React源码分析(二)=> Reac初次渲染分析
文章目录
- 1. render阶段 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
- 1.1. legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer
- 1.1.1. ReactRoot
- 1.1.1.1. createFiberRoot
- 1.1.1.2. createHostRootFiber
- 续1. legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
- 1.2. root.render()
- 1.3. updateContainer 这节内部函数太多, 拆成二级标题, 续1.2.
- 1.3.1. requestCurrentTime
- 1.3.1.1. recomputeCurrentRendererTime
- 1.3.1.2. msToExpirationTime
- 1.3.2 computeExpirationForFiber
- 1.3.2.1. computeInteractiveExpiration
- 1.3.2.2. computeAsyncExpiration
- 1.3.2.3. computeExpirationBucket
- 1.3.3. updateContainerAtExpirationTime
- 1.3.3.1. scheduleRootUpdate
- 1.3.3.2. enqueueUpdate
- 1.4. scheduleWork 这节内部函数太多了, 分出一个2级标题, 续1.3.3.1.
- 1.4.1. scheduleWorkToRoot
- 1.4.2. markPendingPriorityLevel
- 1.4.2.1. findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn
- 1.4.4. requestWork
- 1.4.4.1. addRootToSchedule
- 1.5 performSyncWork 理由同上, 续1.4.4
- 1.5.1. findHighestPriorityRoot
- 1.5.2. performWorkOnRoot
- 1.6. renderRoot 理由同上, 续1.5.2.
- 1.6.1. createWorkInProgress
- 1.6.2. workLoop & performUnitOfWork & beginWork
- 1.7 updateHostRoot, 续1.6.2
- 1.7.1 push & pop
- 1.7.1.1 push
- 1.7.1.2. pop
- 1.7.2. pushHostRootContext
- 1.7.2.1. pushHostContainer
- 1.7.3. processUpdateQueue
- 1.7.4 reconcileChildren
- 1.7.4.1 reconcileChildFibers
- 1.8 completeUnitOfWork, 续1.6.2. workLoop
- 1.8.1. completeWork
- 1.8.1.1 createTextInstance
- 2. commit阶段 completeRoot
- 2.1. commitRoot
- 2.1.1. invokeGuardedCallback
- 2.1.2. commitAllHostEffects
- 2.1.2.1. commitPlacement
- 3. 初次渲染总结
本不该有4级标题, 没办法东西太多, 不加4级标题更不清晰.
继续上一节回来继续看代码, 本章还涉及到了work调度问题, 由于内容太多, 存在if (__DEV__)的判断语句, 本章选择性忽略.
由于React源码使用了flow的静态类型检查器,所以会有:类型这样的语法,对于熟悉Typescript的肯定很熟悉这样的写法,不懂的直接把类型忽略就好(例如第一行的ReactDOM:Object,后面的:Object就是ReactDOM的类型,有些类型是自定义的有些是框架自带的,render函数的参数里React$Element这种类型一看就是自定义的),没什么影响。
源码基于React 16.8.6, 内容极长, 必须配合源码一起来看
单步调试的例子: ReactDOM.render('hello', document.getElementById('root'));
下文基于这个例子来一步一步分析, 你要是有什么见解可以直接在下面的评论区留言, 我会及时查看.
1. render阶段 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
从下面的源码可以看到,调用了ReactDOM.render时首先执行了legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer函数
// 例
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
// packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOM.js
/**
* nodeType 属性返回节点类型。
如果节点是一个元素节点,nodeType 属性返回 1。
如果节点是属性节点, nodeType 属性返回 2。
如果节点是一个文本节点,nodeType 属性返回 3。
如果节点是一个注释节点,nodeType 属性返回 8。
如果节点是一个整个文档(DOM 树的根节点),nodeType 属性返回 9。
如果节点是一个DocumentFragment,nodeType 属性返回 11。
ELEMENT_NODE = 1,
DOCUMENT_NODE = 9,
DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE = 11,
COMMENT_NODE = 8
*/
function isValidContainer(node) {
return !!(
node &&
(node.nodeType === ELEMENT_NODE ||
node.nodeType === DOCUMENT_NODE ||
node.nodeType === DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE ||
(node.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE &&
node.nodeValue === ' react-mount-point-unstable '))
);
}
const ReactDOM: Object = {
render(
element: React$Element<any>,
container: DOMContainer,
callback: ?Function,
) {
invariant(
isValidContainer(container),
'Target container is not a DOM element.',
);
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
null,
element,
container,
false,
callback,
);
},
下面来看下legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer函数内部
// packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOM.js
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>, // 首次渲染, partComponet为null
children: ReactNodeList, // children为使用React编写的组件
container: DOMContainer, // container为真实DOM元素
forceHydrate: boolean, // forceHydrate写死的false, true时为服务端渲染
callback: ?Function,
) {
let root: _ReactSyncRoot = (container._reactRootContainer: any);
let fiberRoot;
if (!root) {
// Initial mount 初始化容器
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate,
);
// !!!未完!!!
1.1. legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer这个函数主要是拿着真是DOM创建一个ReactRoot并返回, 见下方代码
// packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOM.js
function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container: DOMContainer, // 真实DOM元素
forceHydrate: boolean, // 目前为false
): _ReactSyncRoot {
const shouldHydrate =
forceHydrate || shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic(container);
// First clear any existing content.
if (!shouldHydrate) {
let warned = false;
let rootSibling;
while ((rootSibling = container.lastChild)) {
// 删除跟节点内部元素
container.removeChild(rootSibling);
}
}
// Legacy roots are not batched.
