目录
- 1. 概述
- 定义
- 缓冲区
- 2. 典型模型
- 模型一
- 模型二
- 可选需求
- 3. 数据结构队列C语言实现
- 4. 代码实现——互斥锁 + 条件变量
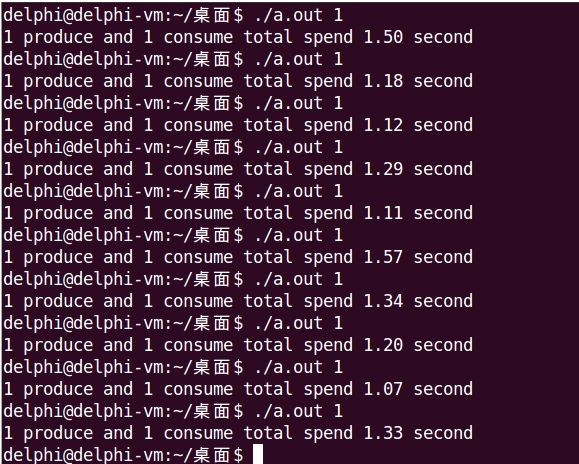
- 5. 代码实现——互斥锁 + Posix有名信号量
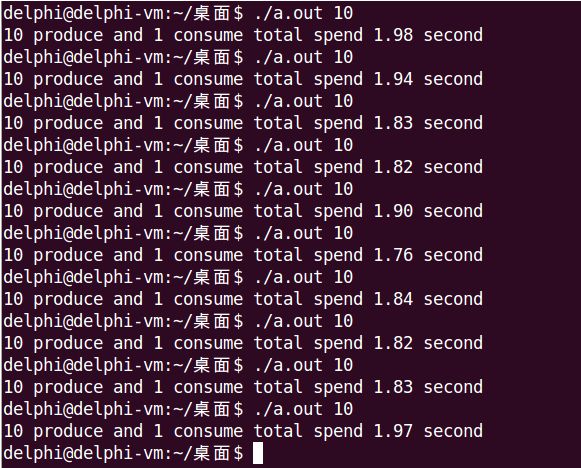
- 6. 代码实现——互斥锁 + Posix无名信号量
- 7. 效率对比
- 结论
- 奇怪的问题
1. 概述
定义
生产者消费者问题是线程同步的经典问题,也称为有界缓冲区问题,问题描述大致如下:
- 生产者和消费者之间共享一个有界数据缓冲区
- 一个或多个生产者(线程或进程)向缓冲区放置数据
- 一个或多个消费者(线程或进程)从缓冲区取出数据
缓冲区
生产者消费者问题中的缓冲区,包括队列缓冲区和环形缓冲区,它们都按照先进先出的顺序处理数据,我们现在只考虑队列缓冲区:
- 队列缓冲区通常使用普通的队列数据结构
- 队列内部实现可以是链表或数组
缓冲区有两个极端状态:缓冲区空,缓冲区满。链表队列和数组队列缓冲区空的含义相同,都是队列中没有一个元素的情形,但两者缓冲区满的含义不同:
- 数组队列在初始化时就必须指定最大容量,缓冲区满的条件很清晰
- 链表队列没有最大容量的概念,需要人为指定
此外,Posix消息队列也可以作为队列缓冲区,Posix当以无优先级消息的方式使用时,也是按照先进先出的顺序进行处理的。
本文只讨论第一种数据结构队列缓冲区,基于Posix消息队列缓冲区的生产者消费者问题,会在后续Posix消息队列中单独讲解。
2. 典型模型
生产者消费者个数的多少、缓冲区的类型都会影响生产者消费者问题模型的复杂度,本文选取两种常见典型模型进行分析。
模型一
- 单个生产者 + 单个消费者
- 生产者线程启动后,立即创建消费者线程
- 缓冲区容量有限,且小于数据条目数量
该模型只需要处理生产者和消费者之间的同步问题,在实际工程很常见,具体的同步详情为:
- 当缓冲区为空时,消费者不能从其中取出数据
- 当缓冲区为满时,生产者不能向其中写入数据
模型二
- 多个生产者 + 单个消费者
- 生产者线程启动后,立即创建消费者线程
- 缓冲区容量有限,且小于数据条目数量
模型二与模型一相比,既需要处理生产者之间的同步问题,又需要处理生产者和消费者之间的同步问题,在实际工程也比较常见,具体的同步详情为:
- 同时只能有一个生产者向缓冲区写入数据
- 当缓冲区为空时,消费者不能从其中取出数据
- 当缓冲区为满时,生产者不能向其中写入数据
可选需求
模型一和模型二所列均为必须处理的同步问题,还有一个根据实际情况、可能会存在的同步需求:
- 共享数据中包含描述缓冲区当前状态的变量,如下标、计数、链表等
- 生产者和消费者在读写缓冲区后都需要更新缓冲区状态变量
- 若满足上述两个条件,则同时只能有一个生产者或消费者可以进行缓冲区操作与状态变量更新
队列缓冲区,不管是数组实现还是链表实现,其内部都符合上述条件,都需要处理该可选同步需求。
3. 数据结构队列C语言实现
网上找了份数据结构队列C语言实现的代码,稍微改了下,可正常使用,本节后续的生产者消费者问题示例代码就是用它作为缓冲区。
#ifndef _LINK_QUEUE_H_
#define _LINK_QUEUE_H_
typedef enum
{
false = 0,
true
} bool;
typedef int data_t;
typedef struct LinkNode
{
data_t data;
struct LinkNode *next;
} LinkNode, *LinkQueue;
typedef struct
{
LinkQueue front;
LinkQueue rear;
} HeadQueue;
HeadQueue *CreateEmptyQueue();
bool EmptyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue);
void EnQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t value);
void DeQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t *value);
void PrintQueue(HeadQueue *queue);
bool ClearLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue);
bool DestroyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue);
int GetCurItemsNum(HeadQueue *queue);
#endif#include "linkqueue.h"
#include
#include
static int nitems;
//创建空链表队列
HeadQueue *CreateEmptyQueue(void)
{
HeadQueue *queue = (HeadQueue *)malloc(sizeof(HeadQueue));
if (queue == NULL)
{
perror("Create empty queue failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
queue->rear = queue->front = NULL;
nitems = 0;
return queue;
}
//判断是否为空链表队列
bool EmptyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue)
{
if (queue == NULL)
{
printf("Empty link queue error!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return queue->front == NULL ? true : false;
}
//增加队列元素
void EnQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t value)
{
LinkQueue new;
if (queue == NULL)
{
printf("EnQueue Error!\n");
return;
}
