编程语言分析及其应用
编程语言分析及其应用
本文系编程语言这门课程的第二个实验,主要要求实现以下三个部分:
- Lisp格式到C格式的转换
- Lisp格式表达式的计算
- Lisp格式表达式的类型检测
实现语言:C++
1. Lisp格式到C格式的转换
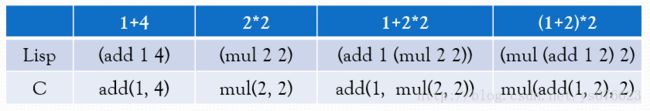
Lisp的函数调用格式为: (函数名 参数1 参数2 … 参数n)
C的函数调用格式为:函数名(参数1, 参数2, …, 参数n)
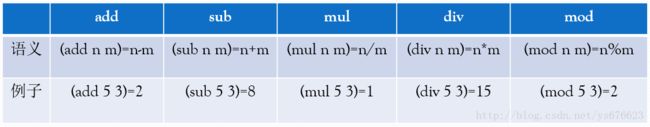
现有五个整数的二元函数add、sub、mul、div、mod和一些使用这些函数的Lisp格式表达式,请实现一个程序转换器,将这些Lisp格式表达式转成C格式的表达式。
2. Lisp格式表达式的计算
Lisp的函数调用格式为: (函数名 参数1 参数2 … 参数n)
现有五个整数的二元函数add、sub、mul、div、mod,请实现一个计算器,计算这些Lisp格式表达式。
请实现一个计算器,计算这些Lisp格式表达式
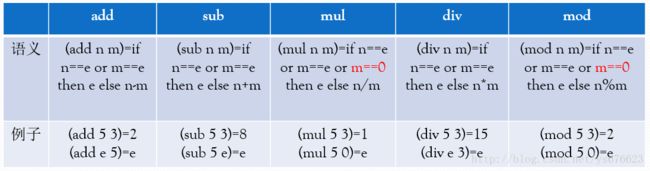
- 扩展前述计算器,使得其能捕获除0的异常
- 语义计算规则如下
3. Lisp格式表达式的类型检测
Lisp的函数调用格式为: (函数名 参数1 参数2 … 参数n)
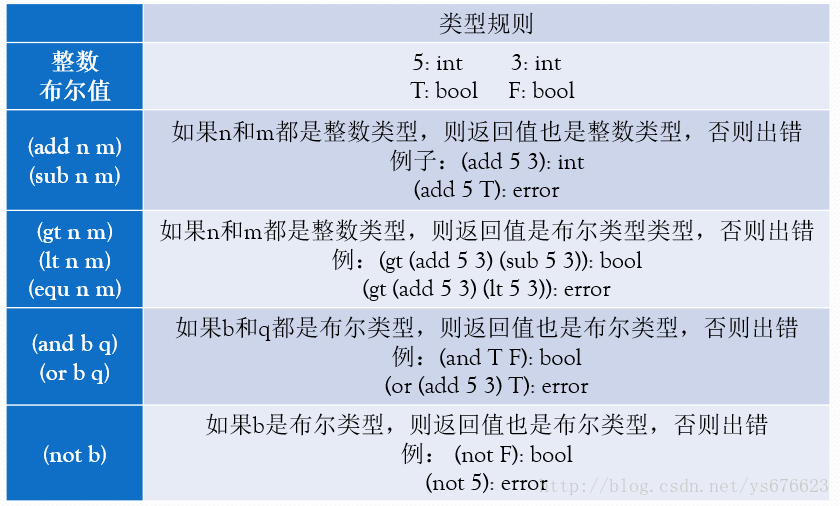
现有两个类型:整数int和布尔类型bool,以及五个整数的二元函数add、sub、gt、lt、equ和三个布尔值的函数and、or、not,请实现一个类型检测器,并检测这些Lisp格式表达式。
请实现一个类型检测器,并检测这些Lisp格式表达式
解决过程
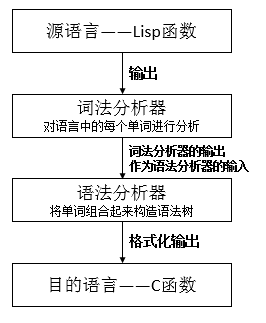
可利用如下所示的结构,对该Lisp语言函数格式进行解析:
任务一:Lisp格式到C格式的转换
1.【词法分析器的构造】:即一个DFA,用于分析输入的字符串,将其拆分为逐个的单词、接着使用自顶向下的语法分析思想构建一个语法树。最后使用C格式将其输出。
2.下边进行程序的编写,通过函数getToken来实现一个DFA,用于词法分析,具体的实现代码如下所示。
void getToken() {
NodeKind currentKind;
StateType state = START;
bool save;
currentToken = "";
while (state != DONE) {
if (pos == str.length()) { currentTokenType = ENDFILE; break; }
int c = str[pos++];
save = true;
switch (state) {
case START:
if (isdigit(c)) { state = INNUM; currentKind = NumK; }
else if (isalpha(c)) { state = INID; currentKind = OpK; }
else if (c == ' ' || c == '(' || c == ')') continue;
case INNUM:
if (c == ' ' || c == ')') { state = DONE; save = false; }
break;
case INID:
if (c == ' ' || c == ')') { state = DONE; save = false; }
break;
case DONE:
default:
break;
}
if (save) { currentToken += (char)c; }
if (state == DONE) {
if (currentKind == OpK) currentTokenType = reservedLookup(currentToken);
if (currentKind == NumK) currentTokenType = NUM;
}
}
}
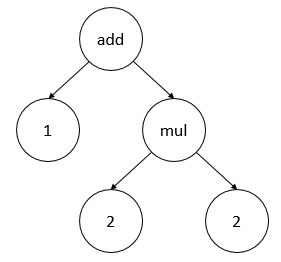
3.【语法分析器的实现】:例如Lisp格式“(add 1 (mul 2 2))”词法分析之后构建语法树,会得到一颗二叉树,如下图所示。
4.下边进行程序的编写,通过函数parse来实现语法分析,利用函数getToken生成的单词来构建语法树。
TreeNode * parse() {
TreeNode * t = NULL;
if (currentTokenType != ENDFILE) {
t = new TreeNode();
t->nodekind = currentTokenType;
t->str = currentToken;
}
getToken();
if (currentTokenType != ENDFILE) {
TreeNode * p = NULL;