// 返回一个ReactRoot对象
const isConcurrent = false;
return new ReactRoot(container, isConcurrent, shouldHydrate);
}
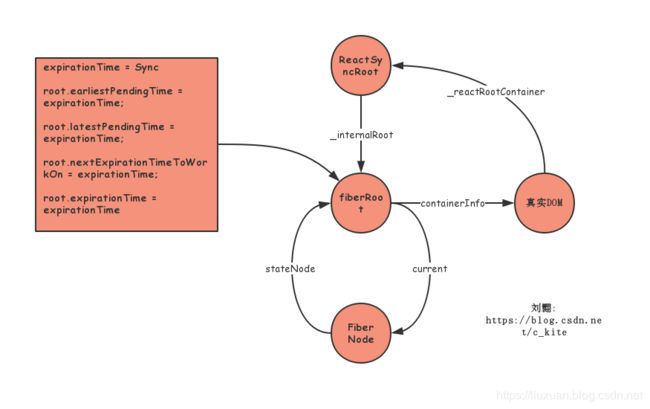
1.1.1. ReactRoot
继续上个函数, 见下方代码:
// packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOM.js
function ReactRoot(
container: DOMContainer, // 真实DOM元素
tag: RootTag, // 0
hydrate: boolean, // false
) {
// Tag is either LegacyRoot or Concurrent Root
const root = createContainer(container, tag, hydrate);
this._internalRoot = root;
}
下面来看下createContainer函数
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberReconciler.js
function createContainer(
containerInfo: Container, // 真实DOM元素
isConcurrent: boolean, // false
hydrate: boolean, // false
): OpaqueRoot {
return createFiberRoot(containerInfo, tag, hydrate);
}
// 直接返回的createFiberRoot函数, 继续
1.1.1.1. createFiberRoot
这个函数返回了一个FiberRoot
function createFiberRoot(
containerInfo: any, // 真实DOM元素
isConcurrent: boolean, // false
hydrate: boolean, // false
): FiberRoot {
// Cyclic construction. This cheats the type system right now because
// stateNode is any.
// Fiber Node
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(isConcurrent);
let root;
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
// react 19的alpha.0版本这里被抽成工厂函数了
root = ({ // 创建一个FiberRootNode
current: uninitializedFiber, // 上面那个Fiber Node
containerInfo: containerInfo, // 真实DOM元素
pendingChildren: null,
earliestPendingTime: NoWork, // 0
latestPendingTime: NoWork, // 0
earliestSuspendedTime: NoWork, // 0
latestSuspendedTime: NoWork, // 0
latestPingedTime: NoWork, // 0
pingCache: null,
didError: false,
pendingCommitExpirationTime: NoWork, // 0
finishedWork: null,
timeoutHandle: noTimeout,
context: null,
pendingContext: null,
hydrate,
nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn: NoWork, // 0
expirationTime: NoWork, // 0
firstBatch: null,
nextScheduledRoot: null,
interactionThreadID: unstable_getThreadID(),
memoizedInteractions: new Set(),
pendingInteractionMap: new Map(),
}: FiberRoot);
} else {
// ...省略
}
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
return ((root: any): FiberRoot);
1.1.1.2. createHostRootFiber
这个函数返回一个FiberNode
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiber.js
function createHostRootFiber(isConcurrent: boolean): Fiber {
// isConcurrent = false; ConcurrentMode = 0b001, StrictMode = 0b010, NoContext = 0b000
let mode = isConcurrent ? ConcurrentMode | StrictMode : NoContext;
if (enableProfilerTimer && isDevToolsPresent) {
// Always collect profile timings when DevTools are present.
// This enables DevTools to start capturing timing at any point–
// Without some nodes in the tree having empty base times.
mode |= ProfileMode;
}
// HostRoot是常量, 值为3, mode = 0b000
return createFiber(HostRoot, null, null, mode);
}
// 下面来看下createFiber
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiber.js
const createFiber = function(
tag: WorkTag, // 3
pendingProps: mixed, // null
key: null | string, // null
mode: TypeOfMode, // 0
): Fiber {
return new FiberNode(tag, pendingProps, key, mode);
};
// 继续
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiber.js
function FiberNode(
tag: WorkTag, // 3
pendingProps: mixed, // null
key: null | string, // null
mode: TypeOfMode, // 0
) {
// Instance
this.tag = tag; // 3
this.key = key; // null
this.elementType = null;
this.type = null;
this.stateNode = null;
// Fiber
this.return = null;
this.child = null;
this.sibling = null;
this.index = 0;
this.ref = null;
this.pendingProps = pendingProps; // null
this.memoizedProps = null;
this.updateQueue = null;
this.memoizedState = null;
this.contextDependencies = null;
this.mode = mode; // 0
// Effects
this.effectTag = NoEffect; // 0b000000000000
this.nextEffect = null;
this.firstEffect = null;
this.lastEffect = null;
this.expirationTime = NoWork; // 0
this.childExpirationTime = NoWork; // 0
this.alternate = null;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
// Note: The following is done to avoid a v8 performance cliff.
// 避免V8性能悬崖
// Learn more about this here:
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/14365
// https://bugs.chromium.org/p/v8/issues/detail?id=8538
this.actualDuration = Number.NaN;
this.actualStartTime = Number.NaN;
this.selfBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
this.treeBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
// It's okay to replace the initial doubles with smis after initialization.
// This won't trigger the performance cliff mentioned above,
// and it simplifies other profiler code (including DevTools).
this.actualDuration = 0;
this.actualStartTime = -1;
this.selfBaseDuration = 0;
this.treeBaseDuration = 0;
}
// ...省略
}
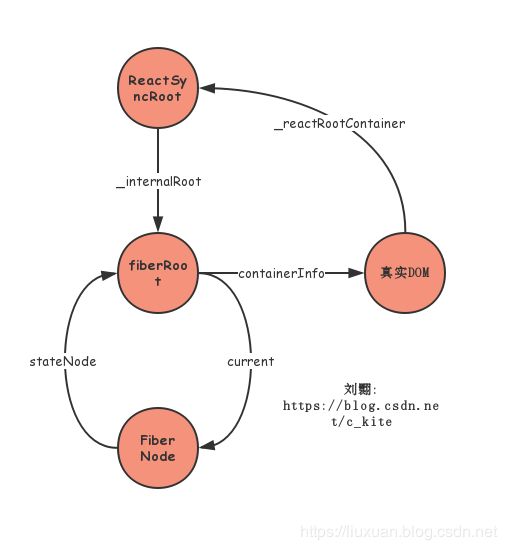
截止到目前为止关于节点总结: (可以打开一个react项目, 选择跟节点的_reactRootContainer属性验证一下)
续1. legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
接着最开始来,
// 接着1.legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer内部的代码
// packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOM.js
// 此处的root是ReactRoot
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate,
);
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);
// 将函数this注入
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// Initial mount should not be batched.
