PCL点云(地面点云)分割:Progressive Morphological Filter
背景:
pcl官方教程:
http://www.pointclouds.org/documentation/tutorials/progressive_morphological_filtering.php#progressive-morphological-filtering
论文:http://users.cis.fiu.edu/~chens/PDF/TGRS.pdf
注:
这个算法本身用于处理高空获取的激光雷达数据,把地面与非地面的物体分割,来获取地貌3d地图的。我跑到数据与这类数据有一个明显的区别,就是x,y的范围与z的范围相差不多,而他们的高空数据,z的变化范围相比其他两个轴较小。但是我同样想试试它是否能帮我鲁棒地去除地面的点来达到分割物体和地面的效果。
还有,因为我的数据本来z轴不是对应着向上的方向,我还旋转点云来调整了一下。
1.使用感受
参数多,不看论文细节,无法调参数。如果参数不调好,算法耗时很长。对使用者极度不友好。
2.算法细节(从代码和论文里理解的)
首先根据数据里x, y的范围值,2d栅格化点云所占的空间。每个格子拥有0个或多个点,只是他们的高度(论文里的evaluation)不同。那么对于这个格子,如果0个点,用插值找一个点;如果多个点,把最低的点留下来。所以说,现在,每个格子都拥有一个格子内最低点(这里用lpt(lowest point)替代)。然后,
遍历每一行()
遍历每一个格子()
做一个“开”运算。开运算需要两个输入: 窗口大小(=窗口包括了四周哪几个的格子),以及窗口内lpt的高度合集。
那么开运算是什么呢,后面会解释。
把开运算的结果设置为以这一个格子为中心的“窗口内最低点”的高度值。
如果当前格子的lpt 高于这个“窗口内最低点”到一定程度(高度差距阈值), 这个格子原本包含的所有点(包括lpt)都
是非地面点,而这个"窗口内最低点"替代这个格子的lpt成为新的lpt。(你可以理解为,我先四周找找附近地区的洼点,如果我现在站的位置比这个洼点高了半层楼那么高,那么我这个地方不算是地面,那个洼点替代我的位置成为地面应该所在的位置。否则,我现在这个位置算是地面点)。
end
end
为了使算法里的“窗口内最低点”参考更大范围的局部点云(也就是我四周看的时候看更远一点),算法每运行完上面那个循环,就增大窗口大小和高度阈值一点,然后再运行循环。只要有一个循环里,一个格子的所有点被视为非地面点,那么这些点以后都是非地面点,以后的循环也不用遍历这个格子了。遍历若干次后,有些格子的lpt被窗口内最低点替代成为新的lpt了,有些没有,但它们现在都有它自己的lpt。最后的这些lpt合集就是地面点云。
2.1 开运算(谷歌上找资料自己理解的)
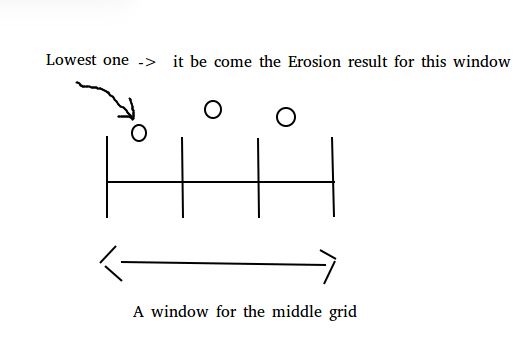
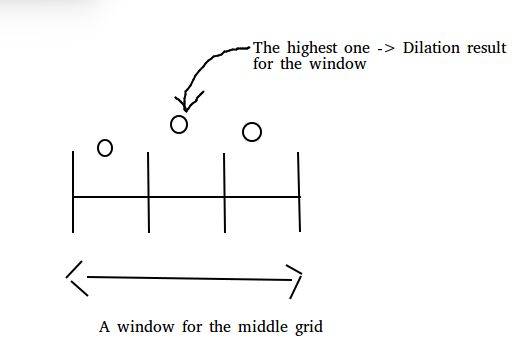
那么,开运算是什么鬼?其实很简单,它先对一整行每一个格子做了一个Erosion操作,用一整行Erosion结果再对做一个Dilation操作,用两幅图说明你就明白。注意,这里的窗口用了一维来方便表示,实际是二维窗口。
等于说,我按顺序地站在每个格子上,四周找找附近最低的位置,如果这个位置就在我脚下,那我什么都不做;如果不是在我脚下,那我所站的位置变成和这个最低的位置一样高度。这是Erosion运算或者说腐蚀运算。
然后在腐蚀运算结果上做反向操作,Dilation稀释运算。我按顺序地站在每个格子上,四周找找附近最高的位置,如果这个位置就在我脚下,那我什么都不做;如果不是在我脚下,那我所站的位置变成和这个最高的位置一样高度。
腐蚀运算好理解,但为什么要做稀释运算,我也不知道。欢迎大家给出意见。
3. 调参
因为不明的原因,算法在我数据上运行时间是半个小时。所以调参研究时间太长,这里不研究。当时为了我本人调参,我把ProgressiveMorphologicalFiltering.cpp的内容抽出来,写成my_pmf这个函数,方便我打印过程的数据。详见底部的代码。my_pmf只需要输入点云,参数都是放在代码上方,都是全局变量。最后生成object.pcd和ground.pcd, 你可以通过运行$ ./pcl_viewer object.pcd ground.pcd。pcl_viewer可执行文件一般被放在了linux系统的usr/bin。
调参也可以参考:
https://github.com/PointCloudLibrary/pcl/blob/master/segmentation/include/pcl/segmentation/progressive_morphological_filter.h4.跑自己的数据集
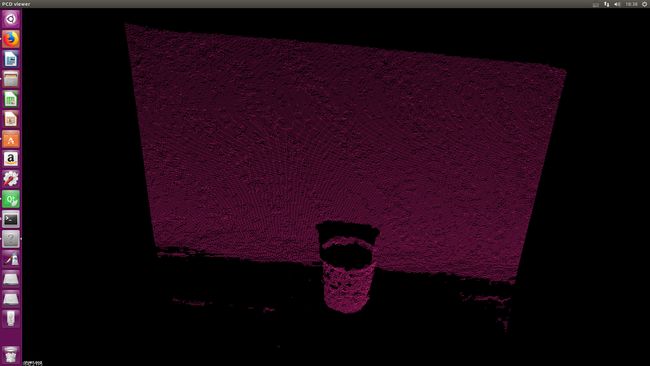
原点云
地面点云:
物体点云:
分割效果还是很好的,就是运行时间长。
5. 总结
很多参数要设置,而且很难设置,参数需要对算法深度理解才能调好。运行时间长,实时性低(即使跑官方的代码和数据集,时间也较长)。算法对地面的分割效果好。
6. 代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define max_window_size 0.05
#define slope 0.7f
#define max_distance 0.1f
#define initial_distance 0.01f
#define cell_size 0.01f
#define base 2.0f
#define exponential true
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr my_pmf (pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_in)
{
// Compute the series of window sizes and height thresholds
std::vector height_thresholds;
std::vector window_sizes;
std::vector ground_indices;
int iteration = 0;
float window_size = 0.0f;
float height_threshold = 0.0f;
while (window_size < max_window_size)
{
// Determine the initial window size.
if (exponential)
window_size = cell_size * (2.0f * std::pow (base, iteration) + 1.0f);
else
window_size = cell_size * (2.0f * (iteration+1) * base + 1.0f);
cout << "window_size " << window_size << endl;
// Calculate the height threshold to be used in the next iteration.
if (iteration == 0)
height_threshold = initial_distance;
