SLAM学习——建图问题(一)
1.单目稠密地图的构建
在上述中,我们讨论的是稀疏地图的构建,但是在实际的定位、导航和壁障过程中,我们需要有稠密地图。常见的单目稠密地图的构建思路有:
1.单目:通过运动,得出运动轨迹,计算出运动的关系,通过三角测量计算出像素深度。(同下)
2.双目:利用俩个相机的视差计算出像素的深度。(吃力不讨好,但是大型场合可能有比较好的效果。)
3.RGBD:自带深度图,可直接得到像素的深度。(比较好,但是不适合大型场合)
对于单目而言,即我们提到的第一种方法,通过单目建立稠密地图:
1.提取特征点,然后在很多图像中,进行特征点的匹配,跟踪特征点在各张图像的轨迹(经常用ORB特征提取)
2.然后通过三角测量估计每一个像素的深度。在这里,我们需要利用很多的三角测量使得某点的深度进行收敛,得到确切的深度信息。
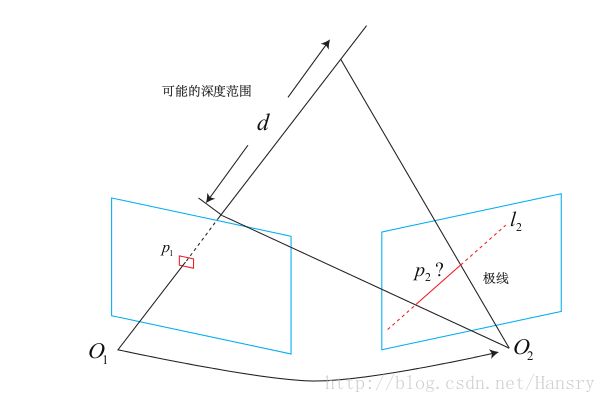
在稠密深度地图中,无法对每个像素计算其描述子,所以在稠密估计问题中,匹配成为很重要的一环,我们用到了极线搜索和块匹配技术,极线搜索的原理如下图所示:
而块匹配技术就相当于把像素的比较换成了块的比较,我们直接上代码可得:
#include //这里使用了sophus这个工具,使用SE3
using Sophus::SE3;
// for eigen
#include 1,0)+boarder<=height;
}
// 显示极线匹配
void showEpipolarMatch( const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& px_ref, const Vector2d& px_curr );
// 显示极线
void showEpipolarLine( const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& px_ref, const Vector2d& px_min_curr, const Vector2d& px_max_curr );
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
// 从数据集读取数据
vector<string> color_image_files;
vectorreturn -1;
}
cout<<"read total "<" files."<// 第一张图
Mat ref = imread( color_image_files[0], 0 ); // gray-scale image
SE3 pose_ref_TWC = poses_TWC[0];
double init_depth = 3.0; // 深度初始值
double init_cov2 = 3.0; // 方差初始值
Mat depth( height, width, CV_64F, init_depth ); // 深度图
Mat depth_cov( height, width, CV_64F, init_cov2 ); // 深度图方差
for ( int index=1; indexcout<<"*** loop "<" ***"<0 );
if (curr.data == nullptr) continue;
SE3 pose_curr_TWC = poses_TWC[index];
SE3 pose_T_C_R = pose_curr_TWC.inverse() * pose_ref_TWC; // 坐标转换关系: T_C_W * T_W_R = T_C_R
update( ref, curr, pose_T_C_R, depth, depth_cov );
plotDepth( depth );
imshow("image", curr);
waitKey(1);
}
cout<<"estimation returns, saving depth map ..."<"depth.png", depth );
cout<<"done."<return 0;
}
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string& path,
vector< string >& color_image_files,
std::vector#pragma omp parallel for
for ( int y=boarder; y// 遍历每个像素
if ( depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x] > max_cov ) // 深度已收敛或发散
continue;
// 在极线上搜索 (x,y) 的匹配
Vector2d pt_curr;
bool ret = epipolarSearch (
ref,
curr,
T_C_R,
Vector2d(x,y),
depth.ptr<double>(y)[x],
sqrt(depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x]),
pt_curr
);
if ( ret == false ) // 匹配失败
continue;
// 取消该注释以显示匹配
// showEpipolarMatch( ref, curr, Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr );
// 匹配成功,更新深度图
updateDepthFilter( Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr, T_C_R, depth, depth_cov );
}
}
// 极线搜索
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R, const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const double& depth_mu, const double& depth_cov,
Vector2d& pt_curr )
{
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref );
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d P_ref = f_ref*depth_mu; // 参考帧的 P 向量
Vector2d px_mean_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*P_ref ); // 按深度均值投影的像素