unbatchedUpdates(() => {
if (parentComponent != null) {
root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer(
parentComponent,
children,
callback,
);
} else {
// 首次进到这里
root.render(children, callback);
}
});
} else {
// 非首次暂时省略
}
return getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);
}
1.2. root.render()
该函数在ReactRoot的原型链上, 下面来看一下代码:
function ReactWork() {
this._callbacks = null;
this._didCommit = false;
this._onCommit = this._onCommit.bind(this); // ReactWork原型链上有这个函数, 暂时不看
}
ReactRoot.prototype.render = function(
children: ReactNodeList, // children为使用React编写的组件
callback: ?() => mixed,
): Work {
const root = this._internalRoot; // FiberRoot
const work = new ReactWork();
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (__DEV__) {
warnOnInvalidCallback(callback, 'render');
}
if (callback !== null) {
work.then(callback);
}
updateContainer(children, root, null, work._onCommit);
return work;
};
1.3. updateContainer 这节内部函数太多, 拆成二级标题, 续1.2.
unbatchedUpdates就不看了, 大体就是立即执行updateContainer函数.
updateContainer函数里面都是调用其他函数直接看代码吧, 代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberReconciler.js
function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList, // 使用React编写的组件
container: OpaqueRoot, // FiberRoot
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>, // null
callback: ?Function, // ReactWork._onCommit
): ExpirationTime {
const current = container.current; // FibeNode
const currentTime = requestCurrentTime(); // 获取当前已经花费的时间
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime, current);
return updateContainerAtExpirationTime(
element,
container,
parentComponent,
expirationTime,
callback,
);
}
具体函数见下面1.3.x.下节
1.3.1. requestCurrentTime
这个函数主要用来计算到期时间, 代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberScheduler.js
function findHighestPriorityRoot() {
let highestPriorityWork = NoWork; // 0
let highestPriorityRoot = null;
// lastScheduledRoot初始化为null
if (lastScheduledRoot !== null) {
// ... 省略
}
nextFlushedRoot = highestPriorityRoot; // null
nextFlushedExpirationTime = highestPriorityWork; // 0
}
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberWorkLoop.js
function requestCurrentTime() { // 计算到期时间
// 通过添加到当前时间(开始时间)来计算到期时间。 但是,如果在同一事件中安排了两次更新,我们应将它们的开始时间视为同步,即使第一次和第二次呼叫之间的实际时钟时间已提前。
// 换句话说, 因为过期时间决定了如何批量更新
// 我们希望在同一事件中发生的所有类似优先级的更新都会收到相同的到期时间。 否则我们会撕裂。
// 我们跟踪两个不同的时间:renderer time和scheduler time。 renderer time可以随时使用`performance.now`更新;
// 但是scheduler time只能更新在 没有待处理的工作,或者我们确定我们不在事件的中间时
if (isRendering) {
// We're already rendering. Return the most recently read time.
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
// Check if there's pending work.
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (
nextFlushedExpirationTime === NoWork ||
nextFlushedExpirationTime === Never
) {
// If there's no pending work, or if the pending work is offscreen, we can
// read the current time without risk of tearing.
// 没有待处理的工作,或者待处理的工作是在屏幕外,
recomputeCurrentRendererTime();
currentSchedulerTime = currentRendererTime; // 上一个函数计算的值赋值到了currentRendererTime
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
// There's already pending work. We might be in the middle of a browser
// event. If we were to read the current time, it could cause multiple updates
// 已经有pending work了。 我们可能正处于浏览器事件的中间。 如果我们要读取当前时间,可能会导致多次更新
// within the same event to receive different expiration times, leading to
// tearing. Return the last read time. During the next idle callback, the
// time will be updated.
// 防止在事件返回不同时间, 返回上次的时间, 下次空闲回调时时间会更新.
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
下面来看一下recomputeCurrentRendererTime函数
1.3.1.1. recomputeCurrentRendererTime
此处now函数就是上一节说的performance.now, 具体:
https://liuxuan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/90641799
function recomputeCurrentRendererTime() {
// originalStartTimeMs = now(); 启动时执行的
const currentTimeMs = now() - originalStartTimeMs;
currentRendererTime = msToExpirationTime(currentTimeMs);
}
1.3.1.2. msToExpirationTime
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberExpirationTime.js
const UNIT_SIZE = 10;
const MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET = MAX_SIGNED_31_BIT_INT - 1;
// 1 unit of expiration time represents 10ms.
// 1个到期时间单位是10ms
export function msToExpirationTime(ms: number): ExpirationTime {
// Always add an offset so that we don't clash with the magic number for NoWork.
// NoWork是常量, 值为0, 应该是怕减数正好为0吧
return MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - ((ms / UNIT_SIZE) | 0);
}
/ 10抹掉10ms时间差, | 0的意思是取整,
1.3.2 computeExpirationForFiber
这个函数主要根据Fiber类型来计算到期时间, 代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberWorkLoop.js
function computeExpirationForFiber(
currentTime: ExpirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
fiber: Fiber, // FiberNode
) {
const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel(); // 初始返回NormalPriority => 3
let expirationTime;
// ConcurrentMode是常量为0b001
// NoContext是常量为0b000
// fiber.mode 为 0
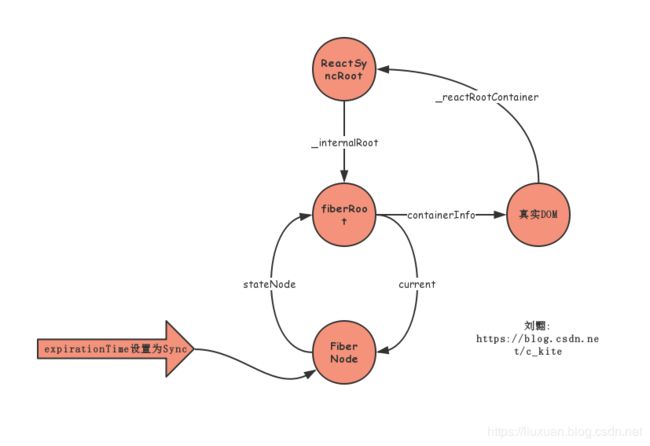
if ((fiber.mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoContext) {
// Outside of concurrent mode, updates are always synchronous.
// 在并发模式之外,更新始终是同步的
// Sync是常量, 值为32位系统的V8中的最大整数, Math.pow(2, 30) - 1
expirationTime = Sync;
} else if (isWorking && !isCommitting) {
// During render phase, updates expire during as the current render.
