java反射机制(2)- 实践:反射机制+动态代理实现模拟RMI远程方法调用
转载请注明出处:反射机制+动态代理实现模拟RMI远程方法调用
1 涉及主要知识点
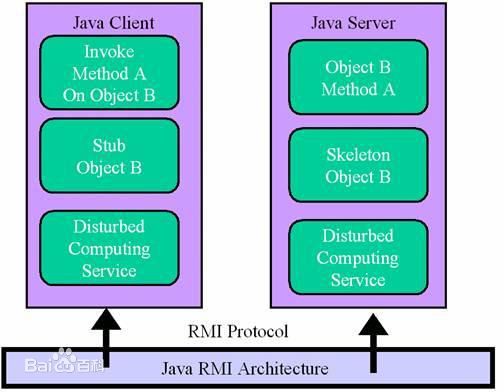
1、RMI(Remote Method Invocation):远程方法调用是一种计算机之间利用远程对象互相调用实现双方通讯的一种通讯机制。使用这种机制,某一台计算机上的对象可以调用另外 一台计算机上的对象来获取远程数据。RMI是Enterprise JavaBeans的支柱,是建立分布式Java应用程序的方便途径。RMI的基本框架如下图所示:
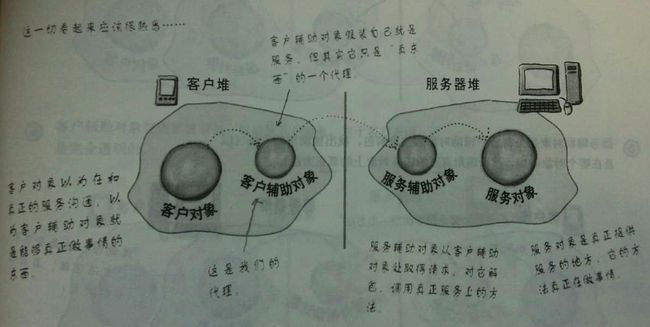
2、代理模式,可具体参考文章:JDK动态代理深入分析 本案例中的远程代理的基本模型如下:
2 项目详解
项目需求:客户端LocalClient请求调用远程服务器端RemoteServer的业务类RemoteService的方法getService,并将方法结果返回。其中将客户端请求方法的信息封装成Call对象,再将方法的返回结果设置进call对象中,即B/S之间传递call对象,因此Call对象需要实现Serializable接口。底层Socket通信由Connector负责。由于涉及到远程代理,这里采用JDK动态代理模式。采用工厂模式,根据给定的服务器的host和port,以及类名,由工厂RemoteServiceProxyFactory获取代理类。代理模式中,代理类和目标类需要实现共同的接口Service,客户端针对Service接口编程。
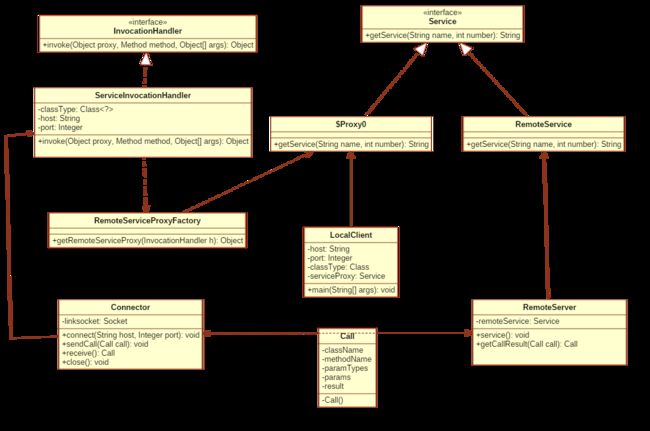
以上过程基本描述了所涉及到了类名,系统类结构图如下:
(1)创建代理类和目标类需要实现共同的接口Service。
package com.markliu.remote.service;
/**
* Service接口。代理类和被代理类抖需要实现该接口
*/
public interface Service {
public String getService(String name, int number);
}(2)服务器端创建RemoteService类,实现了Service 接口。
package com.markliu.remote.serviceimpl;
import com.markliu.remote.service.Service;
/**
* 服务器端目标业务类,被代理对象
*/
public class RemoteService implements Service {
@Override
public String getService(String name, int number) {
return name + ":" + number;
}
} (3)创建封装客户端请求和返回结果信息的Call类。
为了便于按照面向对象的方式来处理客户端与服务器端的通信,可以把它们发送的信息用 Call 类来表示。一个 Call 对象表示客户端发起的一个远程调用,它包括调用的类名或接口名、方法名、方法参数类型、方法参数值和方法执行结果。
package com.markliu.local.bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 请求的javabean
*/
public class Call implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5386052199960133937L;
private String className; // 调用的类名或接口名
private String methodName; // 调用的方法名
private Class[] paramTypes; // 方法参数类型
private Object[] params; // 调用方法时传入的参数值
/**
* 表示方法的执行结果 如果方法正常执行,则 result 为方法返回值,
* 如果方法抛出异常,那么 result 为该异常。
*/
private Object result;
public Call() {}
public Call(String className, String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] params) {
this.className = className;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.paramTypes = paramTypes;
this.params = params;
}
// 省略了get和set方法
}(4)创建动态代理模式中实际的业务处理类,实现了InvocationHandler 接口。
package com.markliu.local.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import com.markliu.local.bean.Call;
public class ServiceInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Class classType;
private String host;
private Integer port;
public Class getClassType() {
return classType;
}
public ServiceInvocationHandler(Class classType, String host, Integer port) {
this.classType = classType;
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 封装请求信息
Call call = new Call(classType.getName(), method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes(), args);
// 创建链接
Connector connector = new Connector();
connector.connect(host, port);
// 发送请求
connector.sendCall(call);
// 获取封装远程方法调用结果的对象
connector.close();
Object returnResult = call.getResult();
return returnResult;
}
}(5)创建获取代理类的工厂RemoteServiceProxyFactory。
package com.markliu.local.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 动态创建RemoteService代理类的工厂
*/
public class RemoteServiceProxyFactory {
public static Object getRemoteServiceProxy(InvocationHandler h) {
Class classType = ((ServiceInvocationHandler) h).getClassType();
// 获取动态代理类
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classType.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{classType}, h);
return proxy;
}
}(6)创建底层Socket通信的Connector类,负责创建拦截、发送和接受Call对象。
package com.markliu.local.service;
// 省略import
/**
* 负责创建链接
*/
public class Connector {
private Socket linksocket;
private InputStream in;
private ObjectInputStream objIn;
private OutputStream out;
private ObjectOutputStream objOut;
public Connector(){}
/**
* 创建链接
*/
public void connect(String host, Integer port) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
linksocket = new Socket(host, port);
