操作系统ucore lab6实验报告
练习0
填写已有实验
本实验依赖实验1~实验5.请把已做的实验2~实验5的代码填入本实验中代码中有lab1、lab2、lab3、lab4、lab5的注释相应部分,并确保编译通过。注意:为了能够正确执行lab6的测试应用程序,可能需对已完成的实验1~实验5的代码进一步改进
发现缺失的是kdebug.c、trap.c、default_pmm.c、pmm.c、swap_fifo.c、vmm.c、proc.c七个文件的相关代码,补全后发现部分文件还需要更改部分代码
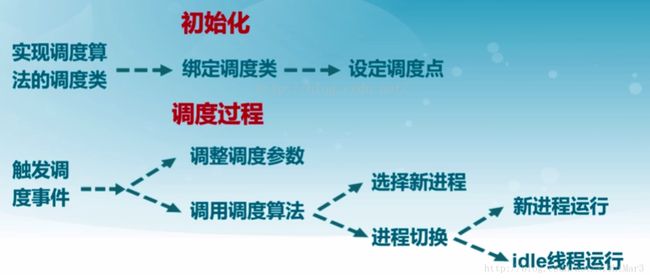
lab6的整体思想
根据整体思想,结合注释的提示,主要是一下两个函数需要额外加以修改。
alloc_proc函数
这里alloc_proc还需要修改一下,完整的代码如下:
// alloc_proc - alloc a proc_struct and init all fields of proc_struct
static struct proc_struct *
alloc_proc(void) {
struct proc_struct *proc = kmalloc(sizeof(struct proc_struct));
if (proc != NULL) {
//LAB4:EXERCISE1 YOUR CODE
/*
* below fields in proc_struct need to be initialized
* enum proc_state state; // Process state
* int pid; // Process ID
* int runs; // the running times of Proces
* uintptr_t kstack; // Process kernel stack
* volatile bool need_resched; // bool value: need to be rescheduled to release CPU?
* struct proc_struct *parent; // the parent process
* struct mm_struct *mm; // Process's memory management field
* struct context context; // Switch here to run process
* struct trapframe *tf; // Trap frame for current interrupt
* uintptr_t cr3; // CR3 register: the base addr of Page Directroy Table(PDT)
* uint32_t flags; // Process flag
* char name[PROC_NAME_LEN + 1]; // Process name
*/
//LAB5 YOUR CODE : (update LAB4 steps)
/*
* below fields(add in LAB5) in proc_struct need to be initialized
* uint32_t wait_state; // waiting state
* struct proc_struct *cptr, *yptr, *optr; // relations between processes
*/
//LAB6 YOUR CODE : (update LAB5 steps)
/*
* below fields(add in LAB6) in proc_struct need to be initialized
* struct run_queue *rq; // running queue contains Process
* list_entry_t run_link; // the entry linked in run queue
* int time_slice; // time slice for occupying the CPU
* skew_heap_entry_t lab6_run_pool; // FOR LAB6 ONLY: the entry in the run pool
* uint32_t lab6_stride; // FOR LAB6 ONLY: the current stride of the process
* uint32_t lab6_priority; // FOR LAB6 ONLY: the priority of process, set by lab6_set_priority(uint32_t)
*/
proc->state = PROC_UNINIT;//设置进程为未初始化状态
proc->pid = -1; //未初始化的进程id=-1
proc->runs = 0; //初始化时间片
proc->kstack = 0; //初始化内存栈的地址
proc->need_resched = 0; //是否需要调度设为不需要
proc->parent = NULL; //置空父节点
proc->mm = NULL; //置空虚拟内存
memset(&(proc->context), 0, sizeof(struct context));//初始化上下文