new = (LinkQueue)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
if (new == NULL)
{
perror("Insert value failed");
return;
}
new->data = value;
new->next = NULL;
if (EmptyLinkQueue(queue))
{
queue->front = queue->rear = new;
}
else
{
queue->rear->next = new;
queue->rear = new;
}
nitems++;
}
//删除队列元素
void DeQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t *value)
{
*value = 0;
LinkQueue remove;
if (queue == NULL)
{
printf("DeQueue error!\n");
return;
}
if (EmptyLinkQueue(queue))
{
printf("queue is empty!\n");
return;
}
remove = queue->front;
queue->front = remove->next;
if (queue->front == NULL)
queue->rear = NULL;
*value = remove->data;
free(remove);
nitems--;
}
//遍历队列元素
void PrintQueue(HeadQueue *queue)
{
LinkQueue node;
printf("queue = {");
node = queue->front;
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("}\n");
return ;
}
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d,", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\b}\n");
}
//清空队列元素
bool ClearLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue)
{
LinkQueue remove = queue->front;
while (remove != NULL)
{
queue->front = queue->front->next;
free(remove);
remove = queue->front;
}
queue->front = NULL;
queue->rear = NULL;
nitems = 0;
return true;
}
//销毁队列
bool DestroyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue)
{
if (queue != NULL)
{
ClearLinkQueue(queue);
free(queue);
nitems = 0;
return true;
}
else
{
printf("DestroyLinkQueue error!\n");
return false;
}
}
//获得当前队列元素个数
int GetCurItemsNum(HeadQueue *queue)
{
return nitems;
} 4. 代码实现——互斥锁 + 条件变量
#include "linkqueue.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MAX_THREADS 10
#define MAX_ITEMS 1000000
#define MAX_BUFFER 10
/*
* 编程技巧:尽量把共享数据和它们的同步变量(互斥锁、条件变量、信号量)收集到同一个结构体中
*/
struct Shared
{
pthread_cond_t cond_nempty; //条件变量:缓冲区不满
pthread_cond_t cond_nstored; //条件变量:缓冲区不空
pthread_mutex_t cond_mutex; //保护条件的锁,用于确保同时只有一个线程可以访问缓冲区
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //同步多个生产者的锁,仅在有多个生产者时使用
HeadQueue *queue; //队列缓冲区
int nput;
int nval;
};
struct Shared shared;
void shared_init()
{
shared.queue = CreateEmptyQueue();
pthread_mutex_init(&shared.mutex, NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&shared.cond_mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&shared.cond_nempty, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&shared.cond_nstored, NULL);
}
void shared_destroy()
{
DestroyLinkQueue(shared.queue);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.mutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.cond_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&shared.cond_nempty);
pthread_cond_destroy(&shared.cond_nstored);
}
void *produce(void *arg)
{
int nthreads = *((int *)arg);
while (1)
{
if (shared.nput >= MAX_ITEMS)
{
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