in = linksocket.getInputStream();
out = linksocket.getOutputStream();
objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
objIn = new ObjectInputStream(in);
}
/**
* 发送请求call对象
*/
public void sendCall(Call call) throws IOException {
objOut.writeObject(call);
}
/**
* 获取请求对象
*/
public Call receive() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
return (Call) objIn.readObject();
}
/**
* 简单处理关闭链接
*/
public void close() {
try {
linksocket.close();
objIn.close();
objOut.close();
in.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}(7)创建远程服务器。
package com.markliu.remote.main;
// 省略import
public class RemoteServer {
private Service remoteService;
public RemoteServer() {
remoteService = new RemoteService();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RemoteServer server = new RemoteServer();
System.out.println("远程服务器启动......DONE!");
server.service();
}
public void service() throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8001);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream(in);
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
// 对象输入流读取请求的call对象
Call call = (Call) objIn.readObject();
System.out.println("客户端发送的请求对象:" + call);
call = getCallResult(call);
// 发送处理的结果回客户端
objOut.writeObject(call);
objIn.close();
in.close();
objOut.close();
out.close();
socket.close();
}
}
/**
* 通过反射机制调用call中指定的类的方法,并将返回结果设置到原call对象中
*/
private Call getCallResult(Call call) throws Exception {
String className = call.getClassName();
String methodName = call.getMethodName();
Object[] params = call.getParams();
Class[] paramsTypes = call.getParamTypes();
Class classType = Class.forName(className);
// 获取所要调用的方法
Method method = classType.getMethod(methodName, paramsTypes);
Object result = method.invoke(remoteService, params);
call.setResult(result);
return call;
}
}(8)创建本地客户端。
package com.markliu.local.main;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import com.markliu.local.service.RemoteServiceProxyFactory;
import com.markliu.local.service.ServiceInvocationHandler;
import com.markliu.remote.service.Service;
public class LocalClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "127.0.0.1";
Integer port = 8001;
Class classType = com.markliu.remote.service.Service.class;
InvocationHandler h = new ServiceInvocationHandler(classType, host, port);
Service serviceProxy = (Service) RemoteServiceProxyFactory.getRemoteServiceProxy(h);
String result = serviceProxy.getService("SunnyMarkLiu", 22);
System.out.println("调用远程方法getService的结果:" + result);
}
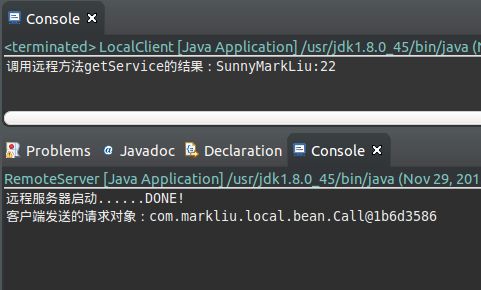
} LocalClient 调用 RemoteServer 端的RemoteService对象的 getService(name,age)方法的运行结果如下:
3 发现的问题
Socket同时使用ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream传输序列化对象时的顺序问题:
在网络通讯中,主机与客户端若使用ObjectInputStream与ObjectOutputStream建立对象通讯,必须注重声明此两个对象的顺序。
服务器端先建立ObjectInputStream后建立ObjectOutputStream,则对应地客户端要先建立ObjectOutputStream后建立ObjectInputStream,否则会造成两方互相等待数据而导致死锁。
原因是建立ObjectInputStream对象时需要先接收一定的header数据,接收到这些数据之前会处于阻塞状态。
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException的官方API显示:
Creates an ObjectInputStream that reads from the specified InputStream. A serialization stream header is read from the stream and verified. This constructor will block until the corresponding ObjectOutputStream has written and flushed the header.
在创建ObjectInputStream对象时会检查ObjectOutputStream所传过来了头信息,如果没有信息将一直会阻塞。
正确的做法:
Server:
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); Client:
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); 此问题摘自ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream传输序列化对象时的顺序
4 极客秘籍
现在我们有一个有趣的问题,就是客户端在创建动态代理类时候,需要有服务器端的Service接口和RemoteService类,否则客户端在调用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法是会报找不到类类型和接口等错误。本案例中简单的采用将这些类复制一份到客户端。
还有一种不错的方式-动态类下载。以上这些类可以“贴上”URL,告诉客户端RMI系统去寻找需要的类文件。创建动态代理类的时候,如果本地没有发现这些类,则从根据URL下载类文件。所以需要一个简单的Web服务器来提供这些类文件,也需要提供客户端的安全参数等。
完整案例源代码:反射机制+代理模式实现模拟RMI远程方法调用.zip