double d_min = depth_mu-3*depth_cov, d_max = depth_mu+3*depth_cov;
if ( d_min<0.1 ) d_min = 0.1;
Vector2d px_min_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*(f_ref*d_min) ); // 按最小深度投影的像素
Vector2d px_max_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*(f_ref*d_max) ); // 按最大深度投影的像素
Vector2d epipolar_line = px_max_curr - px_min_curr; // 极线(线段形式)
Vector2d epipolar_direction = epipolar_line; // 极线方向
epipolar_direction.normalize();
double half_length = 0.5*epipolar_line.norm(); // 极线线段的半长度
if ( half_length>100 ) half_length = 100; // 我们不希望搜索太多东西
// 取消此句注释以显示极线(线段)
// showEpipolarLine( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_min_curr, px_max_curr );
// 在极线上搜索,以深度均值点为中心,左右各取半长度
double best_ncc = -1.0;
Vector2d best_px_curr;
for ( double l=-half_length; l<=half_length; l+=0.7 ) // l+=sqrt(2)
{
Vector2d px_curr = px_mean_curr + l*epipolar_direction; // 待匹配点
if ( !inside(px_curr) )
continue;
// 计算待匹配点与参考帧的 NCC
double ncc = NCC( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_curr );
if ( ncc>best_ncc )
{
best_ncc = ncc;
best_px_curr = px_curr;
}
}
if ( best_ncc < 0.85f ) // 只相信 NCC 很高的匹配
return false;
pt_curr = best_px_curr;
return true;
}
double NCC (
const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr,
const Vector2d& pt_ref, const Vector2d& pt_curr
)
{
// 零均值-归一化互相关
// 先算均值
double mean_ref = 0, mean_curr = 0;
vector<double> values_ref, values_curr; // 参考帧和当前帧的均值
for ( int x=-ncc_window_size; x<=ncc_window_size; x++ )
for ( int y=-ncc_window_size; y<=ncc_window_size; y++ )
{
double value_ref = double(ref.ptr( int(y+pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(x+pt_ref(0,0)) ])/255.0;
mean_ref += value_ref;
double value_curr = getBilinearInterpolatedValue( curr, pt_curr+Vector2d(x,y) );
mean_curr += value_curr;
values_ref.push_back(value_ref);
values_curr.push_back(value_curr);
}
mean_ref /= ncc_area;
mean_curr /= ncc_area;
// 计算 Zero mean NCC
double numerator = 0, demoniator1 = 0, demoniator2 = 0;
for ( int i=0; idouble n = (values_ref[i]-mean_ref) * (values_curr[i]-mean_curr);
numerator += n;
demoniator1 += (values_ref[i]-mean_ref)*(values_ref[i]-mean_ref);
demoniator2 += (values_curr[i]-mean_curr)*(values_curr[i]-mean_curr);
}
return numerator / sqrt( demoniator1*demoniator2+1e-10 ); // 防止分母出现零
}
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const Vector2d& pt_curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
Mat& depth,
Mat& depth_cov
)
{
// 我是一只喵
// 不知道这段还有没有人看
// 用三角化计算深度
SE3 T_R_C = T_C_R.inverse();
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref );
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d f_curr = px2cam( pt_curr );
f_curr.normalize();
// 方程
// d_ref * f_ref = d_cur * ( R_RC * f_cur ) + t_RC
// => [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f_cur ] [d_ref] = [f_ref^T t]
// [ f_cur^T f_ref, -f_cur^T f_cur ] [d_cur] = [f_cur^T t]
