Netty介绍以及源码分析
一. Netty是什么
Netty是一个能支持快速和容易开发网络应用程序的NIO客户端服务器框架,例如协议服务器客户端,它极大的简化了网络编程,例如TCP和UDP套接字编程。
快速和容易并不意味着应用程序将面临维护和性能问题。Netty是在积累了大量协议(例如FTP、SMTP、HTTP、还有各种二进制和基于文本的遗留协议)的经验前提下被精心设计的。因此,Netty成功地找到了一种方式,在不妥协的情况下实现易开发性、高性能、稳定性以及灵活性。
协议是什么
协议其实是一种通信双方遵循的一种规则和约定,制定了数据单元的格式、语义和定时规则(时序),确保通信双方正确的发送、接收和理解数据单元。比如英语其实就是一种协议,只有双方都知道这种协议才可以正常沟通,同样在计算机通信中,网络协议用于实现计算机与网络连接之间的标准,如果没有统一的标准,计算机之间的信息传递就无法实现。
二.为什么用Netty?
因为使用Java原生NIO不太好用,比如ByteBuffer的操作,每次从Channel写数据到Buffer读之前都要flip,如果忘记了这一步会导致读不到数据,所以直接使用NIO开发网络应用对开发人员的要求较高,还有数据的编解码、粘包、半包各种问题都要自己处理,复杂性高、难度大,而且很难保证高性能。Netty对NIO的API进行二次封装,设计优雅,使用方式固定,屏蔽了底层的复杂实现细节,极大的简化了网络应用程序的开发。下面我分别贴用NIO和Netty开发聊天室的代码,可以明显感受到Netty代码的优雅。
1.NIO实现的聊天室
public class NioChatServer {
private static HashMap clientMap = new HashMap();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8899));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("server start up on 8899!");
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
selectionKeys.forEach(selectionKey -> {
SocketChannel socketChannel=null;
try {
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
socketChannel = serverChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
clientMap.put("["+UUID.randomUUID()+"]",socketChannel);
System.out.println(socketChannel+" is connected!");
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = socketChannel.read(readBuffer);
if (read>0){
readBuffer.flip();
Charset charset = Charset.forName("utf-8");
String msg = String.valueOf(charset.decode(readBuffer));
System.out.println(socketChannel+":"+msg);
String sender = "";
for (Map.Entry enty : clientMap.entrySet()){
if (enty.getValue()==socketChannel){
sender= enty.getKey();
}
}
for (Map.Entry enty : clientMap.entrySet()){
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuffer.put((sender+":"+msg).getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
enty.getValue().write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
});
selectionKeys.clear();//remove all
}
}
} public class NioChatClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Selector selector = Selector.open();
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(8899));
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
selectionKeys.forEach(selectionKey -> {
try{
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()){
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
if (client.isConnectionPending()){
client.finishConnect();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuffer.put((LocalDateTime.now() +"连接成功!").getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
client.write(writeBuffer);
client.configureBlocking(false);
client.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
service.submit(()->{
while (true){
try {
writeBuffer.clear();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
writeBuffer.put(line.getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
client.write(writeBuffer);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
});
}
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = client.read(readBuffer);
if (read>0){
readBuffer.flip();
Charset charset = Charset.forName("utf-8");
String msg = String.valueOf(charset.decode(readBuffer));
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
});
}
}
} 2.Netty实现的聊天室
public class ChatServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChatServerInitializer());
System.out.println("server startup at 8899!");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
System.out.println("server closed!");
}
}
}public class ChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String msg) throws Exception {
Channel channel = channelHandlerContext.channel();
channelGroup.forEach(ch->{
if (channel!=ch){
ch.writeAndFlush("["+channel.remoteAddress()+"]发送:"+msg+" \n");
}else{
ch.writeAndFlush("[自己]发送:"+msg+" \n");
}
});
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {//when exception close connection
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//server add
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("server ["+channel.remoteAddress()+"]加入!\n");
channelGroup.add(channel);
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//server remove
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("server ["+channel.remoteAddress()+"]离开!\n");
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("["+channel.remoteAddress()+"]上线了!");
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("["+channel.remoteAddress()+"]下线了!");
}
}
public class ChatServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline channelPipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
channelPipeline.addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(4096,Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
channelPipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
channelPipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
channelPipeline.addLast(new ChatServerHandler());
}
} public class ChatClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChatClientInitializer());
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost",8899).channel();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while(true){
channel.writeAndFlush(bufferedReader.readLine()+" \r\n");
}
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}public class ChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
}
} public class ChatClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline channelPipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
channelPipeline.addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(4096, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
channelPipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
channelPipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
channelPipeline.addLast(new ChatClientHandler());
}
} 三、Netty的线程模型
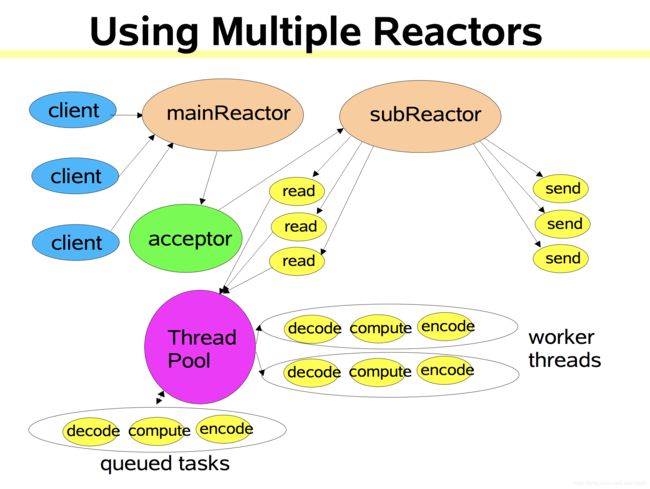
Netty的线程模型是主从Reactor多线程模型,对于Reactor模型具体可以参考我的一篇翻译Doug Lea的文章Scalable IO in Java(Java可伸缩IO)
MainReactor负责客户端的连接请求,并将请求转交给SubReactor。Netty中的MainReactor是bossGroup线程池中的一个线程,专门负责Accept事件。
SubReactor负责相应通道的IO请求。Netty中的SubReactor是workerGroup线程池。
非IO请求的任务直接写入队列,等待worker threads进行处理。
一个Reactor就是一个死循环线程,其实就是Netty中的NioEventLoop,不断的产生新的事件,像这样:
while (true) {
selector.select();
...