if (currentTokenType == NUM) {
p = new TreeNode();
p->nodekind = currentTokenType;
p->value = atoi(currentToken.c_str());
}
else if (currentTokenType == ERROR) {
p = new TreeNode();
p->nodekind = currentTokenType;
p->str = currentToken;
}
else { p = parse(); }
t->child[0] = p;
}
getToken();
if (currentTokenType != ENDFILE) {
TreeNode * p = NULL;
if (currentTokenType == NUM) {
p = new TreeNode();
p->nodekind = currentTokenType;
p->value = atoi(currentToken.c_str());
}
else if (currentTokenType == ERROR) {
p = new TreeNode();
p->nodekind = currentTokenType;
p->str = currentToken;
}
else { p = parse(); }
t->child[1] = p;
}
return t;
}
5.最后,利用函数printTree来按照C格式将语法树进行输出。
void printTree(TreeNode * tree) {
if (tree->nodekind == NUM) { cout << tree->value; }
else if (tree->nodekind == ERROR) { cout << tree->str; }
else { cout << tree->str << "("; }
if (tree->child[0] != NULL) { printTree(tree->child[0]); cout << ", "; }
if (tree->child[1] != NULL) { printTree(tree->child[1]); cout << ")"; }
}
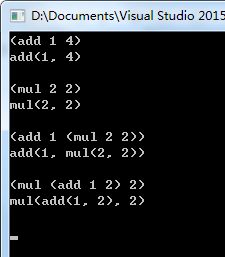
6.测试程序,得到的运行结果如下图所示。
任务二:Lisp格式表达式的计算
7.
词法分析、语法分析部分代码如上所示。
- 针对父节点的类型(比如“add”),对两个子节点执行相应的操作(将两个子节点的数值加起来)。如果子节点是一个操作,则递归调用该计算函数。
具体的代码实现如下所示。
int Calculate(TreeNode * tree) {
if (tree->nodekind == NUM) { return tree->value; }
else if (tree->nodekind == ERROR) { isDigit = false; return NULL; }
else {
int a, b, c;
a = Calculate(tree->child[0]);
b = Calculate(tree->child[1]);
switch (tree->nodekind) {
case ADD: c = a + b; break;
case SUB: c = a - b; break;
case MUL: c = a * b; break;
case DIV: if (b == 0) { isDigit = false; return NULL; } c = a / b; break;
case MOD: if (b == 0) { isDigit = false; return NULL; } c = a % b; break;
}
return c;
}
}
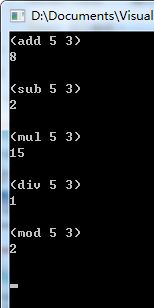
8.对程序进行测试,可以得到如下图所示的运行结果。
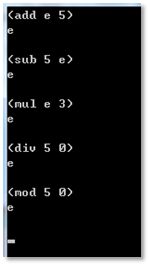
9.以上的程序可以正常捕获一些异常情况,比如除数为0的情况。运行程序进行测试,可以得到如下图所示的结果。
任务三:Lisp格式表达式的类型检测
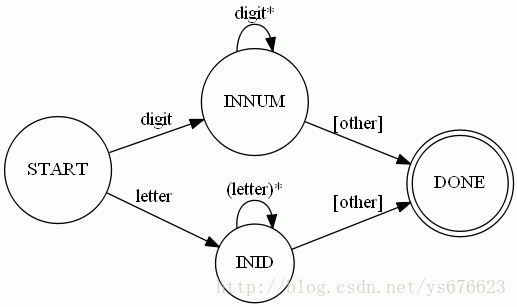
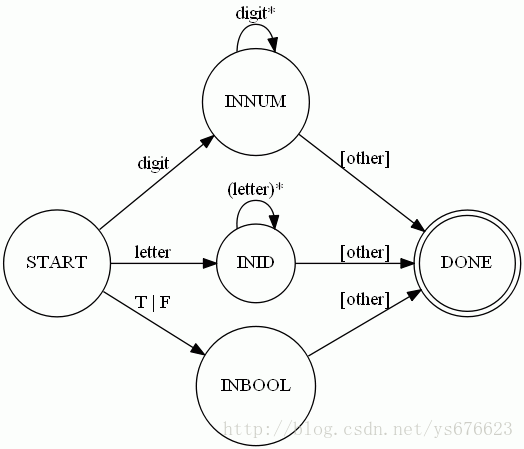
10.【词法分析器的构造】:在任务一的基础上对词法分析器做了一些变动,修改了DFA,给DFA添加了一个“INBOOL”的状态,具体的DFA的结构如下图所示。
11.下边进行程序的编写,具体的实现代码如下所示。
while (state != DONE) {
if (pos == str.length()) { currentTokenType = ENDFILE; break; }
int c = str[pos++];