// 二阶方程用克莱默法则求解并解之
Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation();
Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.rotation_matrix() * f_curr;
Vector2d b = Vector2d ( t.dot ( f_ref ), t.dot ( f2 ) );
double A[4];
A[0] = f_ref.dot ( f_ref );
A[2] = f_ref.dot ( f2 );
A[1] = -A[2];
A[3] = - f2.dot ( f2 );
double d = A[0]*A[3]-A[1]*A[2];
Vector2d lambdavec =
Vector2d ( A[3] * b ( 0,0 ) - A[1] * b ( 1,0 ),
-A[2] * b ( 0,0 ) + A[0] * b ( 1,0 )) /d;
Vector3d xm = lambdavec ( 0,0 ) * f_ref;
Vector3d xn = t + lambdavec ( 1,0 ) * f2;
Vector3d d_esti = ( xm+xn ) / 2.0; // 三角化算得的深度向量
double depth_estimation = d_esti.norm(); // 深度值
// 计算不确定性(以一个像素为误差)
Vector3d p = f_ref*depth_estimation;
Vector3d a = p - t;
double t_norm = t.norm();
double a_norm = a.norm();
double alpha = acos( f_ref.dot(t)/t_norm );
double beta = acos( -a.dot(t)/(a_norm*t_norm));
double beta_prime = beta + atan(1/fx);
double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime;
double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma);
double d_cov = p_prime - depth_estimation;
double d_cov2 = d_cov*d_cov;
// 高斯融合
double mu = depth.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ];
double sigma2 = depth_cov.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ];
double mu_fuse = (d_cov2*mu+sigma2*depth_estimation) / ( sigma2+d_cov2);
double sigma_fuse2 = ( sigma2 * d_cov2 ) / ( sigma2 + d_cov2 );
depth.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = mu_fuse;
depth_cov.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = sigma_fuse2;
return true;
}
bool plotDepth(const Mat& depth)
{
imshow( "depth", depth*0.4 );
waitKey(1);
} Cmakelist 文件如下所示:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
project(dense_mapping)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -march=native -O3 -fopenmp")
set(OpenCV_DIR /usr/local/opencv320/share/OpenCV)
#set(Sophus_LIBRARIES libSophus.so)
find_package(OpenCV 3.2 REQUIRED )
include_directories(SYSTEM ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} /usr/local/opencv320/include)
find_package( "/usr/local/opencv320/include/opencv2" )
## System dependencies are found with CMake's conventions
# find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS system)
find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR})
set( Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS "/usr/local/include" )
set( Sophus_LIBS "/usr/local/lib/libSophus.so" )
include_directories(include)
include_directories(
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_LIBS}
)
add_executable(dense_mapping src/dense_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(dense_mapping
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
${OpenCV_LIBRARIES}
${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR}
${Sophus_LIBS}
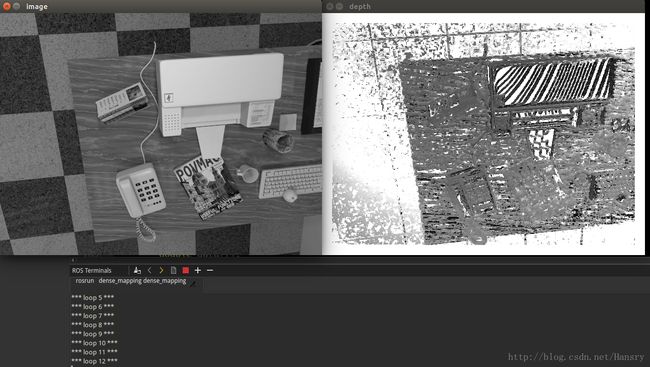
)以上程序较为复杂,其运算的结果如下:
通过不断的循环我们可以不断的更新其相片的深度值.