...
}四、Netty的开发流程和主要组件介绍
4.1开发流程
Netty服务器端的的初始化和启动方式:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//boss线程循环组,处理客户端连接
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//worker线程循环组,处理IO事件
try{
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();//服务器端启动类
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ServerInitializer());//ServerInitializer是自定义的初始化器,继承自ChannelInitializer,我们开发几乎仅仅需要将处理入站和出站处理器添加到管道ChannelPipeline中即可
System.out.println("server startup at 8899!");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();//这里真正的初始化和启动
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();//优雅关闭boss线程循环组
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();//优雅关闭worker线程循环组
System.out.println("server closed!");
}
}
}服务器端自定义的HTTP协议初始化器:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
public class ServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline channelPipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
channelPipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
channelPipeline.addLast(new MyHttpServerHandler());
}
} 服务器端自定义的 HTTP协议处理器:
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class MyHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, HttpObject httpObject) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server received:"+channelHandlerContext.channel().remoteAddress());
ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello word", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
if (httpObject instanceof HttpRequest){
HttpRequest request = (HttpRequest)httpObject;
FullHttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK,content);
httpResponse.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE,"text/plain");
httpResponse.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,content.readableBytes());
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(httpResponse);
}
}
} 可以不写客户端程序启动服务器端直接测试,打开命令行输入telnet 127.0.0.1 8899
Netty客户端的初始化和启动方式:
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();//IO线程循环组
try{
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();//客户端引导器
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ClientInitializer());//ClientInitializer是自定义的初始化器,继承自ChannelInitializer,我们开发几乎仅仅需要将处理入站和出站处理器添加到管道
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost",8899).sync();//真正初始化和发起连接
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}其实服务器端和客户端代码是一模一样的,只不过客户端少了bossGroup,我们日常开发需要自定义一个初始化器,继承自ChannelInitializer,自定义一些入站和出站处理器并添加到channel的管道中。
4.2 主要组件介绍
ServerBootstrap、Bootstrap:服务器端、客户端的启动器类,组装参数并初始化。
NioServerSocketChannel、NioSocketChannel:Netty提供的服务器端、客户端的channel。
ServerSocketChannel、SocketChannel:NIO提供的服务器端、客户端的channel。
NioEventLoopGroup:事件循环组,相当于一个线程池,内部维护了一组事件循环。
NioEventLoop:事件循环,每个事件循环(NioEventLoop)都有一个Selector(选择器),Thread(线程),dispatch loop(分发循环),负责一个或多个Channel的IO事件,而且每个事件循环只有一个线程负责处理,因此一个Channel的读写自始至终都是由一个Thread负责,是线程安全的。
ChannelInitializer:一种特殊的入站处理器,提供将多个处理器一次性的安装到Channel的ChannelPipline上。
Future、ChannelFuture:保存异步结果的类,Netty继承类Java原生的java.util.concurrent.Future做了一些状态的拓展,因为java.util.concurrent.Future的返回结果isDone()无论是任务完成、取消、抛异常都返回true,我们无从得知任务的具体状态。加了一些方法,比如是否成功isSuccess()、是否异常cause()、是否可以取消isCancellable()等。
ChannelPipline:管道,用于保存ChannelHandler的列表,拦截入站和出站事件。
ChannelHandler:IO事件处理器接口,我们自定义的处理器只要继承其两个子类即可,ChannelInboundHandler用于拦截入站 I/O事件,ChannelOutboundHandler用于处理出站 I/O操作。这其实是一个拦截器,但是跟Intercepter的处理方式有相同也有不同,相同点是入站和出站处理的顺序相反,不同点在于Intercepter是进来和出去都要拦截,而ChannelInboundHandler仅拦截入站,ChannelOutboundHandler仅拦截出站。
ChannelHandlerContext:保存Channel相关的上下文信息,同时关联一个ChannelHandler。
五、源码分析
step 1: ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();
这一句代码会真正的开始执行初始化和启动。bind方法会去调用AbstractBootstrap类的doBind方法。
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();//step 2
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
step 2:final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
接着调用AbstractBootstrap类的initAndRegister方法
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();//step 3
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}step 3 : channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
这一步将调用ReflectiveChannelFactory类的newChannel方法生成一个实例。
public class ReflectiveChannelFactory implements ChannelFactory {
private final Class clazz;
public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class clazz) {
if (clazz == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("clazz");
}
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
return clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + clazz, t);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) + ".class";
}
} step 4:init(channel);
这一步将调用ServerBootstrap类的init方法。
@Override
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
//初始化属性开始
final Map, Object> options = options0();
synchronized (options) {
setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger);
}
final Map, Object> attrs = attrs0();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey 未完待续...