构建配置,简化Maven配置
- 尽可能自动配置Spring和第三方库,大部分数据源,Mapper扫描,组件注入都不用再处理,去处理繁琐的Xml配置
- 提供生产就绪功能,例如指标,运行状况检查和外部化配置
- 绝对没有代码生成,也不需要XML配置
- SpringBoot2.1.0官方学习地址
- 依赖管理
每个版本的Spring Boot都提供了它支持的依赖项的精选列表。实际上,您不需要为构建配置中的任何这些依赖项提供版本,因为Spring Boot会为您管理这些依赖项。当您升级Spring Boot时,这些依赖项也会以一致的方式升级。就不用再单独使用properties来提取对应的jar包版本,SpringBoot的parent帮你搞定.在配置对应jar的时候,不需要再写版本号了。SpringBoot没有提供的除外。
<! - 继承默认值为Spring Boot - >
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.0.RELEASE < / version>
如果需要,您仍然可以指定版本并覆盖Spring Boot的建议。当然,每个版本的Spring Boot都与Spring Framework的基本版本相关联。我们强烈建议您不要指定其版本。SpringBoot没有提供的除外.
- SpringBoot提供的应用程序启动器,也就是封装好的Maven配置常用的如下,具体查看帮助文档。
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| spring-boot-starter | 核心启动器,包括自动配置支持,日志记录和YAML |
| spring-boot-starter-aop | 使用Spring AOP和AspectJ进行面向方面编程的入门者 |
| spring-boot-starter-freemarker | 使用FreeMarker视图构建MVC Web应用程序的入门者 |
| spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf | 使用Thymeleaf视图构建MVC Web应用程序的入门者 |
| spring-boot-starter-jdbc | 将JDBC与HikariCP连接池一起使用的入门者 |
| spring-boot-starter-json | 配置jackson,完成对象转换JSON的操作,需要注意的是要转换的JSON对象需要符合JavaBean规范 |
| spring-boot-starter-mail | 使用Java Mail和Spring Framework的电子邮件发送支持的初学者 |
| spring-boot-starter-test | 使用JUnit,Hamcrest和Mockito等库来测试Spring Boot应用程序的初学者 |
| spring-boot-starter-validation | 使用Java Bean Validation和Hibernate Validator的初学者 |
| spring-boot-starter-web | 使用Spring MVC构建Web(包括RESTful)应用程序的入门者。使用Tomcat作为默认嵌入式容器 |
| spring-boot-starter-webflux | 使用Spring Framework的Reactive Web支持构建WebFlux应用程序的初学者 |
| spring-boot-starter-websocket | 使用Spring Framework的WebSocket支持构建WebSocket应用程序的初学者 |
| spring-boot-starter-logging | 使用Logback进行日志记录的入门。默认日志启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-log4j2 | 使用Log4j2进行日志记录的入门。替代spring-boot-starter-logging |
| spring-boot-starter-tomcat | 使用Tomcat作为嵌入式servlet容器的入门者。使用的默认servlet容器启动器spring-boot-starter-web |
| spring-boot-starter-jetty | 使用Jetty作为嵌入式servlet容器的入门。替代spring-boot-starter-tomcat |
- SpringBoot和SpringMVC常用注解
| 注解名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @SpringBootApplication | 包含了@ComponentScan、@Configuration和@EnableAutoConfiguration注解。其中@ComponentScan让spring Boot扫描到Configuration类并把它加入到程序上下文 |
| @ImportResource | 用来加载xml配置文件 |
| @Bean | 用@Bean标注方法等价于XML中配置的bean |
| @Value | 注入SpringBoot 核心配置文件(application.yml > application.properties)中属性对应的值 |
| @Configuration | 等同于spring的XML配置文件;使用Java代码可以检查类型安全。替代xml配置,通过@Bean完成注入,可以使用@ImportResource注解加载xml配置文件 |
| @ConfigurationProperties | 方法注解,用于获取核心配置文件中对应以什么开头的多个属性,并自动注入到对象中 |
| @Import | 用来导入其他配置类 |
| @Primary | 方法注解,用于标注,如果IOC容器中存在多个相同类型的Bean,优先使用被标注的Bean对象 |
