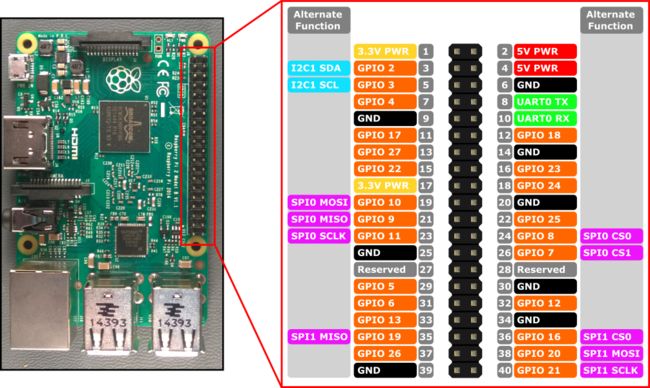
Raspberry Pi2/3引脚介绍
引脚图
Raspberry Pi 3 的硬件接口通过开发板上的 40 排针 J8 公开。功能包括:
- 17x - GPIO 引脚
- 1x - SPI 总线
- 1x - I2C 总线
- 2x - 5V 电源引脚
- 2x - 3.3V 电源引脚
- 8x - 接地引脚
GPIO 引脚
以下 GPIO 引脚可通过 API 访问:
| GPIO | 通电拉 | 排针 |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 上拉 | 7 |
| 5 | 上拉 | 29 |
| 6 | 上拉 | 31 |
| 12 | 下拉 | 32 |
| 13 | 下拉 | 33 |
| 16 | 下拉 | 36 |
| 17 | 下拉 | 11 |
| 18 | 下拉 | 12 |
| 19 | 下拉 | 35 |
| 20 | 下拉 | 38 |
| 21 | 下拉 | 40 |
| 22 | 下拉 | 15 |
| 23 | 下拉 | 16 |
| 24 | 下拉 | 18 |
| 25 | 下拉 | 22 |
| 26 | 下拉 | 37 |
| 27 | 下拉 | 13 |
| 35* | 上拉 | 红色电源 LED |
| 47* | 上拉 | 绿色活动 LED |
* 仅限 Raspberry Pi 2。Raspberry Pi 3 上未提供 GPIO 35 和 47。
使用方法
- 例子一
sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpiot.py
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # set board mode to Broadcom
GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT) # set up pin 17
GPIO.setup(18, GPIO.OUT) # set up pin 18
GPIO.output(17, 1) # turn on pin 17
GPIO.output(18, 1) # turn on pin 18root用户权限启动
sudo python t.py- 例子二: 电机控制PWM
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # set board mode to Broadcom
GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT) # set up pin 17
GPIO.setup(18, GPIO.OUT) # set up pin 18
p = GPIO.PWM(18, 25) # channel=12 frequency=50Hz
p.start(0)
while True:
GPIO.output(17, 0) # turn on pin 17
p.ChangeDutyCycle(25)
time.sleep(0.1)
p.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
串行 UART
RPi2/3 上有一个串行 UART: UART0
Pin 8 - UART0 TX
Pin 10 - UART0 RX
I2C 总线
排针上公开了一个 I2C 控制器 I2C1,带有 SDA 和 SCL 两条线。用于此总线的 1.8KΩ 内部上拉电阻已安装在开发板上。
引脚 3 - I2C1 SDA
引脚 5 - I2C1 SCL
使用方法
连线
Pin 1 - 3.3V connect to VCC
Pin 3 - SDA connect to SDA
Pin 5 - SCL connect to SCL
Pin 6 - Ground connect to GNDsudo apt-get install i2c-tools测试
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 68 -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --sudo i2cget -y 1 0x68 0x75安装python-smbus
sudo apt-get install python-smbus 例子程序
#!/usr/bin/python
import smbus
import math
# Power management registers
power_mgmt_1 = 0x6b
power_mgmt_2 = 0x6c
def read_byte(adr):
return bus.read_byte_data(address, adr)
def read_word(adr):
high = bus.read_byte_data(address, adr)
low = bus.read_byte_data(address, adr+1)
val = (high << 8) + low
return val
def read_word_2c(adr):
val = read_word(adr)
if (val >= 0x8000):
return -((65535 - val) + 1)
else:
return val
def dist(a,b):
return math.sqrt((a*a)+(b*b))
def get_y_rotation(x,y,z):
radians = math.atan2(x, dist(y,z))
return -math.degrees(radians)
def get_x_rotation(x,y,z):
radians = math.atan2(y, dist(x,z))
return math.degrees(radians)
bus = smbus.SMBus(0) # or bus = smbus.SMBus(1) for Revision 2 boards
address = 0x68 # This is the address value read via the i2cdetect command
# Now wake the 6050 up as it starts in sleep mode
bus.write_byte_data(address, power_mgmt_1, 0)
print "gyro data"
print "---------"
gyro_xout = read_word_2c(0x43)
gyro_yout = read_word_2c(0x45)
gyro_zout = read_word_2c(0x47)
print "gyro_xout: ", gyro_xout, " scaled: ", (gyro_xout / 131)
print "gyro_yout: ", gyro_yout, " scaled: ", (gyro_yout / 131)
print "gyro_zout: ", gyro_zout, " scaled: ", (gyro_zout / 131)
print
print "accelerometer data"
print "------------------"
accel_xout = read_word_2c(0x3b)
accel_yout = read_word_2c(0x3d)
accel_zout = read_word_2c(0x3f)
accel_xout_scaled = accel_xout / 16384.0
accel_yout_scaled = accel_yout / 16384.0
accel_zout_scaled = accel_zout / 16384.0
print "accel_xout: ", accel_xout, " scaled: ", accel_xout_scaled
print "accel_yout: ", accel_yout, " scaled: ", accel_yout_scaled
print "accel_zout: ", accel_zout, " scaled: ", accel_zout_scaled
print "x rotation: " , get_x_rotation(accel_xout_scaled, accel_yout_scaled, accel_zout_scaled)
print "y rotation: " , get_y_rotation(accel_xout_scaled, accel_yout_scaled, accel_zout_scaled)SPI 总线
RPi2/3 上提供一个 SPI 总线控制器。SPI0 具有标准的 MOSI、MISO 和 SCLK 线,并且可以配置为使用 SPI0 CS0 和 SPI0 CS1 两种芯片选择线之一。
引脚 19 - SPI0 MOSI
引脚 21 - SPI0 MISO
引脚 23 - SPI0 SCLK
引脚 24 - SPI0 CS0
引脚 26 - SPI0 CS1
参考: https://developer.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/iot/win10/samples/PinMappingsRPi2.htm