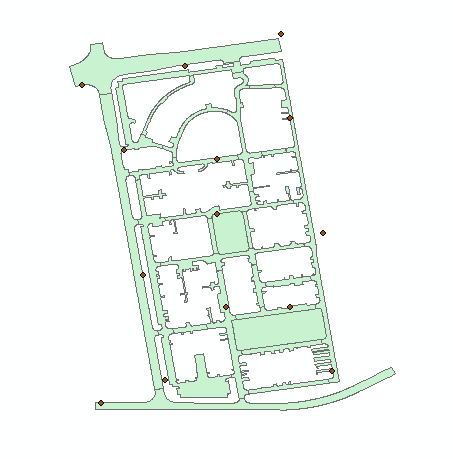
这里先给大家介绍几个坐标系:
1.WGS84:国际坐标系,为一种大地坐标系,也是目前广泛使用的GPS全球卫星定位系统使用的坐标系。
2.GCJ02:火星坐标系,是由中国国家测绘局制订的地理信息系统的坐标系统。由WGS84坐标系经加密后的坐标系。
工作中有时需要将shape数据转换成高德坐标数据,由于目前数据大部分都是WGS84国际坐标系,因此需要通过使用高德地图提供的API将84坐标转换成GCJ02即火星坐标系。
第一步:准备数据
方法1:
从shape图上随机提取一些点,根据shape图形大小提取,如果图形较大,建议多提取一些。一般在拐点和图形的四周均匀选择。
点提取完成后获取坐标点的经纬度值。可以使用Arcgis的计算工具获取x,y值。画红框的地方需要注意,要选择十进制表示的经纬度。
坐标提取完成后新建一个excel表,将x,y值分别复制黏贴在excel表中的前两列。
方法2:
将shape数据存入postgresql,并使用postgis提供的函数随机从shape上提取点,并取出其x,y值。此方法是随机选择,因此选择的点未必均匀分布在图形四周和拐点处。
1 SELECT ST_X(geom), ST_Y(geom) from( 2 SELECT 3 (ST_Dump (ST_GeneratePoints (nanjing.geom, 20))).geom AS geom, 4 md5((random()*random())::text) as id, 5 random()*1000 as val 6 FROM nanjing where name = '浦口区') 7 k1
第二步:执行下面的python代码调取高德API进行坐标转换
1 import xlrd 2 from xlutils.copy import copy 3 from urllib import request 4 import json 5 6 7 class ToGd(): 8 def __init__(self, key, coordsys='gps', output='JSON'): 9 self.key = key # 高德应用的key 10 self.coordsys = coordsys # 原坐标系,默认选择gps,此处实际对应4326的坐标系 11 self.output = output # 设置高德api数据返回类型,可选JSON和xml 12 self.file_path = input('请输入你的文件路径') # 获取文件路径,即上面新建的excel文件名称 13 14 def split_li(self, locations_li): 15 # 拆分坐标列表 16 li = list() 17 for location in locations_li: 18 location_li = location.split(',') 19 # print(location_li) 20 li.append(location_li) 21 # print(li) 22 return li 23 24 def locations(self): 25 # 读取文件中的数据并返回locations字符串及原坐标列表 26 f = xlrd.open_workbook(self.file_path) 27 index = f.sheet_names()[0] 28 sheet = f.sheet_by_name(index) 29 nrows = sheet.nrows 30 data_str = '' 31 old_locations_li = list() 32 for i in range(nrows): 33 if i == (nrows - 1): 34 data_li = str(sheet.row_values(i)[0]) + ',' + str(sheet.row_values(i)[1]) 35 else: 36 data_li = str(sheet.row_values(i)[0]) + ',' + str(sheet.row_values(i)[1]) + '|' 37 data_str += data_li 38 old_locations_li.append(sheet.row_values(i)) 39 return data_str, old_locations_li 40 41 def make_response(self, locations): 