| @EnableAutoConfiguration | 自动配置 |
| @ExceptionHandler | 用在方法上面表示遇到这个异常就执行以下方法 |
| @ControllerAdvice、@RestControllerAdivce | 包含@Component。可以被扫描到。统一处理异常,类注解,需要和@ExceptionHandler配合使用 |
| @ResponseBody | 标注返回的信息使用Json转换 |
| @Controller | 用于定义控制器类,通常方法需要配合注解@RequestMapping |
| @RestController | 是@Controller和@ResponseBody的合集,表示这是个控制器bean,并且是将函数的返回值直 接填入HTTP响应体中,是REST风格的控制器 |
| @PathVariable | 获取参数 |
| @Autowired / @Resource | 自动注入,获取SpringIOC容器中的bean对象 |
| @ComponentScan | 组件扫描,可自动发现和装配一些Bean |
| @Component、@Service、@Repository | 把当前标注的类注入到IOC容器中,需要@ComponentScan配置注解标注类路径,各个注解实现结果一致,只是应用场景不同,属于语义话注解 |
- 其它常用注解
- lombok注解
| 注解名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Data | 注解在类上;提供类所有属性的 getting 和 setting 方法,此外还提供了equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString 方法 |
| @Setter / @Gette r | 注解在属性上;为属性提供 setting 方法/getting方法 |
| @Log4j2 / @Slf4j | 注解在类上;为类提供一个 属性名为log 的 log4j 日志对象,和@Log4j注解类似 |
| @NoArgsConstructor / @AllArgsConstructor | 注解在类上;为类提供一个无参/有参的构造方法 |
| @EqualsAndHashCode | 默认情况下,会使用所有非瞬态(non-transient)和非静态(non-static)字段来生成equals和hascode方法,也可以指定具体使用哪些属性。 |
| @toString | 生成toString方法,默认情况下,会输出类名、所有属性,属性会按照顺序输出,以逗号分割 |
| @Builder | 被注解的类加个构造者模式 |
| @NonNull | 如果给参数加个这个注解 参数为null会抛出空指针异常 |
| @Value | 注解和@Data类似,区别在于它会把所有成员变量默认定义为private final修饰,并且不会生成set方法 |
| @Synchronized | 加个同步锁 |
- jackson注解
| 注解名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @JsonNaming | 字段命名映射策略: KebabCaseStrategy: 肉串策略 - 单词小写,使用连字符’-‘连接,SnakeCaseStrategy: 蛇形策略 - 单词小写,使用下划线’_'连接;UpperCamelCaseStrategy: 驼峰策略 - 单词首字母大写其它小写,不添加连接符 |
| @JsonIgnoreProperties | 类注解,指定序列化时忽略这些属性,可以用于覆盖超类中默认输出的属性 |
| @JsonInclude | 仅在属性不为空时序列化此字段,对于字符串,即null或空字符串 |
| @JsonIgnore | 字段注解,序列化时忽略此字段 |
| @JsonProperty | 指定序列化时的字段名,默认使用属性名 |
| @JsonFormat | 指定Date类字段序列化时的格式,java8 LocalDateTime序列号需要加入jsr310解析包 |
| @JsonUnwrapped | 把成员对象中的属性提升到其容器类,并添加给定的前缀,比如上例中: User类中有name和age两个属性,不使用此注解则序列化为:… “user”: { “name”: “xxx”, “age”: 22 } …使用此注解则为:… “user_name”: “xxx”, “user_age”: 22, |
| @JsonIgnoreType | 类注解,序列化时忽略此类 |
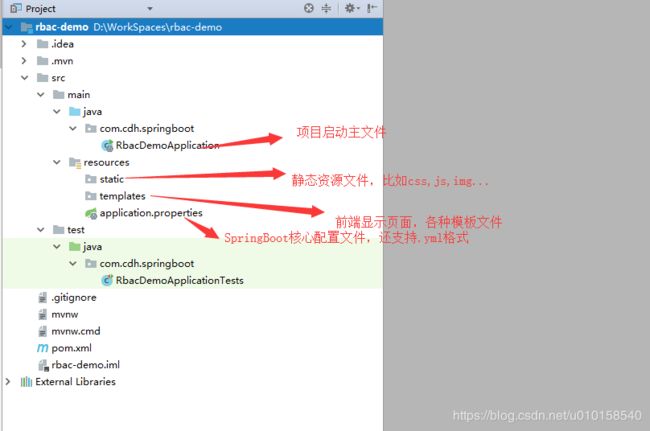
使用IDEA工具快速构建SpringBoot入门案例
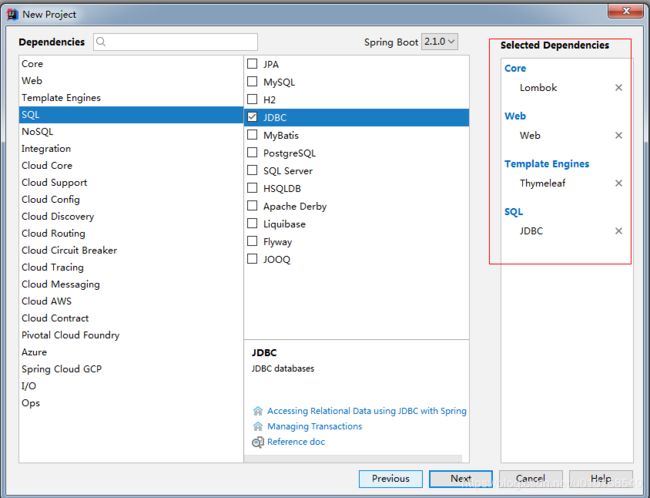
主要目的就是了解Spring的使用原理,以及它的Java替代XML配置的写法,比如拦截器,异常处理,数据源注入,MyBatis配置信息等处理。这里使用的IDEA使用2017.3.5这个版本。
pom.xml文件和之前的springMVC中的略有差异,使用了很多SpringBoot提供的继承配置,直接在parent包中查找,大部分是不用提供版本号的。具体如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cdh.springbootgroupId>
<artifactId>rbac-demoartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<name>rbac-demoname>
<description>description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.0.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.freemarkergroupId>