proc->tf = NULL; //中断帧指针设置为空
proc->cr3 = boot_cr3; //页目录设为内核页目录表的基址
proc->flags = 0; //初始化标志位
memset(proc->name, 0, PROC_NAME_LEN);//置空进程名
proc->wait_state = 0; //初始化进程等待状态
//*cptr-->children | *yptr-->younger | *optr-->older
proc->cptr=proc->yptr=proc->optr = NULL;//进程相关指针初始化
proc->rq = NULL;//置运行队列为空
//该进程的调度链表结构,该结构内部的链接组成了运行队列列表
list_init(&(proc->run_link));//初始化运行队列的指针
//该进程剩余的时间片,只对当前进程有效
proc->time_slice = 0;//初始化时间片
//该进程在优先队列中的节点,仅在lab6中使用
proc->lab6_run_pool.left = proc->lab6_run_pool.right = proc->lab6_run_pool.parent = NULL; //初始化各类指针为空
//该进程的调度步进值,仅在lab6中使用
proc->lab6_stride = 0;//初始化当前运行步数
//该进程的调度优先级,仅在lab6中使用
proc->lab6_priority = 0;//初始化优先级
}
return proc;
}由于实验要求实现调度器,为了保证调度器接口的通用性,添加了几个变量仅在lab6中使用,便于实验
trap_dispatch函数
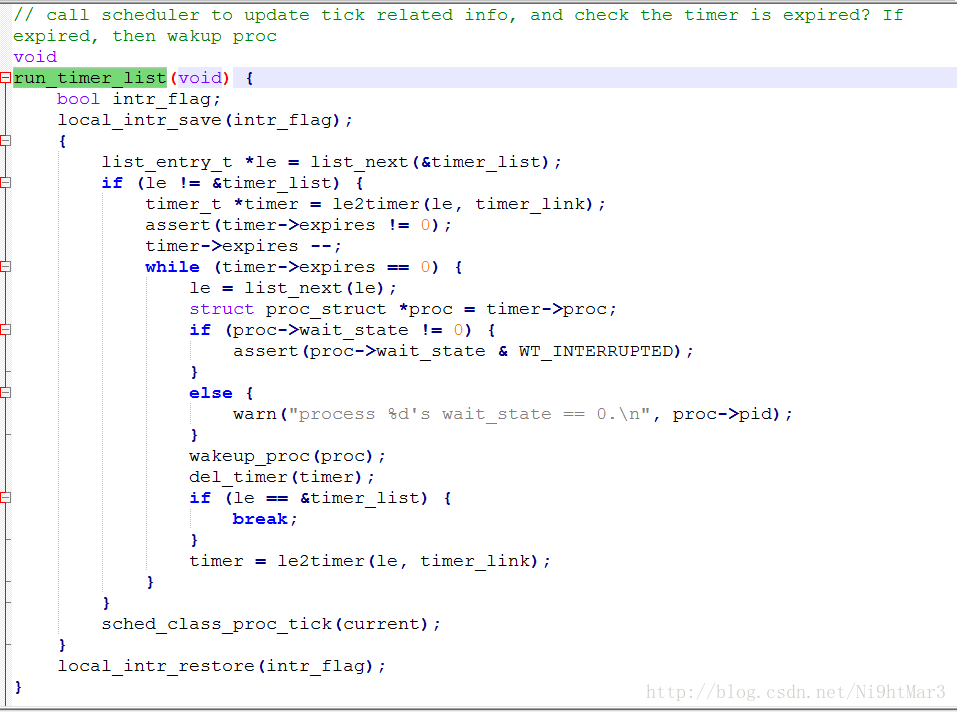
![]()
通过查看一下相关函数的定义,根据提示,每当时钟产生一滴答,更新当前系统时间点,遍历当前所有处在系统管理内的计时器,找出所有应该激活的计数器,并激活他们
代码:
static void
trap_dispatch(struct trapframe *tf) {
......
......
ticks ++;
assert(current != NULL);
run_timer_list(); //更新定时器,并根据参数调用调度算法
break;
......
......
}练习1
使用
Round Robin调度算法(不需要编码)
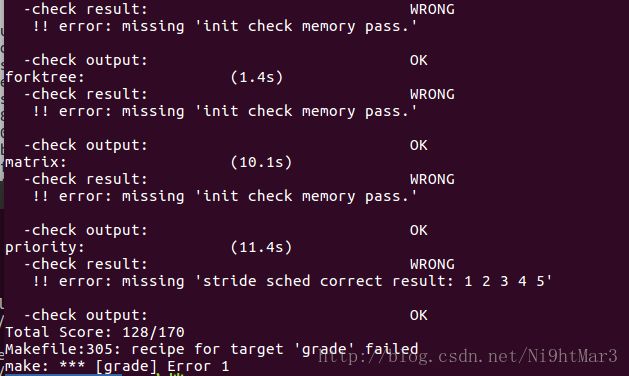
完成练习0后,建议大家比较一下个人完成的lab5和练习0完成后的刚修改的lab6之间的区别,分析了解lab6采用RR调度算法后的执行过程。执行make grade,大部分测试用例应该通过。但执行priority.c应该过不去
算法原理
让所有runnable态的进程分时轮流使用CPU时间。RR调度器维护当前runnable进程的有序运行队列。当前进程的时间片用完之后,调度器将当前进程放置到运行队列的尾部,再从其头部取出进程进行调度。
RR调度算法的就绪队列在组织结构上也是一个双向链表,只是增加了一个成员变量,表明在此就绪进程队列中的最大执行时间片。而且在进程控制块proc_struct中增加了一个成员变量time_slice,用来记录进程当前的可运行时间片段。这是由于RR调度算法需要考虑执行进程的运行时间不能太长。在每个timer到时的时候,操作系统会递减当前执行进程的time_slice,当time_slice为0时,就意味着这个进程运行了一段时间(这个时间片段称为进程的时间片),需要把CPU让给其他进程执行,于是操作系统就需要让此进程重新回到rq的队列尾,且重置此进程的时间片为就绪队列的成员变量最大时间片max_time_slice值,这表示如果进程在当前的执行时间片已经用完,需要等到下一次有机会运行时,才能再执行一段时间,然后再从rq的队列头取出一个新的进程执行。
具体过程
这里Round Robin调度算法的主要实现在default_sched.c之中
RR_init函数
RR_enqueue函数
首先,它把进程的进程控制块指针放入到rq队列末尾,且如果进程控制块的时间片为0,则需要把它重置为max_time_slice。这表示如果进程在当前的执行时间片已经用完,需要等到下一次有机会运行时,才能再执行一段时间。然后在依次调整rq和rq的进程数目加一。

RR_dequeue函数
把就绪进程队列rq的进程控制块指针的队列元素删除,并把表示就绪进程个数的proc_num减一。

RR_pick_next函数
选取函数,即选取就绪进程队列rq中的队头队列元素,并把队列元素转换成进程控制块指针。

RR_proc_tick函数
即每一次时间片到时的时候,当前执行进程的时间片time_slice便减一。如果time_slice降到零,则设置此进程成员变量need_resched标识为1,设置为需要调度,这样在下一次中断来后执行trap函数时,会执行schedule函数,然后把当前执行进程放回就绪队列末尾,而从就绪队列头取出等待时间最久的那个就绪进程执行。

default_sched_class
练习2
实现
Stride Scheduling调度算法
首先需要换掉RR调度器的实现,即用default_sched_stride_c覆盖default_sched.c.然后 根据此文件和后续文档对Strided调度器的相关描述,完成Stride调度算法的实现