save = true;
switch (state) {
case START:
if (isdigit(c)) { state = INNUM; currentKind = NumK; }
else if (c == 'T' || c == 'F') { state = INBOOL; currentKind = BoolK; }
else if (isalpha(c)) { state = INID; currentKind = OpK; }
else if (c == ' ' || c == '(' || c == ')') continue;
case INNUM:
if (c == ' ' || c == ')') { state = DONE; save = false; }
break;
case INID:
if (c == ' ' || c == ')') { state = DONE; save = false; }
break;
case INBOOL:
if (c == ' ' || c == ')') { state = DONE; save = false; }
break;
case DONE:
default:
break;
}
if (save) { currentToken += (char)c; }
if (state == DONE) {
if (currentKind == OpK) currentTokenType = reservedLookup(currentToken);
if (currentKind == NumK) currentTokenType = NUM;
if (currentKind == BoolK) currentTokenType = BOOL;
}
}
12.【语法分析器】:仍旧使用任务一中编写的语法分析器来构建语法树(此处为一个二叉树)。文法同任务一,但是“factor”的类型除了数字“number”还要添加“T”和“F”这两个布尔类型。操作数的合法性放到下边的类型检查函数当中去,此处不做检查,故代码整体结构与任务一中的基本一致。
13.【表达式的类型检测】:主要依靠函数typeDetection来进行类型检测。
与任务二中的计算函数类似,此处是只记录类型不计算具体的数值,遇到非法操作的类型,则将“isError”标记为“true”。如果操作数均符合要求,则需记录最外围的操作得到结果的类型。
类型检测函数的具体实现代码如下所示。
void typeDetection(TreeNode * tree) {
if (tree->nodekind == NUM) { isDigit = true; }
else if (tree->nodekind == BOOL) { isBool = true;}
else {
if (tree->child[0] != NULL) { typeDetection(tree->child[0]); }
if (tree->child[1] != NULL) { typeDetection(tree->child[1]); }
switch (tree->nodekind) {
case ADD: if (isBool || isError) { isError = true; } break;
case SUB: if (isBool || isError) { isError = true; } break;
case GT: if (isBool || isError) { isError = true; } else { isBool=true; } break;
case LT: if (isBool || isError) { isError = true; } else { isBool=true; } break;
case EQU: if (isBool || isError) { isError = true; } else { isBool=true; } break;
case AND: if (isDigit || isError) { isError = true; } break;
case OR: if (isDigit || isError) { isError = true; } break;
case NOT: if (isDigit || isError) { isError = true; } break;
}
}
}
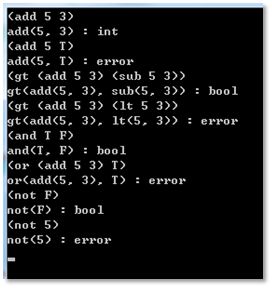
14.对程序进行测试,可以得到如下图所示的测试结果。
15.综合以上,通过使用DFA完成了Lisp语言的词法分析,接着完成了语法分析,成功的构建出了语法树,最后进行语义的解释,成功实现了表达式的计算和表达式的类型检测。
禁止抄袭!!!
最后附上GitHub地址:https://github.com/201419/UniversityCoursework
喜欢的欢迎大家star一下~~