// 在render阶段
expirationTime = nextRenderExpirationTime;
} else {
switch (priorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
expirationTime = Sync;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
// 计算交互状态的过期时间
expirationTime = computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime);
break;
case NormalPriority:
// This is a normal, concurrent update
// 计算异步状态的过期时间
expirationTime = computeAsyncExpiration(currentTime);
break;
case LowPriority:
case IdlePriority:
expirationTime = Never;
break;
default:
invariant(
false,
'Unknown priority level. This error is likely caused by a bug in ' +
'React. Please file an issue.',
);
}
// If we're in the middle of rendering a tree, do not update at the same
// expiration time that is already rendering.
// 如果正在rendering tree, 不要更新过期时间
if (nextRoot !== null && expirationTime === nextRenderExpirationTime) {
expirationTime -= 1;
}
}
// Keep track of the lowest pending interactive expiration time. This
// allows us to synchronously flush all interactive updates
// when needed.
// UserBlockingPriority是常量为2
if (
priorityLevel === UserBlockingPriority &&
(lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime === NoWork ||
expirationTime < lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime)
) {
lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime = expirationTime;
}
return expirationTime; // 返回Sync
}
其中computeInteractiveExpiration和computeAsyncExpiration看一下
1.3.2.1. computeInteractiveExpiration
计算交互情况的过期时间:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberExpirationTime.js
const HIGH_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION = __DEV__ ? 500 : 150;
const HIGH_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE = 100;
function computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime: ExpirationTime) {
return computeExpirationBucket(
currentTime,
HIGH_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION,
HIGH_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE,
);
}
1.3.2.2. computeAsyncExpiration
计算异步情况的过期时间
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberExpirationTime.js
const LOW_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION = 5000;
const LOW_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE = 250;
function computeAsyncExpiration(
currentTime: ExpirationTime,
): ExpirationTime {
return computeExpirationBucket(
currentTime,
LOW_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION,
LOW_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE,
);
}
1.3.2.3. computeExpirationBucket
最后来看下核心计算函数
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberExpirationTime.js
const MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET = MAX_SIGNED_31_BIT_INT - 1;
function ceiling(num: number, precision: number): number {
return (((num / precision) | 0) + 1) * precision;
}
function computeExpirationBucket(
currentTime,
expirationInMs,
bucketSizeMs,
): ExpirationTime {
return (
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET -
ceiling(
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - currentTime + expirationInMs / UNIT_SIZE,
bucketSizeMs / UNIT_SIZE,
)
);
}
我们来结合ceiling函数来分析一下这个算数表达式:
1. currentTime 实际就是 1.2.1节 => requestCurrentTime 函数计算所得, 假定第一次渲染,
实际执行的就是msToExpirationTime函数, 将msToExpirationTime函数内部语句代入上式中, 可以得出
return (
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET -
ceiling(
((now() / UNIT_SIZE) | 0) + expirationInMs / UNIT_SIZE,
bucketSizeMs / UNIT_SIZE,
)
);
2. 被减数MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET 目的应该也是防止和内部常量冲突先忽略,
将computeInteractiveExpiration和computeAsyncExpiration函数传入的参数代入
(((X + 15) / 10 | 0) + 1) * 10
(((X + 500) / 25 | 0) + 1) * 25
这样就清晰多了, X就是当前时间变量, 随便代数发现,
第一个式子也就是computeInteractiveExpiration抹去了10ms内的时间差, 得出的都是一个值,
computeAsyncExpiration抹去了25ms内的时间差
1.3.3. updateContainerAtExpirationTime
功能如其名, 调用scheduleRootUpdate开始安排更新, 代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberReconciler.js
function updateContainerAtExpirationTime(
element: ReactNodeList, // 为使用React编写的组件
container: OpaqueRoot, // FiberRoot
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>, // null
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
callback: ?Function, // ReactWork._onCommit
) {
// TODO: If this is a nested container, this won't be the root.
const current = container.current; // FiberNode
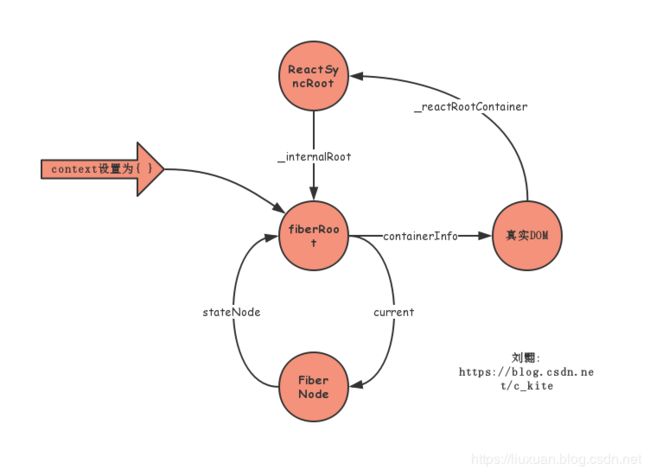
const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent); // 返回的是个空对象{ }
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context;
} else {
container.pendingContext = context;
}
return scheduleRootUpdate(current, element, expirationTime, callback);
}
没什么好说的直接看scheduleRootUpdate:
1.3.3.1. scheduleRootUpdate
这个函数首先创建了一个update对象, 然后将此对象放到Fiber Node的UpdateQueue中, 最后调用scheduleWork函数开始下一步处理.
