《APUE》笔记-第四章-文件和目录
1.引言
本章内容:
struct stat、修改struct stat结构的API,目录、文件系统、符号链接
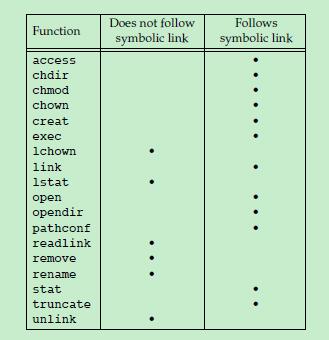
注:因为符号链接也是一种文件,所以很多函数都要区分是否跟随符号链接。跟随,则得到的是符号链接指向的文件信息;不跟随,则得到的是符号链接本身的信息。
2.stat、 fstat、 lstat、 fstatat
文件的信息全部存储在struct stat里
struct stat
{
mode_t st_mode; /* file type & mode (permissions) */
ino_t st_ino; /* i-node number (serial number) */
dev_t st_dev; /* device number (file system) */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device number for special files */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
off_t st_size; /* size in bytes, for regular files */
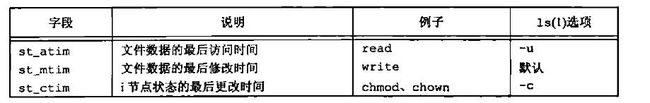
struct timespec st_atim; /* time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* time of last file status change */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* best I/O block size */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of disk blocks allocated */
};
其中:
struct timespec
{
time_t tv_sec;//秒
long tv_nsec;//纳秒
};
#include
int stat(const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf );//跟随符号链接
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf );//跟随符号链接
int lstat(const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf );//不跟随符号链接
int fstatat(int fd, const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf, int flag);//由flag决定,默认跟随
返回值:成功,返回0;出错,返回-1
falg:AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW、0(默认跟随)
练习程序在下节
3.文件类型
7种:普通文件、符号链接、目录、块特殊文件、字符特殊文件、FIFO、套接字
硬链接和软链接区别:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-24807808-id-2569015.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/wangkangluo1/archive/2011/08/05/2128918.html
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-hardandsymb-links/
概括:
对file建立硬链接hardlink和软链接softlink,以及file的拷贝copyfile。则:
硬链接:
file和hardfile索引结点相同,指向的是磁盘上同一个文件,就是同一个文件的不同的名字而已。打开file并修改文件内容,同样也会影响到hardfile,因为他俩压根就是同一个文件。
不可跨文件系统创建硬链接,不能对目录创建硬链接(超级用户可以)
软链接:
softlink新建了一个文件,softlink和file索引结点不同,占据着磁盘上不同文件。softlink的内容是file的路径名,可以是相对也可以是绝对路径。但,打开softlink显示的是file文件的内容,因为软连接就是个快捷方式,通过打开softlink,打开了软连接指向的文件file,所以当然这样了!
可跨文件系统创建软链接
拷贝:
只是把原文件内容拷贝到新文件上来,新的索引结点,新的磁盘文件,拷贝结束后就和原文件没关系了
- 文件类型判断
| 宏 | 文件类型 |
| S_ISREG( ) | 普通文件 |
| S_ISDIR( ) | 目录文件 |
| S_ISLNK( ) | 符号链接 |
| S_ISBLK( ) | 块特殊文件 |
| S_ISCHR( ) | 字符特殊文件 |
| S_ISFIFO( ) | 命名管道 |