if (nthreads > 1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.cond_mutex);
while (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) == MAX_BUFFER)
pthread_cond_wait(&shared.cond_nempty, &shared.cond_mutex);
EnQueue(shared.queue, shared.nval);
shared.nput++;
shared.nval++;
pthread_cond_signal(&shared.cond_nstored);
if (nthreads > 1)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.cond_mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *consume(void *arg)
{
int nval;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.cond_mutex);
while (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) == 0)
pthread_cond_wait(&shared.cond_nstored, &shared.cond_mutex);
DeQueue(shared.queue, &nval);
pthread_cond_signal(&shared.cond_nempty);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.cond_mutex);
if (nval != i)
{
printf("error: buff[%d] = %d\n", i, nval);
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pthread_t tid_produce[MAX_THREADS];
pthread_t tid_consume;
int nthreads;
struct timeval start_time;
struct timeval end_time;
float time_sec;
int i;
nthreads = (atoi(argv[1]) > MAX_THREADS) ? MAX_THREADS : atoi(argv[1]);
shared_init();
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++)
{
pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &nthreads);
}
pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++)
{
pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL);
}
pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL);
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
time_sec = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec) + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec) / 1000000.0;
printf("%d produce and %d consume total spend %.2f second\n", nthreads, 1, time_sec);
shared_destroy();
return 0;
} 运行时通过命令行参数指定生产者个数,来选择模型一或模型二,其中,在produce()中,第57-56行、第74-77行会根据生产者个数,选择是否使用第二把锁。
下面分别是模型一和模型二的运行结果。
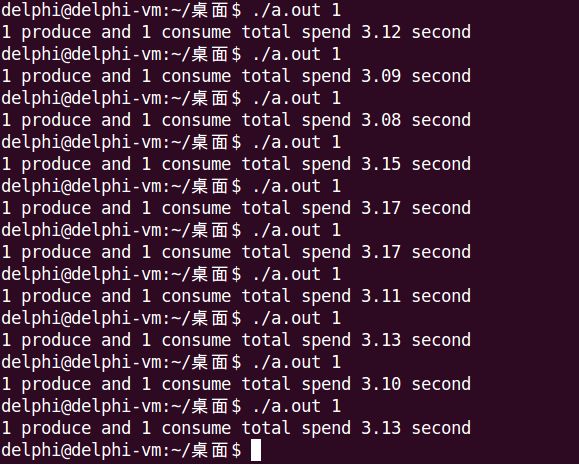
5. 代码实现——互斥锁 + Posix有名信号量
#include "linkqueue.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define SEM_NEMPTY "/sem_nempty"
#define SEM_NSTROED "/sem_nstored"
#define MAX_THREADS 10
#define MAX_ITEMS 1000000
#define MAX_BUFFER 10
/*
* 编程技巧:把共享数据和它们的同步变量(互斥锁、条件变量、信号量)收集到同一个结构体中
*/
struct Shared
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
sem_t *nempty;
sem_t *nstored;
HeadQueue *queue;
int nput;
int nval;
};
struct Shared shared;
void shared_init()
{
shared.queue = CreateEmptyQueue();
pthread_mutex_init(&shared.mutex, NULL);
shared.nempty = sem_open(SEM_NEMPTY, O_CREAT, 0666, MAX_BUFFER);
shared.nstored = sem_open(SEM_NSTROED, O_CREAT, 0666, 0);
}
void shared_destroy()
{
DestroyLinkQueue(shared.queue);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.mutex);
sem_close(shared.nempty);
sem_close(shared.nstored);
sem_unlink(SEM_NEMPTY);
sem_unlink(SEM_NSTROED);
}
void *produce(void *arg)
{
while (1)
{
if (shared.nput >= MAX_ITEMS)
{