else
height_threshold = slope * (window_size - window_sizes[iteration-1]) * cell_size + initial_distance;
cout << "height_threshold " << height_threshold << endl;
// Enforce max distance on height threshold
if (height_threshold > max_distance)
height_threshold = max_distance;
window_sizes.push_back (window_size);
height_thresholds.push_back (height_threshold);
iteration++;
}
// Ground indices are initially limited to those points in the input cloud we
// wish to process
for (int i=0;ipoints.size();i++){
ground_indices.push_back(i);
}
// Progressively filter ground returns using morphological open
for (size_t i = 0; i < window_sizes.size (); ++i)
{
cout<< "Iteration " << i << "height threshold = " << height_thresholds[i] << " window size = " <<
window_sizes[i] << endl;
// Limit filtering to those points currently considered ground returns
typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::copyPointCloud (*cloud_in, ground_indices, *cloud);
// Create new cloud to hold the filtered results. Apply the morphological
// opening operation at the current window size.
typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_f (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::applyMorphologicalOperator (cloud, window_sizes[i], pcl::MORPH_OPEN, *cloud_f);
// Find indices of the points whose difference between the source and
// filtered point clouds is less than the current height threshold.
std::vector pt_indices;
//cout << "ground.size() = " << ground.size() << endl;
for (size_t p_idx = 0; p_idx < ground_indices.size (); ++p_idx)
{
float diff = cloud->points[p_idx].z - cloud_f->points[p_idx].z;
//cout << "diff " << diff << endl;
if (diff < height_thresholds[i])
pt_indices.push_back (ground_indices[p_idx]);
}
// Ground is now limited to pt_indices
ground_indices.swap (pt_indices);
cout << "ground now has " << ground_indices.size () << " points" << endl;
}
typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_out (new pcl::PointCloud);
// Extract cloud_in with ground indices
pcl::copyPointCloud (*cloud_in, ground_indices, *cloud_out);
return cloud_out;
}
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointIndicesPtr ground (new pcl::PointIndices);
// Fill in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
// Replace the path below with the path where you saved your file
reader.read ("test_pcd_from_topview.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud << std::endl;
// Run progressive morphological filter
cloud_filtered = my_pmf(cloud);
std::cerr << "Ground cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud_filtered << std::endl;
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write ("ground.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
// Extract non-ground returns
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
extract.setInputCloud (cloud);
extract.setIndices (ground);
//extract.filter (*cloud_filtered);
extract.setNegative (true);
extract.filter (*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "Object cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud_filtered << std::endl;
writer.write ("object.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
return (0);
}