| S_ISSOCK( ) | 套接字 |
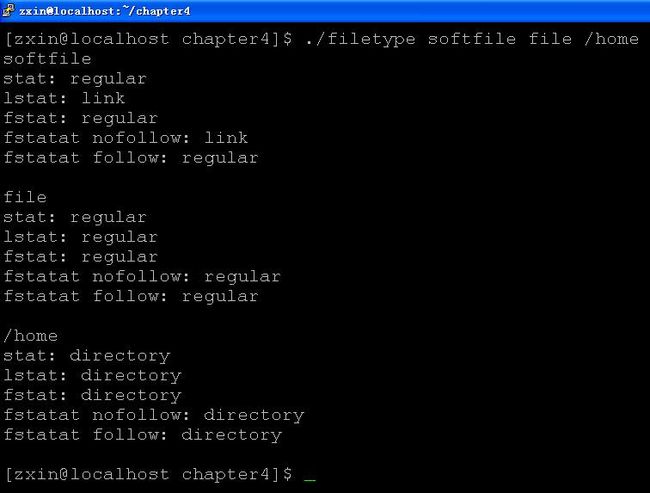
判断文件类型,程序如下:
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 char *type(mode_t mode)
6 {
7 char *p = NULL;
8 if (S_ISREG(mode))
9 p = "regular";
10 if (S_ISDIR(mode))
11 p = "directory";
12 if (S_ISLNK(mode))
13 p = "link";
14 if (S_ISCHR(mode))
15 p = "character special";
16 if (S_ISBLK(mode))
17 p = "block special";
18 if (S_ISFIFO(mode))
19 p = "FIFO";
20 if (S_ISSOCK(mode))
21 p = "socket";
22
23 return p;
24 }
25
26 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
27 {
28 int i;
29 struct stat buf;
30 for (i = 1; i < argc; i++)
31 {
32 printf("%s\n", argv[i]);
33 if (stat(argv[i], &buf) == 0)
34 {
35 printf("stat: ");
36 printf("%s\n", type(buf.st_mode));
37 }
38
39 if (lstat(argv[i], &buf) == 0)
40 {
41 printf("lstat: ");
42 printf("%s\n", type(buf.st_mode));
43 }
44
45 if (fstat(open(argv[i], O_RDONLY), &buf) == 0)
46 {
47 printf("fstat: ");
48 printf("%s\n", type(buf.st_mode));
49 }
50
51 int fd = open("/home/zxin/chapter4", O_RDONLY);
52 if (fstatat(fd, argv[i], &buf, AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW) == 0)
53 {
54 printf("fstatat nofollow: ");
55 printf("%s\n", type(buf.st_mode));
56 }
57
58
59 if (fstatat(fd, argv[i], &buf, 0) == 0)
60 {
61 printf("fstatat follow: ");
62 printf("%s\n", type(buf.st_mode));
63 }
64 printf("\n");
65 }
66 return 0;
67 }
结果:
分析:
1.和文件信息有关的程序要 #include
2.stat和fstat跟随符号链接,lstat不跟随符号链接,fstatat取决于flag参数
3.fstatat的flag参数要么取O_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW,要么取0(默认情况,代表跟随符号链接,而不是取O_SYMLINK_FOLLOW)
4.进程相关ID、文件访问权限、 chmod、 fchmod、 fchmodat
- 进程相关ID:
与进程相关的ID有6个(或更多?),分别是:
实际用户ID、实际组ID:表示我们实际是谁
有效用户ID、有效组ID、附属组ID:用于文件访问权限检查
保存的设置用户ID、保存的设置组ID:由exec函数保存
通过ps命令查看进程ID
- 文件的访问权限:
| st_mode | 说明 |
| S_IRUSR S_IWUSR S_IXUSR S_IRWXU |
所有者读 所有者写 所有者执行 所有者读、写、执行 |
| S_IRGRP S_IWGRP S_IXGRP S_IRWXGRP |
组读 组写 组执行 组读、写、执行 |
| S_IROTH S_IWOTH S_IXOTH S_IRWXOTH |
其他人读 其他人写 其他人执行 其他人读、写、执行 |
| S_ISUID S_ISGID S_ISVTX |
执行时设置用户ID 执行时设置组ID 保存正文(粘着位) |
文件的ID有:所有者ID,组所有者ID,设置用户ID,设置组ID。
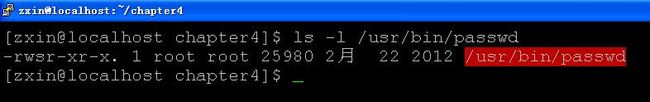
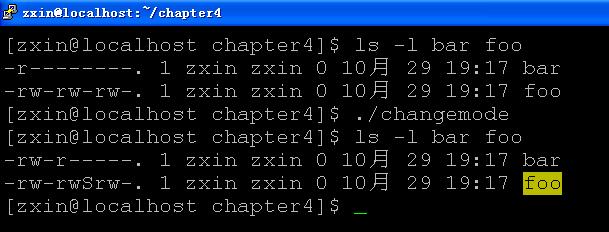
设置用户ID位和设置组ID位:若文件设置了这两位,则当一个进程执行该文件时,会将该进程的有效用户ID设置为文件的所有者的用户ID(st_uid),将进程的有效组ID设置为文件的组所有者ID(st_gid),如passwd命令就设置了设置用户ID位,用S表示,如下图所示:
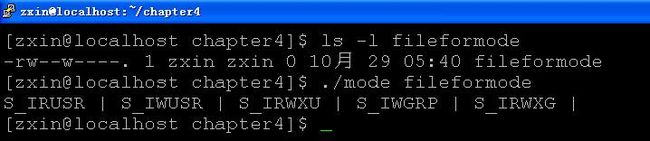
写个程序,输出文件的访问权限:
1 #include
2 #include
3
4 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
5 {
6 if (argc != 2)
7 {
8 printf("argument error\n");
9 exit(-1);
10 }
11 struct stat buf;
12 stat(argv[1], &buf);
13
14 if (buf.st_mode & S_IRUSR)
15 printf("S_IRUSR | ");
16 if (buf.st_mode & S_IWUSR)
17 printf("S_IWUSR | ");
18 if (buf.st_mode & S_IXUSR)
19 printf("S_IXUSR | ");
20 if (buf.st_mode & S_IRWXU)
21 printf("S_IRWXU | ");
22
23 if (buf.st_mode & S_IRGRP)
24 printf("S_IRGRP | ");
25 if (buf.st_mode & S_IWGRP)
26 printf("S_IWGRP | ");
27 if (buf.st_mode & S_IXGRP)
28 printf("S_IXGRP | ");
29 if (buf.st_mode & S_IRWXG)
30 printf("S_IRWXG | ");
31
32 if (buf.st_mode & S_IROTH)
33 printf("S_IROTH | ");
34 if (buf.st_mode & S_IWOTH)
35 printf("S_IWOTH | ");
36 if (buf.st_mode & S_IXOTH)
37 printf("S_IXOTH | ");
38 if (buf.st_mode & S_IRWXO)
39 printf("S_IRWXO | ");
40
41 if (buf.st_mode & S_ISUID)
42 printf("S_ISUID | ");
43 if (buf.st_mode & S_ISGID)
44 printf("S_ISGID | ");
45 if (buf.st_mode & S_ISVTX)
46 printf("S_ISVTX\n");
47 printf("\n");
48
49 return 0;
50 }
结果:
分析:
1.用st_mode & S_IRUSR的方法来测试是否有相应权限
2.只要“读” “写” “执行”这三个里面有一个满足,则“读、写、执行”就满足用上面的程序验证passwd命令设置了设置用户ID位(最后那位S_ISUID):
进程相关ID和文件ID:
http://www.cnblogs.com/kunhu/p/3699883.html
概括:
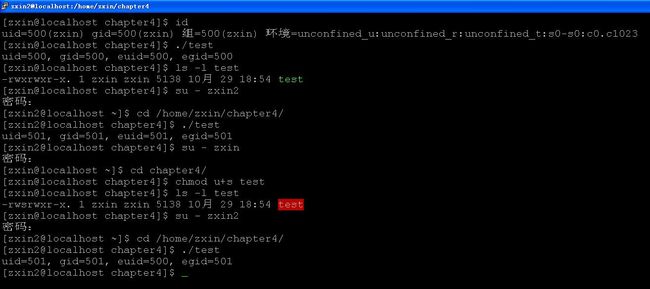
写个程序,测试当时的进程相关ID,如下:
1 #include
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 printf("uid=%d, gid=%d, euid=%d, egid=%d\n",
6 getuid(), getgid(), geteuid(), getegid());
7 return 0;
8 }
分析:
分析:用户zxin创建了文件test,未设置设置用户ID位时,当切换到用户zxin2后,euid变为zxin2的euid=501;当设置了设置用户ID位时,切换到zxin2后,euid变为zxin的euid=500。就是说,用户zxin2执行test文件时,zxin2的euid=501变成了zxin的euid=500,此时zxin2获得了zxin的权限。- chmod、fchmod、fchmodat
#include
int chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode);
int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);
int fchmodat(int fd, const char *path, mode_t mode, int flag);
返回值:成功,返回0;出错,返回-1
chmod,fchmod跟随符号链接;fchmodat取决于flag
注:因为要改变文件的访问权限,所以调用上述函数的进程的有效用户ID必须等于文件的所有者ID,或者该进程是超级进程。
练习程序:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
struct stat buf;
if (stat("foo", &buf) != 0)
{
perror("stat() error");
exit(-1);
}
//int status = chmod("/home/zxin/chapter4/foo", S_ISGID | S_ISUID);