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberReconciler.js
function scheduleRootUpdate(
current: Fiber, // FiberNode
element: ReactNodeList, // 为使用React编写的组件
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
callback: ?Function, // ReactWork._onCommit
) {
if (__DEV__) {
if (
ReactCurrentFiberPhase === 'render' &&
ReactCurrentFiberCurrent !== null &&
!didWarnAboutNestedUpdates
) {
didWarnAboutNestedUpdates = true;
warningWithoutStack(
false,
'Render methods should be a pure function of props and state; ' +
'triggering nested component updates from render is not allowed. ' +
'If necessary, trigger nested updates in componentDidUpdate.\n\n' +
'Check the render method of %s.',
getComponentName(ReactCurrentFiberCurrent.type) || 'Unknown',
);
}
}
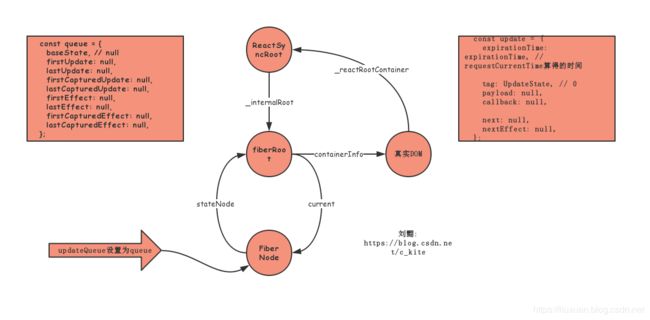
const update = createUpdate(expirationTime);
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
update.payload = {element};
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
warningWithoutStack(
typeof callback === 'function',
'render(...): Expected the last optional `callback` argument to be a ' +
'function. Instead received: %s.',
callback,
);
update.callback = callback; // ReactWork._onCommit
}
flushPassiveEffects(); // 初次执行不到不看了
enqueueUpdate(current, update);
scheduleWork(current, expirationTime);
return expirationTime;
}
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactUpdateQueue.js
function createUpdate(expirationTime: ExpirationTime): Update<*> {
return {
expirationTime: expirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
tag: UpdateState,
payload: null,
callback: null,
next: null,
nextEffect: null,
};
}
一层又一层, 继续来看下enqueueUpdate
1.3.3.2. enqueueUpdate
把update对象插到FiberNode上
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactUpdateQueue.js
function enqueueUpdate<State>(
fiber: Fiber, // FiberNode
update: Update<State>, // createUpdate函数生成的update对象
) {
// Update queues are created lazily.
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
let queue1;
let queue2;
if (alternate === null) {
// There's only one fiber.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue;
queue2 = null;
if (queue1 === null) {
// 返回一个对象
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(fiber.memoizedState);
}
} else {
// 非首次忽略
}
if (queue2 === null || queue1 === queue2) {
// There's only a single queue.
// 插入操作
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
} else {
// 非首次忽略
}
}
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactUpdateQueue.js
function createUpdateQueue<State>(baseState: State): UpdateQueue<State> {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = {
baseState,
firstUpdate: null,
lastUpdate: null,
firstCapturedUpdate: null,
lastCapturedUpdate: null,
firstEffect: null,
lastEffect: null,
firstCapturedEffect: null,
lastCapturedEffect: null,
};
return queue;
}
function appendUpdateToQueue<State>(
queue: UpdateQueue<State>,
update: Update<State>,
) {
// Append the update to the end of the list.
// 将更新插入到列表的尾部
if (queue.lastUpdate === null) {
// Queue is empty 队列为空
queue.firstUpdate = queue.lastUpdate = update;
} else {
// 注意queue.lastUpdate拿到是那个节点真实的地址
queue.lastUpdate.next = update;
queue.lastUpdate = update;
}
}
1.4. scheduleWork 这节内部函数太多了, 分出一个2级标题, 续1.3.3.1.
该函数在处理完过期时间之后, 调用requestWork开始进一步安排, 代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberScheduler.js
function scheduleWork(
fiber: Fiber, // FiberNode
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
) {
const root = scheduleWorkToRoot(fiber, expirationTime); // 返回的是FiberRoot
// isWorking是变量, 初始值为false
// NoWork是常量值为0
// nextRenderExpirationTime是变量, 初始值为NoWork
if (
!isWorking &&
nextRenderExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
expirationTime > nextRenderExpirationTime
) { // 初次不会到这次循环内
// This is an interruption. (Used for performance tracking.)
// 这是一次中断, 用于性能追踪
interruptedBy = fiber;
resetStack();
}
markPendingPriorityLevel(root, expirationTime);
if (
// If we're in the render phase, we don't need to schedule this root
// for an update, because we'll do it before we exit...
!isWorking ||
isCommitting ||
// ...unless this is a different root than the one we're rendering.
nextRoot !== root
) {
const rootExpirationTime = root.expirationTime;
requestWork(root, rootExpirationTime);
}
if (nestedUpdateCount > NESTED_UPDATE_LIMIT) {
// Reset this back to zero so subsequent updates don't throw.
nestedUpdateCount = 0;
invariant(
false,
'Maximum update depth exceeded. This can happen when a ' +
'component repeatedly calls setState inside ' +
'componentWillUpdate or componentDidUpdate. React limits ' +
'the number of nested updates to prevent infinite loops.',
);
}
}
1.4.1. scheduleWorkToRoot
该函数主要是处理下过期时间, 具体代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberScheduler.js
function scheduleWorkToRoot(
fiber: Fiber, // FiberNode
expirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
): FiberRoot | null {
recordScheduleUpdate(); // 只有dev环境运行
if (__DEV__) {
// ClassComponent是常量值为1
if (fiber.tag === ClassComponent) {
const instance = fiber.stateNode;
// 警告操作不要在getChildContext(已弃用)和render中使用setState
warnAboutInvalidUpdates(instance);
}
}
// Update the source fiber's expiration time
if (fiber.expirationTime < expirationTime) {
fiber.expirationTime = expirationTime; // 更新一下
}
let alternate = fiber.alternate; // 镜像fiber, 这时候还没
if (alternate !== null && alternate.expirationTime < expirationTime) {
alternate.expirationTime = expirationTime;
}
// Walk the parent path to the root and update the child expiration time.
let node = fiber.return; // 指向当前fiber的父级
let root = null;
if (node === null && fiber.tag === HostRoot) {
root = fiber.stateNode; // FiberRoot
} else {
// 当前节点所有父节点过期时间都更新一下
while (node !== null) {
alternate = node.alternate;
if (node.childExpirationTime < expirationTime) {
node.childExpirationTime = expirationTime;
if (
alternate !== null &&
alternate.childExpirationTime < expirationTime
) {
alternate.childExpirationTime = expirationTime;
}
} else if (
alternate !== null &&
alternate.childExpirationTime < expirationTime
) {
alternate.childExpirationTime = expirationTime;
}
if (node.return === null && node.tag === HostRoot) {
// 到跟节点退出
root = node.stateNode;
break;
}
node = node.return;
}
}
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
if (root !== null) {
// __interactionsRef里面就一个current, 其数据类型为SET
const interactions = __interactionsRef.current;
if (interactions.size > 0) {
// 这时interactions为空, 省略
}
}
}
return root;
}
1.4.2. markPendingPriorityLevel
这个函数主要设置了FiberRoot的4个属性, 分别是nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn,earliestPendingTime, latestPendingTime, expirationTime, 代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberPendingPriority.js
function markPendingPriorityLevel(
root: FiberRoot,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
): void {
// If there's a gap between completing a failed root and retrying it,
// additional updates may be scheduled. Clear `didError`, in case the update
// is sufficient to fix the error.