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
/*
* produce和consume都必须先sem_wait,确保sem_wait返回后再上锁;
* 防止先上锁后sem_wait阻塞,导致另一方二次上锁而死锁.
*/
sem_wait(shared.nempty);
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
EnQueue(shared.queue, shared.nval);
/* 如果队列缓冲区中的元素个数超过了MAX_BUFFER,就输出提示信息 */
if (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) > MAX_BUFFER)
{
printf("notice: queue buffer capacity > %d\n", MAX_BUFFER);
}
shared.nput++;
shared.nval++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
sem_post(shared.nstored);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *consume(void *arg)
{
int nval;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++)
{
/*
* produce和consume都必须先sem_wait,确保sem_wait返回后再上锁;
* 防止先上锁后sem_wait阻塞,导致另一方二次上锁而死锁.
*/
sem_wait(shared.nstored);
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
DeQueue(shared.queue, &nval);
if (nval != i)
{
printf("error: buff[%d] = %d\n", i, nval);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
sem_post(shared.nempty);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pthread_t tid_produce[MAX_THREADS];
pthread_t tid_consume;
int nthreads;
struct timeval start_time;
struct timeval end_time;
float time_sec;
int i;
nthreads = (atoi(argv[1]) > MAX_THREADS) ? MAX_THREADS : atoi(argv[1]);
shared_init();
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++)
{
pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &nthreads);
}
pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++)
{
pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL);
}
pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL);
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
time_sec = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec) + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec) / 1000000.0;
printf("%d produce and %d consume total spend %.2f second\n", nthreads, 1, time_sec);
shared_destroy();
return 0;
} 6. 代码实现——互斥锁 + Posix无名信号量
#include "linkqueue.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MAX_THREADS 10
#define MAX_ITEMS 1000000
#define MAX_BUFFER 10
/*
* 编程技巧:把共享数据和它们的同步变量(互斥锁、条件变量、信号量)收集到同一个结构体中
*/
struct Shared
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
sem_t nempty;
sem_t nstored;
HeadQueue *queue;
int nput;
int nval;
};
struct Shared shared;
void shared_init()
{
shared.queue = CreateEmptyQueue();
pthread_mutex_init(&shared.mutex, NULL);
sem_init(&shared.nempty, 0, MAX_BUFFER);
sem_init(&shared.nstored, 0, 0);
}
void shared_destroy()
{
DestroyLinkQueue(shared.queue);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.mutex);
sem_destroy(&shared.nempty);
sem_destroy(&shared.nstored);
}
void *produce(void *arg)
{
while (1)
{
if (shared.nput >= MAX_ITEMS)
{
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
/*
* produce和consume都必须先sem_wait,确保sem_wait返回后再上锁;
* 防止先上锁后sem_wait阻塞,导致另一方二次上锁而死锁.