<artifactId>freemarkerartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.12version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pengglegroupId>
<artifactId>kaptchaartifactId>
<version>2.3.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.belerwebgroupId>
<artifactId>pinyin4jartifactId>
<version>2.5.1version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
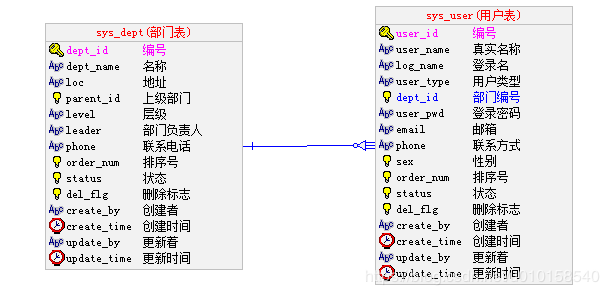
在数据库中创建两张表,用于测试
创建表可以直接使用SQL语句完成,也可以直接在数据库UI工具中完成,当然比较建议大家使用建模工具,这样不仅可以提高建表速度,也可以提高对工具的熟练度,不要觉得麻烦,这是必须要掌握的,常用的建模工具有Power Designer和EZDML,我经常用的是后者,如果要学习它,可以查看我博客中有一篇是介绍这个工具的使用表设计工具EZDML使用详细教程
表结构和字段说明如下:
SQL脚本:
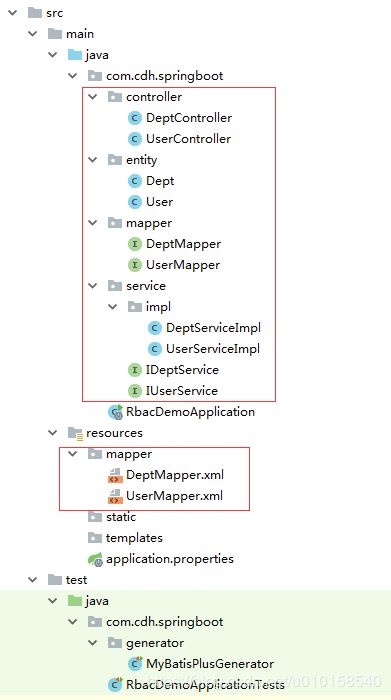
使用MybatisPlus 的代码生成器获取所需文件
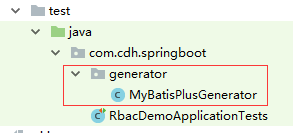
AutoGenerator 是 MyBatis-Plus 的代码生成器,通过 AutoGenerator 可以快速生成 Entity、Mapper、Mapper XML、Service、Controller 等各个模块的代码,极大的提升了开发效率。而要完成这一功能,只需要提供一个Java 可运行方法即可。文件结构如下:
-- sys_dept
/*
警告: 字段名可能非法 - status
*/
create table `sys_dept`(
`dept_id` INT auto_increment primary key not null comment '编号',
`dept_name` VARCHAR(25) comment '名称',
`loc` VARCHAR(300) comment '地址',
`parent_id` INT comment '上级部门',
`level` VARCHAR(64) comment '层级',
`leader` VARCHAR(16) comment '部门负责人',
`phone` VARCHAR(16) comment '联系电话',
`order_num` INT(4) comment '排序号',
`status` INT(1) comment '状态',
`del_flg` INT(1) comment '删除标志',
`create_by` VARCHAR(64) comment '创建者',
`create_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT 0 comment '创建时间',
`update_by` VARCHAR(64) comment '更新着',
`update_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP comment '更新时间'
);
alter table `sys_dept` comment= '部门表';
-- sys_user
/*
警告: 字段名可能非法 - status
*/
create table `sys_user`(
`user_id` INT auto_increment primary key not null comment '编号',
`user_name` VARCHAR(32) comment '真实名称',
`log_name` VARCHAR(32) comment '登录名',
`user_type` VARCHAR(8) comment '用户类型 系统用户,临时用户',
`dept_id` INT comment '部门编号',
`user_pwd` VARCHAR(64) comment '登录密码',
`email` VARCHAR(32) comment '邮箱',
`phone` VARCHAR(14) comment '联系方式',
`sex` INT(1) comment '性别',
`order_num` INT(4) comment '排序号',
`status` INT(1) comment '状态',
`del_flg` INT(1) comment '删除标志',
`create_by` VARCHAR(64) comment '创建者',
`create_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT 0 comment '创建时间',
`update_by` VARCHAR(64) comment '更新者',
`update_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP comment '更新时间'
);
alter table `sys_user` comment= '用户表';
alter table `sys_user` add constraint `FK_sys_user_dept_id` foreign key (`dept_id`) references `sys_dept`(`dept_id`);
需要注意的是在MySQL5.7之前的版本在同一张表中写入两个日期字段必须有一个default 0否则无法执行.