// 如果在完成失败和重试之间存在空隙,则可能会安排其他更新。 如果更新足以修复错误,设回didError为false
root.didError = false;
// Update the latest and earliest pending times
const earliestPendingTime = root.earliestPendingTime; // 初始时为0
// NoWork是常量值为0
if (earliestPendingTime === NoWork) {
// No other pending updates.
root.earliestPendingTime = root.latestPendingTime = expirationTime;
} else {
if (earliestPendingTime < expirationTime) {
// This is the earliest pending update.
root.earliestPendingTime = expirationTime;
} else {
const latestPendingTime = root.latestPendingTime;
if (latestPendingTime > expirationTime) {
// This is the latest pending update
root.latestPendingTime = expirationTime;
}
}
}
findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn(expirationTime, root);
}
1.4.2.1. findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn
再来看下findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn这个函数:
function findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn(
completedExpirationTime, // requestCurrentTime算得的时间
root, // FiberRoot
) {
const earliestSuspendedTime = root.earliestSuspendedTime; // 0
const latestSuspendedTime = root.latestSuspendedTime; // 0
const earliestPendingTime = root.earliestPendingTime; // completedExpirationTime
const latestPingedTime = root.latestPingedTime; // completedExpirationTime
// Work on the earliest pending time. Failing that, work on the latest
// pinged time.
let nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn =
earliestPendingTime !== NoWork ? earliestPendingTime : latestPingedTime;
// If there is no pending or pinged work, check if there's suspended work
// that's lower priority than what we just completed.
if (
nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn === NoWork &&
(completedExpirationTime === NoWork ||
latestSuspendedTime < completedExpirationTime)
) {
// The lowest priority suspended work is the work most likely to be
// committed next. Let's start rendering it again, so that if it times out,
// it's ready to commit.
nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn = latestSuspendedTime;
}
let expirationTime = nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn;
if (expirationTime !== NoWork && earliestSuspendedTime > expirationTime) {
// Expire using the earliest known expiration time.
// 使用最早的已知过期时间
expirationTime = earliestSuspendedTime;
}
root.nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn = nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn; // expirationTime
root.expirationTime = expirationTime;
}
1.4.4. requestWork
只要root收到更新,调度程序就会调用requestWork。由渲染器决定在将来的某个时刻调用renderRoot。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberScheduler.js
function requestWork(root: FiberRoot, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
addRootToSchedule(root, expirationTime);
if (isRendering) {
// Prevent reentrancy. Remaining work will be scheduled at the end of
// the currently rendering batch.
return;
}
if (isBatchingUpdates) { // 初值为false, 不会进到这个判断里
// Flush work at the end of the batch.
if (isUnbatchingUpdates) {
// ...unless we're inside unbatchedUpdates, in which case we should
// flush it now.
nextFlushedRoot = root;
nextFlushedExpirationTime = Sync;
performWorkOnRoot(root, Sync, false);
}
return;
}
// TODO: Get rid of Sync and use current time?
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
performSyncWork(); // 这里
} else {
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime); // 这个函数之后系列再看
}
}
1.4.4.1. addRootToSchedule
把当前FiberRoot放到Schedule循环链表中, 看下代码
function addRootToSchedule(root: FiberRoot, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
// Add the root to the schedule.
// Check if this root is already part of the schedule.
if (root.nextScheduledRoot === null) {
// This root is not already scheduled. Add it.
root.expirationTime = expirationTime;
if (lastScheduledRoot === null) {
// 进到这个判断里
firstScheduledRoot = lastScheduledRoot = root;
root.nextScheduledRoot = root; // 自身循环, 就一个节点
} else {
// 循环链表
lastScheduledRoot.nextScheduledRoot = root;
lastScheduledRoot = root;
lastScheduledRoot.nextScheduledRoot = firstScheduledRoot;
}
} else {
// This root is already scheduled, but its priority may have increased.
// 如果已经安排过了, 那就判断下过期时间
const remainingExpirationTime = root.expirationTime;
if (expirationTime > remainingExpirationTime) {
// Update the priority.
root.expirationTime = expirationTime;
}
}
}
1.5 performSyncWork 理由同上, 续1.4.4
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberScheduler.js
function performSyncWork() {
performWork(Sync, false);
}
function performWork(
minExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
isYieldy: boolean, // false
) {
// Keep working on roots until there's no more work, or until there's a higher
// priority event.
// 继续工作直到没有更多的工作,或者直到有更高优先级的事件。
// 寻找优先级最高的跟节点
findHighestPriorityRoot();
// ...未完
1.5.1. findHighestPriorityRoot
该函数寻找优先级最高的跟节点
function findHighestPriorityRoot() {
let highestPriorityWork = NoWork; // 0
let highestPriorityRoot = null;
// lastScheduledRoot初始化为null
if (lastScheduledRoot !== null) { // lastScheduledRoot为addRootToSchedule设置的FiberRoot
let previousScheduledRoot = lastScheduledRoot;
let root = firstScheduledRoot; // 也为FiberRoot
while (root !== null) {
const remainingExpirationTime = root.expirationTime;
if (remainingExpirationTime === NoWork) {
// 省略
} else {
if (remainingExpirationTime > highestPriorityWork) {
// Update the priority, if it's higher
highestPriorityWork = remainingExpirationTime; // Sync
highestPriorityRoot = root; // FiberRoot
}
if (root === lastScheduledRoot) {
break; // 退出循环
}
if (highestPriorityWork === Sync) {
// Sync is highest priority by definition so
// we can stop searching.
break;
}
previousScheduledRoot = root;
root = root.nextScheduledRoot;
}
}
}
nextFlushedRoot = highestPriorityRoot; // FiberRoot
nextFlushedExpirationTime = highestPriorityWork; // Sync
}
注意上一个函数把nextFlushedRoot和 nextFlushedExpirationTime 改了, 下面的代码续1.5 performWork:
// 续1.5 performWork函数
// 寻找优先级最高的跟节点
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (isYieldy) {
// ...省略
} else {
while (
nextFlushedRoot !== null &&
nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
minExpirationTime <= nextFlushedExpirationTime
) {
performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime, false);
findHighestPriorityRoot();
}
}
1.5.2. performWorkOnRoot
这个函数主要用来判断是执行renderRoot还是completeRoot(render阶段, 还是commit阶段), 代码如下
function performWorkOnRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
isYieldy: boolean, // false
) {
isRendering = true;
// Check if this is async work or sync/expired work.
if (!isYieldy) {
let finishedWork = root.finishedWork; // null
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// This root is already complete. We can commit it.