int status = chmod("/home/zxin/chapter4/foo", (buf.st_mode & ~S_IXGRP) | S_ISGID);
if (status != 0)
{
perror("chmod() error");
exit(-1);
}
int status2 = fchmodat(AT_FDCWD, "bar", S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IRGRP, 0);
if (status2 != 0)
{
perror("fchmodat() error");
exit(-1);
}
return 0;
}
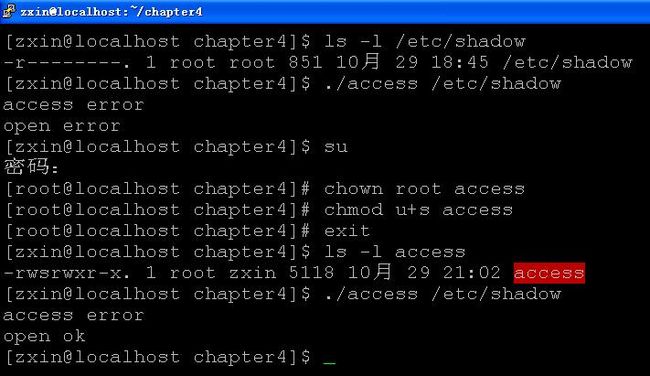
5.access和accessat
#include
int access(const char *path, int mode);
int accessat(int fd, const char *path, int mode, int flag);
返回值:成功,返回0;出错,返回-1
功能:按实际用户ID和实际组ID测试对文件的访问权限
mode:F_OK、R_OK、W_OK、X_OK
flag:E_ACCESS(按有效用户ID和有效组ID测试)
程序如下:
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
6 {
7 if (argc != 2)
8 {
9 printf("argument error\n");
10 exit(-1);
11 }
12 if (access(argv[1], R_OK) < 0)
13 printf("access error\n");
14 else
15 printf("access ok\n");
16 if (open(argv[1], O_RDONLY) < 0)
17 printf("open error\n");
18 else
19 printf("open ok\n");
20
21 return 0;
22 }
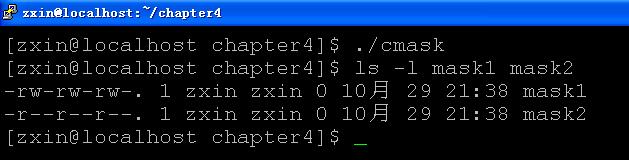
6.umask
#include
#include
#define RWRWRW (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH)
int main()
{
umask(0);
if (creat("mask1", RWRWRW) < 0)
{
perror("creat() error");
return 0;
}
umask(S_IWUSR | S_IWGRP | S_IWOTH);
if (creat("mask2", RWRWRW) < 0)
{
perror("creat() error");
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
7.chown
int chown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int fchown(int fd, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int fchownat(int fd, const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group, int flag);
int lchown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
All four return: 0 if OK, −1 on error
#include
#include
int main()
{
struct stat buf;
if (stat("chownfile", &buf) == 0)
{
printf("chownfile:\nst_uid=%d, st_gid=%d\n", buf.st_uid, buf.st_gid);
if (chown("chownfile", 501, 501) == 0)
{
printf("after chown()\n");
stat("chownfile", &buf);
printf("chownfile:\nst_uid=%d, st_gid=%d\n", buf.st_uid, buf.st_gid);
}
}
exit(-1);
}
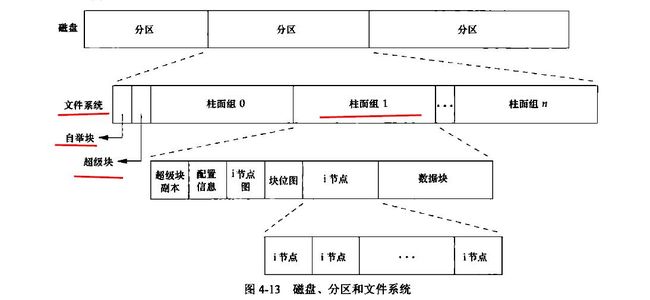
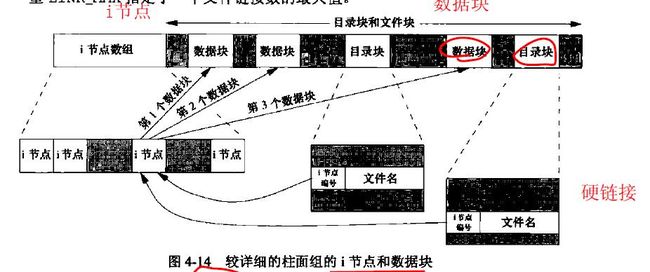
8.文件系统
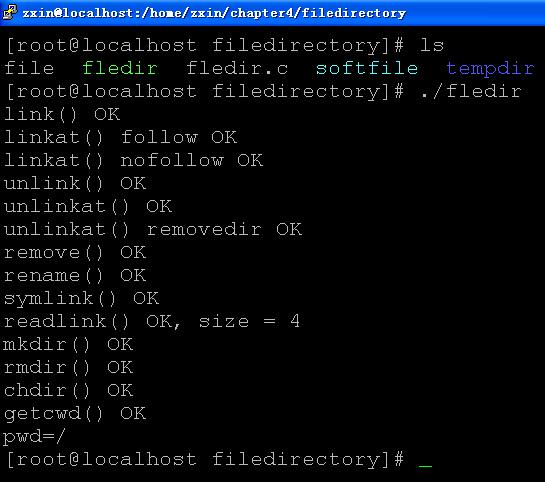
9.link, unlink, remove, rename, symlink, futimens, mkdir, rmdir, chdir, getcwd
int link(const char *existingpath, const char *newpath);