首先,根据的要求覆盖掉Round Robin调度算法。
覆盖掉之后需要在该框架上实现Stride Scheduling调度算法。
基本思想
- 1、为每个
runnable的进程设置一个当前状态stride,表示该进程当前的调度权。另外定义其对应的pass值,表示对应进程在调度后,stride 需要进行的累加值。 - 2、每次需要调度时,从当前
runnable态的进程中选择 stride最小的进程调度。对于获得调度的进程P,将对应的stride加上其对应的步长pass(只与进程的优先权有关系)。 - 3、在一段固定的时间之后,回到步骤2,重新调度当前stride最小的进程
proc_stride_comp_f函数
/* You should define the BigStride constant here*/
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE */
#define BIG_STRIDE 0x7FFFFFFF /* 定义一个大整数处以优先级 */
/* The compare function for two skew_heap_node_t's and the
* corresponding procs*/
static int
proc_stride_comp_f(void *a, void *b)
{
struct proc_struct *p = le2proc(a, lab6_run_pool);
struct proc_struct *q = le2proc(b, lab6_run_pool);
int32_t c = p->lab6_stride - q->lab6_stride;//步数相减,通过正负比较大小关系
if (c > 0) return 1;
else if (c == 0) return 0;
else return -1;
}stride_init函数
首先初始化调度器类的信息,初始化运行队列为一个空的容器结构,然后设置当前运行队列内进程数目为0。
/*
* stride_init initializes the run-queue rq with correct assignment for
* member variables, including:
*
* - run_list: should be a empty list after initialization.
* - lab6_run_pool: NULL
* - proc_num: 0
* - max_time_slice: no need here, the variable would be assigned by the caller.
*
* hint: see libs/list.h for routines of the list structures.
*/
static void
stride_init(struct run_queue *rq) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE
* (1) init the ready process list: rq->run_list
* (2) init the run pool: rq->lab6_run_pool
* (3) set number of process: rq->proc_num to 0
*/
list_init(&(rq->run_list));//初始化调度器类的信息
rq->lab6_run_pool = NULL;//初始化当前的运行队列为一个空的容器结构。
rq->proc_num = 0;//设置rq->proc_num为 0
}stride_enqueue函数
- 初始化刚进入运行队列的进程
proc的stride属性。 - 比较队头元素与当前进程的步数大小,选择步数最小的运行,将
proc插入放入运行队列中去(注意:这里并不要求放置在队列头部)。 - 最后初始化时间片,然后将运行队列进程数目加一。
/*
* stride_enqueue inserts the process ``proc'' into the run-queue
* ``rq''. The procedure should verify/initialize the relevant members
* of ``proc'', and then put the ``lab6_run_pool'' node into the
* queue(since we use priority queue here). The procedure should also
* update the meta date in ``rq'' structure.
*
* proc->time_slice denotes the time slices allocation for the
* process, which should set to rq->max_time_slice.
*
* hint: see proj13.1/libs/skew_heap.h for routines of the priority
* queue structures.