42 # 构造请求url,并获取响应数据,返回拆分后的坐标列表 43 url = 'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/assistant/coordinate/convert?locations=%s&coordsys=%s&output=%s&key=%s' % \ 44 (locations, self.coordsys, self.output, self.key) 45 # 返回值为json 46 resp_json = request.urlopen(url) 47 # json转换成字典 48 resp_dict = json.loads(resp_json.read().decode()) 49 # 提取转换为高德坐标后的坐标 50 locations_str = resp_dict.get('locations') 51 # 字符串分割 52 locations_li = locations_str.split(';') 53 new_locations_li = self.split_li(locations_li) 54 return new_locations_li 55 56 def save(self, old_locations_li, new_locations_li): 57 # 保存成excel或txt文件 58 # new_file = copy(f) 59 # new_sheet = new_file.get_sheet(0) 60 # for m in range(len(locations_li)): 61 # for n in range(len(locations_li[m])): 62 # new_sheet.write(m, n + 2, locations_li[m][n]) 63 # file_path = self.file_path + '2' 64 # new_file.save(file_path) 65 file_path = 'result.txt' 66 with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8')as f: 67 for m in range(len(new_locations_li)): 68 # for n in range(len(new_locations_li[m])): 69 f.write(str(old_locations_li[m][0])) 70 f.write(' ') 71 f.write(str(old_locations_li[m][1])) 72 f.write(' ') 73 f.write(str(new_locations_li[m][0])) 74 f.write(' ') 75 f.write(str(new_locations_li[m][1])) 76 f.write('\n') 77 78 def run(self): 79 data_str, old_locations_li = self.locations() 80 new_locations_li = self.make_response(data_str) 81 self.save(old_locations_li, new_locations_li) 82 83 84 if __name__ == '__main__': 85 test = ToGd('154c586add07ef456b90b079935f47a4') # 输入高德应用的key,实例化对象 86 test.run()
代码由我自己编写,水平不高还请理解。
执行上面的代码需要申请高德应用的key,相关申请方法可查看https://lbs.amap.com/dev/key
代码执行完成后会在本地生成一个result.txt的文件,下面需要用这个文件做空间校正。
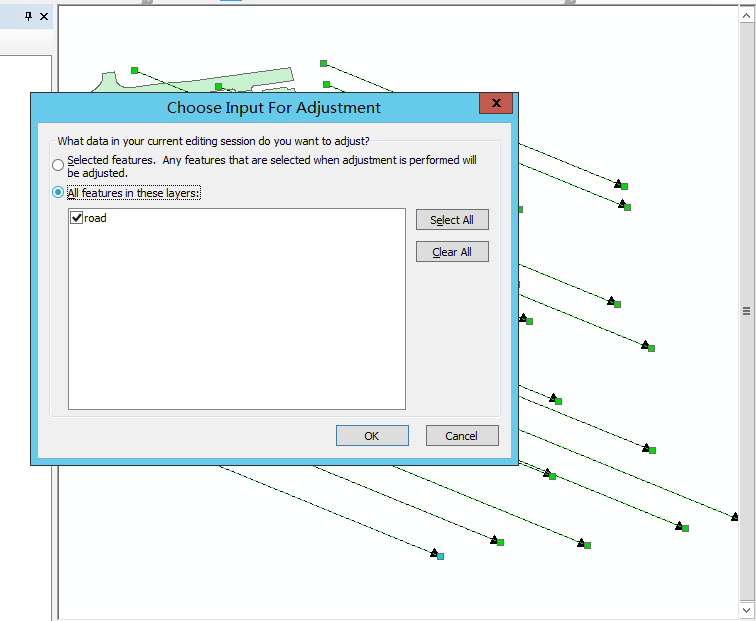
第三步:空间校正
在Arcgis中对需要做坐标转换的数据开启编辑功能,打开空间校正工具栏,输入连接文件。连接文件即第二步得出的result.txt文件。
可以点击View Link Table查看误差值,如果误差值太大,需要重新做连接文件。
选择需要校正的数据。
点击校正。
校正完成后即可得到与高德地图匹配的shape数据。
上述方法只能用于小范围测试使用,未做精度评估。如需大规模商业化使用,还需再想别的方法。