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
} else {
root.finishedWork = null;
// If this root previously suspended, clear its existing timeout, since
// we're about to try rendering again.
const timeoutHandle = root.timeoutHandle; // -1
// noTimeout值为-1
if (timeoutHandle !== noTimeout) { // 没有超时
root.timeoutHandle = noTimeout;
// $FlowFixMe Complains noTimeout is not a TimeoutID, despite the check above
cancelTimeout(timeoutHandle);
}
renderRoot(root, isYieldy);
finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// We've completed the root. Commit it.
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
}
}
} else {
// Flush async work.
// .. 省略
}
isRendering = false;
}
1.6. renderRoot 理由同上, 续1.5.2.
这节代码非常多…
部分代码如下:
function renderRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
isYieldy: boolean, // false
): void {
flushPassiveEffects(); // 执行不到不看了
isWorking = true; // 用来标志当前是否有工作正在执行
const previousDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current; // null
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
const expirationTime = root.nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn; // 1.4.2.1 findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn的这个函数设置的Sync
// Check if we're starting from a fresh stack, or if we're resuming from
// previously yielded work.
// nextRenderExpirationTime为变量值为0
if (
expirationTime !== nextRenderExpirationTime ||
root !== nextRoot ||
nextUnitOfWork === null
) {
// Reset the stack and start working from the root.
resetStack();
// resetStack只是把以下变量重置了:
/**
nextRoot = null;
nextRenderExpirationTime = NoWork;
nextLatestAbsoluteTimeoutMs = -1;
nextRenderDidError = false;
nextUnitOfWork = null;
*/
nextRoot = root;
nextRenderExpirationTime = expirationTime;
nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(
nextRoot.current, // FiberNode
null,
nextRenderExpirationTime, // Sync
);// 创建镜像fiber
// ...未完
1.6.1. createWorkInProgress
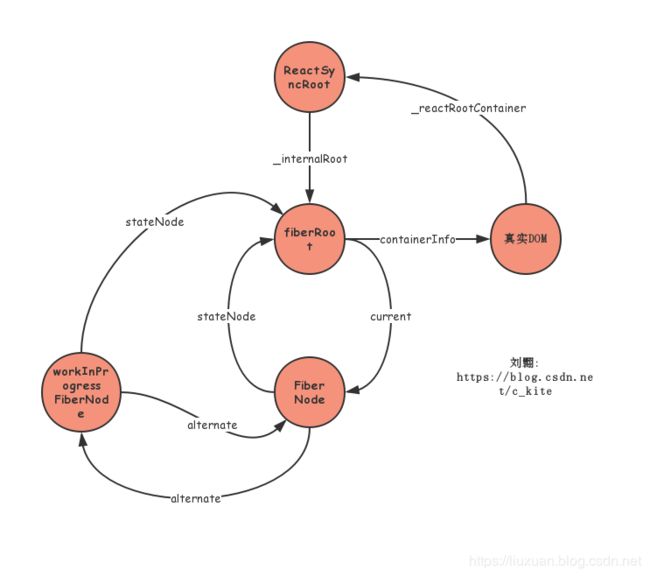
先来看看这个createWorkInProgress函数, 它创建了一个镜像FiberNode
function createWorkInProgress(
current: Fiber, // FiberNode
pendingProps: any, // null
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
): Fiber {
let workInProgress = current.alternate; // 这时候还为null
if (workInProgress === null) {
// We use a double buffering pooling technique because we know that we'll
// only ever need at most two versions of a tree. We pool the "other" unused
// node that we're free to reuse. This is lazily created to avoid allocating
// extra objects for things that are never updated. It also allow us to
// reclaim the extra memory if needed.
// 镜像fiber
workInProgress = createFiber(
current.tag, // 3
pendingProps, // null
current.key, // null
current.mode, // 0
); // 此处调用 new FiberNode(tag, pendingProps, key, mode);返回一个FiberNode
// 此处又可以总结一下画个图了
workInProgress.elementType = current.elementType;
workInProgress.type = current.type;
workInProgress.stateNode = current.stateNode;
if (__DEV__) {
// DEV-only fields
workInProgress._debugID = current._debugID;
workInProgress._debugSource = current._debugSource;
workInProgress._debugOwner = current._debugOwner;
workInProgress._debugHookTypes = current._debugHookTypes;
}
workInProgress.alternate = current;
current.alternate = workInProgress;
} else {
workInProgress.pendingProps = pendingProps;
// We already have an alternate.
// Reset the effect tag.
// 如果已经有镜像fiber的话就重置effect
workInProgress.effectTag = NoEffect;
// The effect list is no longer valid.
workInProgress.nextEffect = null;
workInProgress.firstEffect = null;
workInProgress.lastEffect = null;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
// We intentionally reset, rather than copy, actualDuration & actualStartTime.
// This prevents time from endlessly accumulating in new commits.
// This has the downside of resetting values for different priority renders,
// But works for yielding (the common case) and should support resuming.
workInProgress.actualDuration = 0;
workInProgress.actualStartTime = -1;
}
}
// 部分对象复用
workInProgress.childExpirationTime = current.childExpirationTime;
workInProgress.expirationTime = current.expirationTime;
workInProgress.child = current.child;
workInProgress.memoizedProps = current.memoizedProps;
workInProgress.memoizedState = current.memoizedState;
workInProgress.updateQueue = current.updateQueue;
workInProgress.contextDependencies = current.contextDependencies;
// These will be overridden during the parent's reconciliation
workInProgress.sibling = current.sibling;
workInProgress.index = current.index;
workInProgress.ref = current.ref;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
workInProgress.selfBaseDuration = current.selfBaseDuration;
workInProgress.treeBaseDuration = current.treeBaseDuration;
}
return workInProgress;
}
继续看renderRoot函数:
nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(
nextRoot.current, // FiberNode
null,
nextRenderExpirationTime, // Sync
); // 创建镜像fiber, 返回FiberNode
root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = NoWork; // 0
// 跟踪每个交互触发的每个commit.
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
// 这一期不看, 没有任何交互就是React.render('', dom)
}
}
let prevInteractions: Set<Interaction> = (null: any);
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
// We're about to start new traced work.