MyBatisPlusGenerator.java文件信息
package com.cdh.springboot.generator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.StringPool;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.AutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.InjectionConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.*;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.po.TableInfo;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.rules.NamingStrategy;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.engine.FreemarkerTemplateEngine;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyBatisPlusGenerator {
@Test
public void codeGenerator() {
// 代码生成器
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
// 全局配置
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
gc.setOutputDir(projectPath + "/src/main/java");
gc.setAuthor("CDHong");//Mapper,Service类注解中显示创建人信息
//gc.setBaseColumnList(true); //在Mapper.xml文件中是否生成公用SQL代码段
//gc.setBaseResultMap(true); //在Mapper.xml文件中是否生成公用返回集合ResultMap
gc.setOpen(false); //文件生成完毕后,是否需要打开所在路径
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
// 数据源配置
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dsc.setUsername("root");
dsc.setPassword("root");
mpg.setDataSource(dsc);
// 包配置
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
pc.setParent("com.cdh.springboot"); //父级公用包名,就是自动生成的文件放在项目路径下的那个包中
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc);
// 自定义配置
InjectionConfig cfg = new InjectionConfig() {
@Override
public void initMap() {
// to do nothing
}
};
List<FileOutConfig> focList = new ArrayList<>();
focList.add(new FileOutConfig("/templates/mapper.xml.ftl") {
@Override
public String outputFile(TableInfo tableInfo) {
// 自定义Mapper.xml文件存放的路径
return projectPath + "/src/main/resources/mapper/"
+ tableInfo.getEntityName() + "Mapper" + StringPool.DOT_XML;
}
});
cfg.setFileOutConfigList(focList);
mpg.setCfg(cfg);
mpg.setTemplate(new TemplateConfig().setXml(null));
// 策略配置
StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig();
strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel); //Entity文件名称命名规范
strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel); //Entity字段名称
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true); //是否使用lombok完成Entity实体标注Getting Setting ToString 方法
//strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true); //Controller注解使用是否RestController标注,否则是否开启使用Controller标注
strategy.entityTableFieldAnnotationEnable(true); //是否在Entity属性上通过注解完成对数据库字段的映射
strategy.setControllerMappingHyphenStyle(true); //Controller注解名称,不使用驼峰,使用连字符
strategy.setTablePrefix("sys_"); //表前缀,添加该表示,则生成的实体,不会有表前缀,比如sys_dept 生成就是Dept
//strategy.setFieldPrefix("sys_"); //字段前缀
mpg.setStrategy(strategy);
mpg.setTemplateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine());
mpg.execute();
}
}
SpringBoot启动类
SpringBoot启动类就是用于项目的启动,而启动方式是使用java的applications方式启动,即在包根目录下添加启动类,必须包含main方法,再添加Spring Boot启动方法:
- SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args);
- new SpringApplicationBuilder().run(args);
不再使用之间的Tomcat部署,war包启动。简化了我们项目部署的步骤。文件内容如下:
package com.cdh.springboot;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
//这是一个组合注解,包含了@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan。
//@Configuration : 标识这为一个配置文件类型,可以通过@Bean注解来标注配置文件中的Bean对象
//@EnableAutoConfiguration : 能够自动配置spring的上下文,试图猜测和配置你想要的bean类,通常会自动根据你的类路径和你的bean定义自动配置。
//@ComponentScan : 会自动扫描指定包下的全部标有@Component的类,并注册成bean,当然包括@Component下的子注解@Service,@Repository,@Controller。
// 前提是标注的类是当前类的子孙包中。
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.cdh.springboot.mapper") //扫描自定义的Mapper接口,并注入对应的SqlSession实例
public class RbacDemoApplication {
//SpringBoot的启动方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RbacDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
集成配置MyBatisPlus以及数据源
在SpringMVC中数据源配置和MyBatis相关配置都是在xml中进行的,而SpringBoot中不推荐这么写,且大部分功能都通过自动配置完成了,极少部分需要手动配置,那么这些配置都是通过Java+Annotation的方式来完成的。
新建一个包(config)用于后续的其他配置(拦截器,异常…)在这个包中创建一个MyBatisPlusConfig类用于Druid数据源和MP的分页注入:
package com.cdh.springboot.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.PaginationInterceptor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration //标注它是一个配置类,类似于新建一个spring的xml配置文件
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
/**
* Druid数据源配置
* @return
*/
@Bean("druidDataSource") //标注这是一个Bean对象,并取一个特有的名字,避免冲突