*/
sem_wait(&shared.nempty);
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
EnQueue(shared.queue, shared.nval);
/* 如果队列缓冲区中的元素个数超过了MAX_BUFFER,就输出提示信息 */
if (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) > MAX_BUFFER)
{
printf("notice: queue buffer capacity > %d\n", MAX_BUFFER);
}
shared.nput++;
shared.nval++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
sem_post(&shared.nstored);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *consume(void *arg)
{
int nval;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++)
{
/*
* produce和consume都必须先sem_wait,确保sem_wait返回后再上锁;
* 防止先上锁后sem_wait阻塞,导致另一方二次上锁而死锁.
*/
sem_wait(&shared.nstored);
pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex);
DeQueue(shared.queue, &nval);
if (nval != i)
{
printf("error: buff[%d] = %d\n", i, nval);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex);
sem_post(&shared.nempty);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pthread_t tid_produce[MAX_THREADS];
pthread_t tid_consume;
int nthreads;
struct timeval start_time;
struct timeval end_time;
float time_sec;
int i;
nthreads = (atoi(argv[1]) > MAX_THREADS) ? MAX_THREADS : atoi(argv[1]);
shared_init();
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++)
{
pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &nthreads);
}
pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++)
{
pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL);
}
pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL);
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
time_sec = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec) + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec) / 1000000.0;
printf("%d produce and %d consume total spend %.2f second\n", nthreads, 1, time_sec);
shared_destroy();
return 0;
} 7. 效率对比
结论
- 只有Posix无名信号量使用多生产者获得了效率正提升,其余都是负提升
- 单生产者效率,Posix有名信号量 > Posix无名信号量 > 条件变量
- 多生产者效率,Posix无名信号量 > Posix有名信号量 > 条件变量
该结论仅限于本文使用的示例代码,仅作结果陈述,不代表具有普适性,也没有进行深层原因分析。
奇怪的问题
在使用条件变量的示例代码中,当有多个生产者时用了两把锁:
- mutex同步多个生产者,确保多个生产者不会同时访问缓冲区
- cond_mutex确保生产者消费者不会同时访问缓冲区
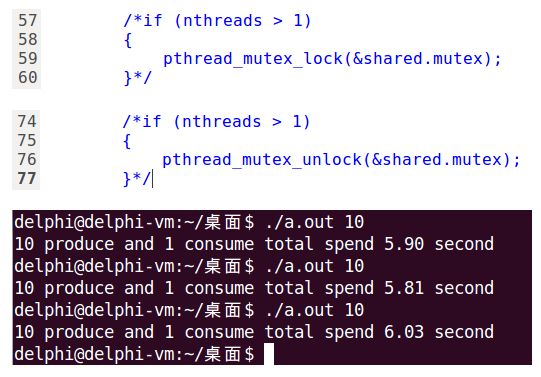
实际上,只需要一个cond_mutex就够了,但经过测试发现这样运行时间会明显增加,如下图所示:
先从理论上分析下,10个生产者1个消费者:
- 只能同时有一个生产者访问缓冲区
- 只能同时有一个生产者或消费者访问缓冲区
总结起来就是:只能同时有一个线程访问缓冲区。从这个结论来看,确实不需要第二把锁,在一把锁就够用的情况下,再加第二把锁反而多了不必要的开销。
经过测试,Posix有名和无名信号量都符合这个理论,运行时间明显增加了,有名信号量从1.9s增加到2.3s,无名信号量从1.4s增加到2.5s。
但邪门就邪门在,条件变量却相反,一把锁效率低,两把锁反而效率有大幅提升,想不通为什么!