int linkat(int efd, const char *existingpath, int nfd, const char *newpath, int flag); //flag: AT_SYMLINK_FOLLOW, 0
int unlinkat(int fd, const char *pathname, int flag); //flag: AT_REMOVEDIR
int renameat(int oldfd, const char *oldname, int newfd, const char *newname);
int symlinkat(const char *actualpath, int fd, const char *sympath);
ssize_t readlinkat(int fd, const char* restrict pathname, char *restrict buf, size_t bufsize);
int utimensat(int fd, const char *path, const struct timespec times[2], int flag); //flag: AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW,0
int mkdirat(int fd, const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
int fchdir(int fd);
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define BUFSIZE 100
int main()
{
if (link("softfile", "linktosoft") == 0)
printf("link() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (linkat(AT_FDCWD, "softfile", AT_FDCWD, "followsoft", AT_SYMLINK_FOLLOW) == 0)
printf("linkat() follow OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (linkat(AT_FDCWD, "softfile", AT_FDCWD, "nofollowsoft", 0) == 0)
printf("linkat() nofollow OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (unlink("followsoft") == 0)
printf("unlink() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (unlinkat(AT_FDCWD, "nofollowsoft", 0) == 0)
printf("unlinkat() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (unlinkat(AT_FDCWD, "tempdir", AT_REMOVEDIR) == 0)
printf("unlinkat() removedir OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (remove("linktosoft") == 0)
printf("remove() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (rename("softfile", "namesoft") == 0)
printf("rename() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (symlink("no such file", "soft") == 0)
printf("symlink() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
char buf[BUFSIZE];
ssize_t size;
if ((size = readlink("namesoft", buf, BUFSIZE)) != -1)
printf("readlink() OK, size = %d\n", size);
else
exit(-1);
if (mkdir("new dir", S_IRUSR | S_IXUSR) == 0)
printf("mkdir() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (rmdir("new dir") == 0)
printf("rmdir() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (chdir("/") == 0)
printf("chdir() OK\n");
else
exit(-1);
if (getcwd(buf, BUFSIZE) != NULL)
printf("getcwd() OK\npwd=%s\n", buf);
else
exit(-1);
return 0;
}