@Primary //如果在IOC容器中找到相同类型的Bean对象,则优先使用这个
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid") //读取核心配置文件application.properties中前缀是spring.datasource.druid的数据注入到当前Bean中
//注意配置文件中的key值需要和DataSource中对应的set方法名称一致,注意不是属性值,是set方法
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
/**
* 注册一个Servlet ,把Druid提供的监控Servlet注册进去,并提供一个访问路径,用户名和密码
* 当前自定义Servlet的注册方式一致,你也可以在web.xml中配置,只是SpringBoot项目中不建议这么做
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean druidStatViewServlet(){
//监控界面Servlet的访问设置,访问路劲为根目录下的/druid/**,Druid数据源提供了一套显示页面,StatViewServlet,只需要注入即可,
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistration = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(),"/druid/*");
//添加Servlet的初始值,访问这个监控界面的用户名和密码,如果不配置,则默认不需要密码,不显示登录界面
servletRegistration.addInitParameter(ResourceServlet.PARAM_NAME_USERNAME,"admin");
servletRegistration.addInitParameter(ResourceServlet.PARAM_NAME_PASSWORD,"admin");
return servletRegistration;
}
/**
* 过滤器注册,需要配置Druid监控器需要监控的请求和操作
* 配置一下过滤规则,让静态资源和它自己的视图界面不拦截
* @return
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean druidStatFilter(){
//那些信息要监控,需要定义该过滤器来进行拦截,Druid是数据源,当然只拦截请求操作了,静态资源需要放行
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistration = new FilterRegistrationBean(new WebStatFilter());
//过滤器拦截路径
filterRegistration.addUrlPatterns("/*");
//不拦截的请求
filterRegistration.addInitParameter(WebStatFilter.PARAM_NAME_EXCLUSIONS,"*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*");
return filterRegistration;
}
/**
* MyBatisPlus分页插件启用,比较简单,只需要实例化即可
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor(){
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
}
SpringBoot核心配置文件
添加一些Druid数据源冬天配置新和MyBatisPlus的相关配置信息,这些动态信息可以直接在SpringBoot的核心配置文件中application.properites中配置,在java文件中通过@Value(key)注解注入单个值,或 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “spring.datasource.druid”)注入多个值。
#durid 数据源配置 特别注意 常规的4个字符串连接的名字,必须符合DruidDataSource的命名规则,注意是set方法,不是字段名称,比如url
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#####自定义的配置信息,即SpringBoot中没有提供的配置,是我们自己额外提供的动态配置信息###########
spring.datasource.druid.username=root
spring.datasource.druid.password=root
spring.datasource.druid.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8
# 初始化大小,最小,最大
spring.datasource.druid.initialSize=5
spring.datasource.druid.minIdle=2
spring.datasource.druid.maxActive=20
# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间
spring.datasource.druid.maxWait=60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
spring.datasource.druid.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=60000
spring.datasource.druid.dbType=mysql
# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
spring.datasource.druid.filters=stat,wall
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能(参数不同的sql合并统计)、慢SQL记录(执行时间长的sql)
spring.datasource.druid.connectionProperties=druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
#############################SpringBoot内置的配置信息,它会自动读取注入
#mybatisplus配置
mybatis-plus.mapper-locations=mapper/*.xml
mybatis-plus.configuration.use-column-label=true
mybatis-plus.configuration.auto-mapping-behavior=full
mybatis-plus.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#配置SpringBoot默认的日志环境,开启打印SQL语句的Debug模式,语法:logging.level.<mapper所在包名>=debug
logging.level.com.cdh.springboot.mapper=debug
#Tomcat端口号 默认是8080端口
server.port=80
整合测试
到此整合基本完毕,我们通过启动项目访问数据源的监控页面,确认我们配置的监控没有问题,还可以通过数据源配置信息的显示来查看我们注入的druid是否成功。即核心配置文件中的信息生效没有。
- 运行SpringBoot启动类查看打印信息
- 访问localhost/druid/ 来打开监控界面,并查看数据源配置信息

在浏览器上输入localhost/durid/进入数据源监控界面,因为我们配置了登录名和密码,所以会被拦截器,需要登录才能正常方法,如果没有配置则可以直接进入,不用登录。
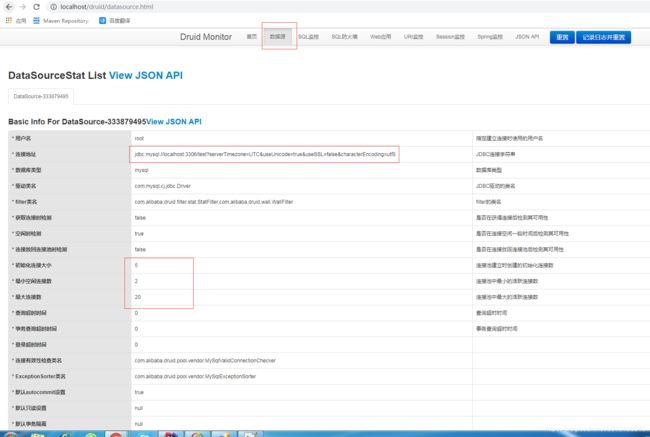
输入正确的用户名和密码,我们就可以进入到监控界面如下,可以查看到我们在核心配置文件中配置的信息生效了。到此整合就完毕了。
MyBatisPlus 封装的CRUD接口
MyBatisPlus为我们封装了一套CRUD接口,提供了我们常用的方法及实现,不仅仅是Mapper接口,还有Service接口和实现以及封装了一个条件构造器,为我们的简单条件提供了便利,具体情况可以通过官网去了解,在这里我就简单罗列一下:
Mapper CRUD 接口
说明:
通用 CRUD 封装BaseMapper接口,为 Mybatis-Plus 启动时自动解析实体表关系映射转换为 Mybatis 内部对象注>入容器
泛型 T 为任意实体对象
参数 Serializable 为任意类型主键 Mybatis-Plus 不推荐使用复合主键约定每一张表都有自己的唯一 id 主键
对象 Wrapper 为 条件构造器
| Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 | Mapper接口 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| insert | deleteById | deleteByMap | delete | deleteBatchIds | updateById | update | selectById | selectBatchIds |
| selectByMap | selectOne | selectCount | selectList | selectMaps | selectObjs | selectPage | selectMapsPage |
