Spring AOP面向切面编程详解(基于XML方式 注解方式 注入Aspectj方式)
前言
AOP即面向切面编程,是一种编程思想,OOP的延续。在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题,比如日志,事务,权限等等。在阅读本文前希望您已经对Spring有一定的了解
注:在能对代码进行添加注解方式实现AOP的话,并不推荐使用XML方式。换言之在XML方式配置更适用于不能对代码添加注解的情况下(注解配置方式推荐值>XML配置方式推荐值)
AOP相关术语
1.通知(Advice):在切面的某个特定的连接点上执行的动作,即当程序到达一个执行点后会执行相对应的一段代码,也称为增强处理。通知共有如下5种类型[前置通知 后置通知 返回通知 环绕通知 抛出异常后通知]
2.连接点(JoinPoint):程序执行的某个特定位置,例如类初始化前,类初始化后,方法执行前,方法执行后,方法抛出异常时等,Spring只支持方法级别的连接点,即方法执行前,方法执行后,方法抛出异常时
3.切入点(Pointcut):切入点是一个筛选连接点的过程,因为在你的工程中可能有很多连接点,你只是想让其中几个,在调用这几个方法之前、之后或者抛出异常时干点什么,那么就用切入点来定义这几个方法,让切点来筛选连接点,选中那几个你想要的方法
4.切面(Aspect):切面通常是指一个类,是通知和切入点的结合。到这里会发现连接点就是为了让你好理解切点产生的。通俗来说切面的配置可以理解为:什么时候在什么地方做什么事。切入点说明了在哪里干(指定到方法),通知说明了什么时候干什么
5.引入(Introduction):引入允许我们向现有的类添加新方法或属性
6.织入(Weaving):把切面应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程,织入一般发生在如下几个时机:
(1)编译时:当一个类文件被编译时进行织入,这需要特殊的编译器才可以做的到,例如AspectJ的织入编译器
(2)类加载时:使用特殊的ClassLoader在目标类被加载到程序之前增强类的字节代码
(3)运行时:切面在运行的某个时刻被织入,SpringAOP就是以这种方式织入切面的,原理应该是使用了JDK的动态代理技术基于XML方式配置AOP
正常通知
1.编写业务类
public class HelloWorldBusiness {
public String sayHelloWorld(String language) {
String result = "Hello World " + language;
System.out.println("真正的业务方法执行啦~~~");
return result;
}
}2.编写切面类
public class HelloWorldBusinessAspect {
public void beforeSayHelloWorld(String language) {
System.out.println("执行方法前运行,参数为:" + language);
}
public void afterSayHelloWorld(String language) {
System.out.println("执行方法后运行,参数为:" + language);
}
public void afterReturningSayHelloWorld(String language, String result) {
System.out.println("执行方法返回后运行,参数为:" + language + " 方法返回值为:" + result);
}
public void afterThrowingHelloWorld(String language, Throwable e) {
System.out.println("执行方法抛出异常后运行,参数为:" + language + "异常为:" + e);
}
}3.编写配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorldBusiness" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness" />
<bean id="helloWorldBusinessAspect" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusinessAspect" />
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="helloWorldAspect" ref="helloWorldBusinessAspect">
<aop:pointcut id="sayHelloWorldPoint" expression="execution(public * roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness.sayHelloWorld(..)) and args(language)" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="sayHelloWorldPoint" method="beforeSayHelloWorld" arg-names="language"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="sayHelloWorldPoint" method="afterSayHelloWorld" arg-names="language"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="sayHelloWorldPoint" method="afterReturningSayHelloWorld" arg-names="language,result" returning="result" />
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="sayHelloWorldPoint" method="afterThrowingHelloWorld" arg-names="language,e" throwing="e" />
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>4.运行HelloWorldBusiness的sayHelloWorld方法输出结果为
执行方法前运行,参数为:JAVA
真正的业务方法执行啦~~~
执行方法后运行,参数为:JAVA
执行方法返回后运行,参数为:JAVA 方法返回值为:Hello World JAVA环绕通知
1.编写业务类
public class HelloWorldBusiness {
public String sayHelloWorld(String language) {
String result = "Hello World " + language;
System.out.println("真正的业务方法执行啦~~~");
return result;
}
}2.编写切面类
public class HelloWorldBusinessAspect {
public void aroundSayHelloWorld(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
String language = (String) joinPoint.getArgs()[0];
try {
System.out.println("执行方法前运行,参数为:" + language);
String result = (String) joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("执行方法后运行,参数为:" + language + " 方法返回值为:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("执行方法抛出异常后运行,参数为:" + language + "异常为:" + e);
}
}
}3.编写配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorldBusiness" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness" />
<bean id="helloWorldBusinessAspect" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusinessAspect" />
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="helloWorldAspect" ref="helloWorldBusinessAspect">