*/
static void
stride_enqueue(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE */
#if USE_SKEW_HEAP
//在使用优先队列的实现中表示当前优先队列的头元素
rq->lab6_run_pool = skew_heap_insert(rq->lab6_run_pool, &(proc->lab6_run_pool), proc_stride_comp_f);//比较队头元素与当前进程的步数大小,选择步数最小的运行
#else
assert(list_empty(&(proc->run_link)));
list_add_before(&(rq->run_list), &(proc->run_link));//将 proc插入放入运行队列中去
#endif
if (proc->time_slice == 0 || proc->time_slice > rq->max_time_slice)
{//初始化时间片
proc->time_slice = rq->max_time_slice;
}
proc->rq = rq;
rq->proc_num ++;
}stride_dequeue函数
从运行队列中删除相应的元素,完成将一个进程从队列中移除的功能,使用优先队列。最后运行队列数目减一。
/*
* stride_dequeue removes the process ``proc'' from the run-queue
* ``rq'', the operation would be finished by the skew_heap_remove
* operations. Remember to update the ``rq'' structure.
*
* hint: see proj13.1/libs/skew_heap.h for routines of the priority
* queue structures.
*/
static void
stride_dequeue(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE */
#if USE_SKEW_HEAP
rq->lab6_run_pool =
skew_heap_remove(rq->lab6_run_pool, &(proc->lab6_run_pool), proc_stride_comp_f);// 在斜堆中删除相应元素
#else
assert(!list_empty(&(proc->run_link)) && proc->rq == rq);
list_del_init(&(proc->run_link));// 从运行队列中删除相应元素
#endif
rq->proc_num --;
}stride_pick_next函数
- 扫描整个运行队列,返回其中stride值最小的对应进程。
- 更新对应进程的stride值,即pass = BIG_STRIDE / P->priority; P->stride += pass。将步长设置为优先级的倒数,如果为0则设置为最大的步长。
/*
* stride_pick_next pick the element from the ``run-queue'', with the
* minimum value of stride, and returns the corresponding process
* pointer. The process pointer would be calculated by macro le2proc,
* see proj13.1/kern/process/proc.h for definition. Return NULL if
* there is no process in the queue.
*
* When one proc structure is selected, remember to update the stride
* property of the proc. (stride += BIG_STRIDE / priority)
*
* hint: see proj13.1/libs/skew_heap.h for routines of the priority
* queue structures.
*/
static struct proc_struct *
stride_pick_next(struct run_queue *rq) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE */
#if USE_SKEW_HEAP
if (rq->lab6_run_pool == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//找到相应指针指向rq->lab6_run_pool
struct proc_struct *p = le2proc(rq->lab6_run_pool, lab6_run_pool);
#else
list_entry_t *le = list_next(&(rq->run_list));
if (le == &rq->run_list)
{
return NULL;
}
struct proc_struct *p = le2proc(le, run_link);
le = list_next(le);
while (le != &rq->run_list)
{
struct proc_struct *q = le2proc(le, run_link);
if ((int32_t)(p->lab6_stride - q->lab6_stride) > 0)
{
p = q;
}
le = list_next(le);
}
#endif
if (p->lab6_priority == 0)//优先级设置
{
//步长为0则设置为最大步长保持相减的有效性
p->lab6_stride += BIG_STRIDE;
}
else
{
//步长设置为优先级的倒数
p->lab6_stride += BIG_STRIDE / p->lab6_priority;
}
return p;
} stride_proc_tick函数
- 检测当前进程是否已用完分配的时间片。如果时间片用完,应该正确设置进程结构的相关标记来引起进程切换。
- 一个* process *最多可以连续运行
rq.max_time_slice个时间片。
具体思想同RR算法思想
/*
* stride_proc_tick works with the tick event of current process. You
* should check whether the time slices for current process is
* exhausted and update the proc struct ``proc''. proc->time_slice
* denotes the time slices left for current
* process. proc->need_resched is the flag variable for process
* switching.
*/
static void
stride_proc_tick(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE */
if (proc->time_slice > 0)
{
proc->time_slice --;
}
if (proc->time_slice == 0)
{
proc->need_resched = 1;
}
} default_sched_class
定义一个c语言类的实现,提供调度算法的切换接口
struct sched_class default_sched_class = {
.name = "stride_scheduler",
.init = stride_init,
.enqueue = stride_enqueue,
.dequeue = stride_dequeue,
.pick_next = stride_pick_next,
.proc_tick = stride_proc_tick,
}; 实验结果
对比实验指导书,实验成功!
收获
通过这次实验,掌握了进程切换的原理,并且对RR调度算法的原理和在Ucore中的实现方法更加熟悉,通过对Stride Schedule算法的分析,对其原理和算法可控性和确定性有了更深的认识。但是,对优先队列的实现方法和操作过程还是存在不熟悉的地方,不能熟练的掌握