Service CRUD 接口
说明:
通用 Service CRUD 封装IService接口,进一步封装 CRUD 采用 get 查询单行 remove 删除 list
查询集合 page 分页 前缀命名方式区分 Mapper 层避免混淆, 泛型 T 为任意实体对象 建议如果存在自定义通用 Service
方法的可能,请创建自己的 IBaseService 继承 Mybatis-Plus 提供的基类 对象 Wrapper 为 条件构造器
| Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 | Service接口 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| save | saveBatch | saveOrUpdateBatch | removeById | removeByMap | remove | removeByIds | updateById | update |
| updateBatchById | saveOrUpdate | getById | listByIds | listByMap | getOne | getMap | getObj | count |
| list | page | listMaps | listObjs | pageMaps |
条件构造器
QueryWrapper(LambdaQueryWrapper) 和 UpdateWrapper(LambdaUpdateWrapper) 的父类
用于生成 sql 的 where 条件, entity 属性也用于生成 sql 的 where 条件,特别注意的是,因为是直接应用于SQL,所以它们其中使用的参数key都是数据库中表的字段名称,和实体属性没有关系。
| 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 | 条件方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| allEq | eq | ne | gt | ge | lt | le | between | notBetween |
| like | notLike | likeLeft | likeRight | isNull | isNotNull | in | notIn | inSql |
| notInSql | groupBy | orderByAsc | orderByDesc | orderBy | having | or | and | last |
- QueryWrapper对象特有的方法:select
- UpdateWrapper对象特有的方法:set , setSql
使用SpringBootTest熟悉一下MyBatisPlus提供的CRUD接口
SpringBootTest的使用方式和之前的spring-test+junit的模式差不多,只需要在测试类上配置如下几个点:
- 在类上添加第一个注解: @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
- 在类上添加第二个注解: @SpringBootTest
- 在需要测试的方法上添加@Test即可,需要注意的是,测试的方法必须是
public void开头的 - 如果需要注入对象在类中直接使用@Autowired 或 @Resource 放在对应的字段上即可
package com.cdh.springboot;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RbacDemoApplicationTests {
@Resource
private IDeptService deptService; //这里可以使用接口类型接收(多态),也可以使用实现类接收。
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
}
}
接下来我们测试几个常见的方法
- 添加一个 ,代码如下:
@Test
public void saveDeptTest() {
//给Dept实体类添加lombok的@Builder注解,就可以使用如下的方式构建对象
Dept dept = Dept.builder().deptName("科技部").loc("广州").parentId(0).level("0").phone("12345678901")
.orderNum(1).status(0).delFlg(0).createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).build();
boolean flg = deptService.save(dept);
System.out.println(flg);
}
- 添加多个,代码如下
@Test
public void saveBatchDeptTest(){
Dept dept1 = Dept.builder().deptName("科技部1").loc("广州1").parentId(1).level("0").phone("12345678901").orderNum(1).status(0).delFlg(0).createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).build();
Dept dept2 = Dept.builder().deptName("科技部2").loc("广州2").parentId(1).level("0.1").phone("12345677701").orderNum(2).status(0).delFlg(0).createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).build();
Dept dept3 = Dept.builder().deptName("科技部3").loc("广州3").parentId(1).level("0.2").phone("12345668901").orderNum(3).status(0).delFlg(0).createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).build();
List<Dept> list = Arrays.asList(dept1,dept2,dept3);
boolean flg = deptService.saveBatch(list);
//这里使用日志打印,在要打印的类上添加lombok注解@Slf4j,它会提供一个log对象,我们就可以使用它打印统一样式的日志信息了
log.info("添加多个部门,结果为:{}",flg);
}
@Test
public void delByIdTest(){
boolean flg = deptService.removeById(1);
log.info("删除1号部门,执行结果为:{}",flg);
}
- 根据ids删除,代码如下:
@Test
public void delByIdsTest(){
List<Integer> ids = Arrays.asList(4, 5);
boolean flg = deptService.removeByIds(ids);
log.info("删除多个部门,执行结果为:{}",flg);
}
- 根据id修改,代码如下:
@Test
public void updateById(){
Dept dept = Dept.builder().deptId(1).deptName("市场部").build();
boolean flg = deptService.updateById(dept);
log.info("修改部门,执行结果为:{}",flg);
}
- 查询所有,代码如下:
@Test
public void findAll(){
//查询所有,注意需要添加有参构造和无参构造 @AllArgsConstructor , @NoArgsConstructor
List<Dept> list = deptService.list();
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
- 根据id查询,代码如下:
@Test
public void findById(){
Dept dept = deptService.getById(7);
log.info(dept.toString());
}
- 根据自定义条件查询,代码如下:
@Test
public void findByInfo(){
//自定义查询条件,这个时候就需要使用MyBatisPlus提供的条件构造器QueryWrapper了
//条件如下loc like '广州%' and status = 0 and create_time between '2018-11-28 02:02:20' and '2018-11-28 02:05:15' order by dept_id
Map<String,Object> where = new HashMap<>();
where.put("status",0);
QueryWrapper<Dept> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.likeRight("loc","广州")
.eq("status",0)
.between("create_time","2018-11-28 02:02:20","2018-11-28 02:05:15")
.orderByAsc("dept_id");