<aop:pointcut id="sayHelloWorldPoint" expression="execution(public * roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness.sayHelloWorld(..))" />
<aop:around pointcut-ref="sayHelloWorldPoint" method="aroundSayHelloWorld" />
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>4.运行HelloWorldBusiness的sayHelloWorld方法输出结果为
执行方法前运行,参数为:JAVA
真正的业务方法执行啦~~~
执行方法后运行,参数为:JAVA 方法返回值为:Hello World JAVA使用MethodInterceptor实现AOP
1.编写业务类
public class HelloWorldBusiness {
public String sayHelloWorld(String language) {
String result = "Hello World " + language;
System.out.println("真正的业务方法执行啦~~~");
return result;
}
}2.编写拦截器类 实现MethodInterceptor方法
public class HelloWorldBusinessAspect implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取被增强对象参数列表
String language = (String) invocation.getArguments()[0];
// 获取被增强对象的方法
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
// 继续执行业务方法
System.out.println("执行" + method.getName() + "方法前运行,参数为: " + language);
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("执行方法返回后运行,参数为:" + language + " 方法返回值为:" + result);
return result;
}
}3.编写配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorldBusiness" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness" />
<bean id="helloWorldBusinessAspect" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusinessAspect" />
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="sayHelloWorldPoint" expression="execution(public * roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness.sayHelloWorld(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="helloWorldBusinessAspect" pointcut-ref="sayHelloWorldPoint" />
aop:config>
beans>4.运行HelloWorldBusiness的sayHelloWorld方法输出结果为
执行sayHelloWorld方法前运行,参数为: JAVA
真正的业务方法执行啦~~~
执行方法返回后运行,参数为:JAVA 方法返回值为:Hello World JAVA注意事项
1.在Spring的配置文件中,所有的切面和通知都必须定义在<aop:config>元素内部。(一个application context可以包含多个<aop:config>)。一个<aop:config>可以包含pointcut,advisor和aspect元素(注意这三个元素必须按照这个顺序进行声明)
2.当我们使用<aop:config/>方式进行配置时,可能与Spring的自动代理方式相互冲突(<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>),因此,建议要么全部使用<aop:config/>配置方式,要么全部使用自动代理方式,不要把两者混合使用基于注解方式配置AOP
正常通知
1.编写业务类
@Component
public class HelloWorldBusiness {
public String sayHelloWorld(String language) {
String result = "Hello World " + language;
System.out.println("真正的业务方法执行啦~~~");
return result;
}
}2.编写切面类
@Aspect
@Component
public class HelloWorldBusinessAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness.sayHelloWorld(..)) && args(language)")
public void sysHelloWorldPointCut(String language) {
}
@Before("sysHelloWorldPointCut(language)")
public void beforeSayHelloWorld(String language) {
System.out.println("执行方法前运行,参数为:" + language);
}
@After("sysHelloWorldPointCut(language)")
public void afterSayHelloWorld(String language) {
System.out.println("执行方法后运行,参数为:" + language);
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "sysHelloWorldPointCut(language)", returning = "result")
public void afterReturningSayHelloWorld(String language, String result) {
System.out.println("执行方法返回后运行,参数为:" + language + " 方法返回值为:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "sysHelloWorldPointCut(language)", throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowingHelloWorld(String language, Throwable e) {
System.out.println("执行方法抛出异常后运行,参数为:" + language + "异常为:" + e);
}
}3.编写配置类(使用EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解启用自动代理功能)
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "roberto.growth.process")
public class ApplicationConfig {
}4.运行HelloWorldBusiness的sayHelloWorld方法输出结果为
执行方法前运行,参数为:JAVA
真正的业务方法执行啦~~~
执行方法后运行,参数为:JAVA
执行方法返回后运行,参数为:JAVA 方法返回值为:Hello World JAVA环绕通知
1.编写业务类
@Component
public class HelloWorldBusiness {
public String sayHelloWorld(String language) {
String result = "Hello World " + language;
System.out.println("真正的业务方法执行啦~~~");
return result;
}
}2.编写切面类
@Aspect
@Component
public class HelloWorldBusinessAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * roberto.growth.process.aop.HelloWorldBusiness.sayHelloWorld(..))")