List<Dept> list = deptService.list(queryWrapper);
list.forEach(dept -> log.info(dept.toString()));
}
- 分页查询,代码如下:
@Test
public void page(){
Page<Dept> page = new Page<>(1,3); //current:页码 , size:每页显示的条数
QueryWrapper<Dept> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("loc","广州").orderByAsc("dept_id");
IPage<Dept> pageInfo = deptService.page(page, queryWrapper);
log.info("总条数:{}",pageInfo.getTotal());
log.info("显示数据:{}:",pageInfo.getRecords());
log.info("页码:{}",page.getCurrent());
log.info("每页显示的条数:{}",page.getSize());
}
- 多表带条件分页查询 ,多表查询需要自定义SQL,也就是需要在Mapper映射文件中添加自己的需求,这个时候需要自定映射实体,也就是经常所见的VO。我们先添加一个员工,外键关联部门表,然后查询该员工对应的部门信息。
添加多个员工:
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
@Test
public void saveBatch(){
//给User实体添加三个注解@NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder
User user1 = User.builder().userName("admin").userPwd("admin").createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).deptId(7).build();
User user2 = User.builder().userName("zhangsan").userPwd("zhangsan").createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).deptId(8).build();
User user3 = User.builder().userName("lis").userPwd("lisi").createTime(LocalDateTime.now()).deptId(9).build();
List<User> users = Arrays.asList(user1,user2,user3);
boolean flg = userService.saveBatch(users);
log.info("添加多个员工,执行结果为:{}",flg);
}
在entity包中添加一个vo包,在该包下添加一个UserDeptVO类,定义要获取的信息字段。如下:
import lombok.Data;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
public class UserDeptVO {
private Integer userId;
private String userName;
private Integer deptId;
private String deptName;
private String loc;
private String level;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
}
在UserMapper中添加两个接口,一个查询员工详细信息,一个带条件的分页查询。
package com.cdh.springboot.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.metadata.IPage;
import com.cdh.springboot.entity.User;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.cdh.springboot.entity.vo.UserDeptVO;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* 用户表 Mapper 接口
*
*
* @author CDHong
* @since 2018-11-27
*/
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
UserDeptVO findByUserId(Integer userId);
/**
* 分页查询一定要添加IPage作为参数,传入页码和每页显示的条数
* @param page
* @param vo 查询的条件
* @return
*/
List<UserDeptVO> userPage(IPage<UserDeptVO> page,@Param("vo") UserDeptVO vo);
}
Mapper.xml中SQL映射信息如下;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.cdh.springboot.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="findByUserId" resultType="com.cdh.springboot.entity.vo.UserDeptVO">
SELECT user_id,user_name,d.dept_id,dept_name,loc,level,u.create_time user_create_time
FROM sys_user u
JOIN sys_dept d ON u.dept_id = d.dept_id WHERE user_id = #{userId}
</select>
<select id="userPage" resultType="com.cdh.springboot.entity.vo.UserDeptVO">
SELECT user_id,user_name,d.dept_id,dept_name,loc,level,u.create_time user_create_time
FROM sys_user u
JOIN sys_dept d ON u.dept_id = d.dept_id
<where>
<if test="vo!=null">
<if test="vo.userId!=null"> AND user_id = #{vo.userId}</if>
<if test="vo.userName!=null"> AND user_name like '%${vo.userName}%' </if>
<if test="vo.deptId!=null"> AND d.dept_id = #{vo.deptId} </if>
<if test="vo.deptName!=null"> AND dept_name like '${vo.deptName}' </if>
<if test="vo.loc!=null"> AND d.loc like '${vo.loc}' </if>
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
IUserService接口中添加一个查询方法,基本上和UserMapper接口中的方法一致,你可以直接粘贴复制过去,这里就不在提供代码了,接着在UserServiceImp实现类中完成接口的实现,这里需要注入UserMapper的实例,注意这里想要获取到UserMapper实例,需要在SpringBoot的启动类中添加注解扫描Mapper接口(
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.cdh.springboot.mapper")),否则会报找不到对应的方法`
package com.cdh.springboot.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.metadata.IPage;
import com.cdh.springboot.entity.User;
import com.cdh.springboot.entity.vo.UserDeptVO;
import com.cdh.springboot.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.cdh.springboot.service.IUserService;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* 用户表 服务实现类
*
*
* @author CDHong
* @since 2018-11-27
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements IUserService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDeptVO findById(Integer userId) {
return userMapper.findByUserId(userId);
}
@Override
public List<UserDeptVO> userPage(IPage<UserDeptVO> page, UserDeptVO vo) {
return userMapper.userPage(page,vo);
}
}
Junit测试,根据ID获取对应的多表数据
@Test
public void findUserAndDeptByUserId(){
UserDeptVO userDeptVO = userService.findById(2);
log.info(userDeptVO.toString());
}
@Test
public void userPage(){
UserDeptVO vo = new UserDeptVO();
vo.setDeptName("科技部");
vo.setUserName("m");
Page<UserDeptVO> page = new Page<>(1,3);
List<UserDeptVO> list = userService.userPage(page, vo);
log.info("总条数:{}",page.getTotal());
list.forEach(userDeptVO -> log.info(userDeptVO.toString()));
}
接下来是把我们写好的方法通过Thymeleaf模板进行数据展示。
Thymeleaf模板引擎简单入门
SpringBoot建议使用模板引擎Thymeleaf替代JSP的操作,Thymeleaf是面向Web和独立环境的现代服务器端Java模板引擎,能够处理HTML,XML,JavaScript,CSS甚至纯文本。
Thymeleaf的主要目标是提供一个优雅和高度可维护的创建模板的方式。为了实现这一点,它建立在自然模板的概念上,将其逻辑注入到模板文件中,不会影响模板被用作设计原型。这改善了设计的沟通,弥合了设计和开发团队之间的差距。也就是可以动态更改路径和数据。
注意在SpringBoot中Thymeleaf是开箱即用的,不需要做什么配置,当然如果你有其他需求,也可以更改默认配置,直接在SpringBoot的核心配置文件中写入对应的键值对即可。
- SpringBoot中 Thymeleaf常见配置项:
# Thymeleaf模板引擎配置
#开启模板缓存(默认值:true)
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true
#在呈现模板之前检查模板是否存在
spring.thymeleaf.check-template=true
#检查模板位置是否正确(默认值:true)
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true
#Content-Type的值(默认值:text/html)
spring.thymeleaf.servlet.content-type=text/html
#开启MVC Thymeleaf视图解析(默认值:true)
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true
#模板编码
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
#要被排除在解析之外的视图名称列表,用逗号分隔
spring.thymeleaf.excluded-view-names=
#在构建URL时添加到视图名称前的前缀(默认值:classpath:/templates/)
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
#在构建URL时添加到视图名称后的后缀(默认值:.html)
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
#可解析的视图名称列表,用逗号分隔
spring.thymeleaf.view-names=
- Thymeleaf使用详情:
Thymeleaf模板引擎使用其实功能和JSP差不多,都是在静态页面对后台作用域中的数据进行相应的处理,替换默认值,逻辑判断,循环遍历,简单表达式计算,路径映射…1. 语法
- 引入静态资源文件: 在html中,资源文件路径是一个头痛的问题,而模板引擎中,只需要使用
@{/url}包裹路径,则代表该路径从项目根目录开始。之前的路径不用删除,它会自动替换。th:href="@{/css/public.css}" - 访问后端作用域数据: 访问model中的数据,和EL表达式一致,
th:attr="class= ${btn.code}", 访问session中的数据需要加上作用域,th:text="${session.currUser.relName}" - 条件判断:在html标签中,加入th:if = 表达式,可以根据条件显示html元素
- 循环迭代:在要循环的标签上添加 th:each 或者单独构建一个块标签:th:block:
- 引入静态资源文件: 在html中,资源文件路径是一个头痛的问题,而模板引擎中,只需要使用
<th:block th:each="job : ${jobs}">
<option th:text="${job.name}" th:value="${job.id}">option>
th:block>
2. 表达式
-
简单表达式 : ${…} 变量表达式 , *{…} 选择变量表达式 , @{…} 链接url表达式
-
字面量表达式: 文本 ->‘one text’ , 数值->5 ,布尔->true ,空值->null ,
-
操作符: 算术运算符,布尔运算符(and,or,!,not),关系运算符(gt , lt , ge , le , eq , ne ,>= , <= , == ),三目运算
-
表达式工具对象:
1. #dates 与java.util.Date对象的方法对应,格式化、日期组件抽取等等
2. #calendars 类似#dates,与java.util.Calendar对象对应
3. #numbers 格式化数字对象的工具方法
4. #strings 与java.lang.String对应的工具方法:contains、startsWith、prepending/appending等等
5. #objects 用于对象的工具方法
6. #bools 用于布尔运算的工具方法
7. #arrays 用于数组的工具方法
8. #lists 用于列表的工具方法
9. #sets 用于set的工具方法
10. #maps 用于map的工具方法
11. #aggregates 用于创建数组或集合的聚合的工具方法
12. #messages 用于在变量表达式内部获取外化消息的工具方法,与#{…}语法获取的方式相同
13. #ids 用于处理可能重复出现(例如,作为遍历的结果)的id属性的工具方法 -
页面操作:
内嵌标记 内嵌标记 内嵌标记 内嵌标记 内嵌标记 内嵌标记 内嵌标记 内嵌标记 th:action th:align th:alt-title th:autocomplete th:cellpadding th:cellspacing th:class th:attr :async th:autofocus th:autoplay th:checked th:disabled th:hidden th:readonly th:required :selected th:each th:classappend th:styleappend th:attrappend 以上写法可能比较怪异,可以使用HTML5友好的属性及元素名来完成操作,
或 ... 条件运算: th.switch 、 th:if 不只运算布尔条件,它对以下情况也运算为true:
- 值不为null , 为boolean且为true ,值为数字且非0 , 值为字符且非0 , 值是字符串且不是:“false”,“off”,“no” , 值不是boolean、数字、字符、字符串 , 如果值为null,则th:if运算结果为false
- th:if的反面是th:unless
<div th:switch="${user.role}"> <p th:case="'admin'">User is an administratorp> <p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a managerp> <p th:case="*">User is some other thingp> div>- 循环遍历: th:each 除了获取对象外,还可以得到获取一些遍历状态,通过指定状态变量iterStat获取:拥有的属性(index ,count,size,current,even,odd,first,last),
若不指定状态变量,Thymeleaf会默认生成一个名为“变量名Stat”的状态变量:
<tr th:each="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'"> <td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd> <td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td> <td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd> tr> <tr th:each="prod : ${prods}" th:class="${prodStat.odd}? 'odd'"> <td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd> <td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td> <td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd> tr>你可能感兴趣的:(SpringBoot,MyBatisPlus)