public void sysHelloWorldPointCut() {
}
@Around("sysHelloWorldPointCut()")
public void aroundSayHelloWorld(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
String language = (String) joinPoint.getArgs()[0];
try {
System.out.println("执行方法前运行,参数为:" + language);
String result = (String) joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("执行方法后运行,参数为:" + language + " 方法返回值为:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("执行方法抛出异常后运行,参数为:" + language + "异常为:" + e);
}
}
}3.编写配置类(使用EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解启用自动代理功能)
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "roberto.growth.process")
public class ApplicationConfig {
}4.运行HelloWorldBusiness的sayHelloWorld方法输出结果为
执行方法前运行,参数为:JAVA
真正的业务方法执行啦~~~
执行方法后运行,参数为:JAVA 方法返回值为:Hello World JAVA纯AspectJ方式配置AOP
虽然Spring AOP能够满足许多应用的切面要求,但是与AspectJ相比,Spring AOP是一个功能比较弱的AOP解决方案,AspectJ提供了Spring AOP所不能支持的许多类型的切点,例如构造器切点等
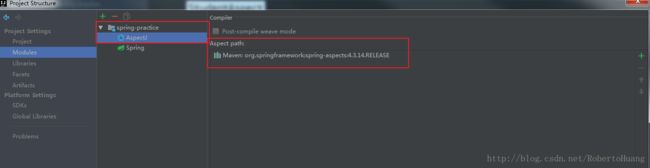
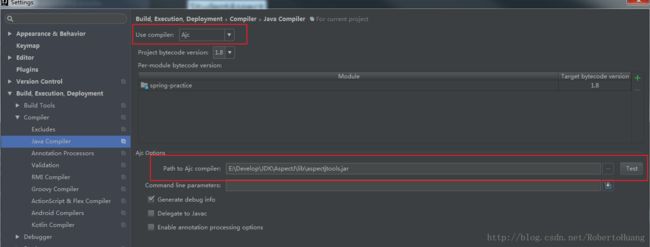
1.本地安装好AspectJ环境(具体安装自行百度)
3.编写Aspect Demo使用AspectJ实现AOP功能
3.1.创建学生类
public class Student {
public Student() {
System.out.println("构造方法执行了");
}
public void doHomeWork(){
System.out.println("学生开始做功课啦~~~");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.doHomeWork();
}
}3.2.创建AspectJ切面
public aspect StudentAspect {
// 创建构造器切点
pointcut constructPointCut():call(roberto.growth.process.aop.Student.new());
before():constructPointCut(){
System.out.println("创建学生对象前调用");
}
after():constructPointCut(){
System.out.println("创建学生对象后调用");
}
// 创建学生做功课方法切点
pointcut doHomeWorkPointCut():execution(public * roberto.growth.process.aop.Student.doHomeWork(..));
before():doHomeWorkPointCut(){
System.out.println("学生做功课前");
}
after():doHomeWorkPointCut(){
System.out.println("学生做功课后");
}
}3.3.运行学生类的main方法,查看输出结果
创建学生对象前调用
构造方法执行了
创建学生对象后调用
学生做功课前
学生开始做功课啦~~~
学生做功课后注意:由于AspectJ是在编译时期进行织入,所以在运行main方法前最好先手动编译一下
切入点相关
切入点表达式
本篇文章不介绍切入点表达式语法,与需要的读者可以参考切入点表达式可参考: 切入点表达式
切入点执行顺序
在配置切面和通知的时候,可以指定order参数来区分切入执行先后顺序,order的值越小说明越先被执行
XML方式:"helloWorldAspect" ref="helloWorldBusinessAspect" order="0">
Aspect类添加注解:org.springframework.core.annotation.Order
Aspect类实现接口:org.springframework.core.Ordered实现Ordered接口的getOrder()方法即可 基于注解方式引入新功能
Demo:为程序员添加歌手的属性,让程序员成为斜杠青年
1.编写程序员类
public interface Programmer {
public void coding();
}
@Component
public class ProgrammerImpl implements Programmer{
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("写最好的代码");
}
}2.编写歌手类
public interface Singer {
void sing();
}
public class DefaultSinger implements Singer{
@Override
public void sing() {
System.out.println("唱最动听的歌");
}
}3.编写歌手引入切面 为程序员添加歌手特性
@Aspect
@Component
public class SingerAspect {
@DeclareParents(value = "roberto.growth.process.aop.Programmer+", defaultImpl = DefaultSinger.class)
public static Singer singer;
}4.编写配置类(使用EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解启用自动代理功能)
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "roberto.growth.process")
public class ApplicationConfig {
}5.测试输出结果如下:(程序员即可以写代码也可以唱歌)
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = ApplicationConfig.class)
public class StudentTest {
@Autowired
private Programmer programmer;
@Test
public void testSayHelloWorld() {
System.out.println("这个程序员是个歌手吗:" + (programmer instanceof Singer));
programmer.coding();
((Singer) programmer).sing();
}
}
控制台输出:
这个程序员是个歌手吗:true
写最好的代码
唱最动听的歌基于XML方式引入新功能
Demo:为程序员添加歌手的属性,让程序员成为斜杠青年
1.编写程序员类
public interface Programmer {
public void coding();
}
public class ProgrammerImpl implements Programmer{
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("写最好的代码");
}
}2.编写歌手类
public interface Singer {
void sing();
}
public class DefaultSinger implements Singer{
@Override
public void sing() {
System.out.println("唱最动听的歌");
}
}3.编写配置文件引入切面 为程序员添加歌手特性
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="programmer" class="roberto.growth.process.aop.ProgrammerImpl" />
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect>
<aop:declare-parents types-matching="(roberto.growth.process.aop.Programmer+)" implement-interface="roberto.growth.process.aop.Singer" default-impl="roberto.growth.process.aop.DefaultSinger" />
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>
4.测试输出结果如下:(程序员即可以写代码也可以唱歌)
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class StudentTest {
@Autowired
private Programmer programmer;
@Test
public void testSayHelloWorld() {
System.out.println("这个程序员是个歌手吗:" + (programmer instanceof Singer));
programmer.coding();
((Singer) programmer).sing();
}
}
控制台输出:
这个程序员是个歌手吗:true
写最好的代码
唱最动听的歌