// Restore pending interactions so cascading work triggered during the render phase will be accounted for.
prevInteractions = __interactionsRef.current;
__interactionsRef.current = root.memoizedInteractions;
}
let didFatal = false;
// 此函数只在dev环境执行, 使用performance.mark搞个时间戳
startWorkLoopTimer(nextUnitOfWork);
do {
try {
workLoop(isYieldy);
// ...未完
1.6.2. workLoop & performUnitOfWork & beginWork
workLoop函数用来循环执行performUnitOfWork
function workLoop(
isYieldy, // false
) {
if (!isYieldy) {
// Flush work without yielding
// nextUnitOfWork为FiberNode
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {
// Flush asynchronous work until there's a higher priority event
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYieldToRenderer()) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
}
}
performUnitOfWork这个函数主要通过调用beginWork函数, 得到其返回值来判断是执行新work还是完成当前work:
function performUnitOfWork(workInProgress: Fiber): Fiber | null {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate.
// Ideally nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here
// means that we don't need an additional field on the work in
// progress.
// 这时候不需要继续使用镜像Fiber了, 指回来
// 理想情况下,没有什么可以依赖于此,但在此依赖它意味着我们在正在进行的工作中不需要额外的字段。
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
// ...
let next;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
if (workInProgress.mode & ProfileMode) {
startProfilerTimer(workInProgress);
}
next = beginWork(current, workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
// ... 未完
beginWork根据下面的这几个if条件是否进行更新, 如果判断需要更新, 根据FiberNode的tag来执行各自的更新函数.
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null, // FiberNode
workInProgress: Fiber, // 上面的镜像Fiber
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
): Fiber | null {
const updateExpirationTime = workInProgress.expirationTime;
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
if (oldProps !== newProps || hasLegacyContextChanged()) {
// If props or context changed, mark the fiber as having performed work.
// This may be unset if the props are determined to be equal later (memo).
didReceiveUpdate = true;
} else if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
// This fiber does not have any pending work. Bailout without entering
// the begin phase. There's still some bookkeeping we that needs to be done
// in this optimized path, mostly pushing stuff onto the stack.
// 首次进不来, 先不看
switch(...){...}
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(...)
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
// Before entering the begin phase, clear the expiration time.
// 在进入开始阶段之前, 清除过期时间
workInProgress.expirationTime = NoWork;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent: {
// ...省略
}
case LazyComponent: {
// ...省略
}
case FunctionComponent: {
// ...省略
}
case ClassComponent: {
// ...省略 }
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
// ...后面还有好多case省略
}
}
1.7 updateHostRoot, 续1.6.2
继续updateHostRoot
function updateHostRoot(
current, // FiberNode
workInProgress, // 镜像FiberNode
renderExpirationTime, // Sync
) {
pushHostRootContext(workInProgress);
// ...未完
真多层啊
在看pushHostRootContext之前, 先看两个基础函数, 这块会频繁调用
1.7.1 push & pop
1.7.1.1 push
function push<T>(cursor: StackCursor<T>, value: T, fiber: Fiber): void {
index++;
valueStack[index] = cursor.current;
if (__DEV__) { // 只在dev执行
fiberStack[index] = fiber;
}
// 此处重点, cursor.current执行的地址发生了变化, 原来指向的地址被压到valueStack栈中了
cursor.current = value;
}
1.7.1.2. pop
function pop<T>(cursor: StackCursor<T>, fiber: Fiber): void {
cursor.current = valueStack[index]; // 恢复成原来的对象
valueStack[index] = null; // 引用-1
if (__DEV__) { // 引用-1
fiberStack[index] = null;
}
index--;
}
1.7.2. pushHostRootContext
该函数主要把一些关键信息入栈, 便于恢复或者追踪等, 具体代码如下:
function pushTopLevelContextObject(
fiber: Fiber, // 镜像FiberNode
context: Object, // react.context
didChange: boolean, // false
): void {
// 当前context和FiberNode入栈valueStack和fiberStack
push(contextStackCursor, context, fiber);
push(didPerformWorkStackCursor, didChange, fiber);
}
function pushHostRootContext(workInProgress) {
const root = (workInProgress.stateNode: FiberRoot);
if (root.pendingContext) {
pushTopLevelContextObject(
workInProgress,
root.pendingContext,
root.pendingContext !== root.context,
);
} else if (root.context) { // 进到这个判断里
// Should always be set
pushTopLevelContextObject(workInProgress, root.context, false);
}
pushHostContainer(workInProgress, root.containerInfo);
}
1.7.2.1. pushHostContainer
getRootHostContext就不单独细看了, 其他为什么push可以看看如下官方的注释:
function pushHostContainer(
fiber: Fiber, // 镜像FiberNode
nextRootInstance: Container, // 真实DOM
) {
// Push current root instance onto the stack;
// This allows us to reset root when portals are popped.
// 当前root实例入栈
push(rootInstanceStackCursor, nextRootInstance, fiber);
// Track the context and the Fiber that provided it.
// This enables us to pop only Fibers that provide unique contexts.
push(contextFiberStackCursor, fiber, fiber);
// Finally, we need to push the host context to the stack.
// However, we can't just call getRootHostContext() and push it because
// we'd have a different number of entries on the stack depending on
// whether getRootHostContext() throws somewhere in renderer code or not.
// So we push an empty value first. This lets us safely unwind on errors.
push(contextStackCursor, NO_CONTEXT, fiber);
// getRootHostContext函数在packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOMHostConfig.js => 111
// getRootHostContext返回如下对象
/* {
ancestorInfo: {
aTagInScope: null,
buttonTagInScope: null,
current: { tag: "div" },
dlItemTagAutoclosing: null,
formTag: null,
listItemTagAutoclosing: null,
nobrTagInScope: null,
pTagInButtonScope: null,
},
namespace: "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml",
} */
const nextRootContext = getRootHostContext(nextRootInstance);
// Now that we know this function doesn't throw, replace it.
pop(contextStackCursor, fiber);
push(contextStackCursor, nextRootContext, fiber);
}
接下来继续1.7 updateHostRoot函数
// 续1.7 updateHostRoot函数
pushHostRootContext(workInProgress);
const updateQueue = workInProgress.updateQueue; // 1.3.3.2.的那个updateQueue对象
invariant(
updateQueue !== null,
'If the root does not have an updateQueue, we should have already ' +
'bailed out. This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please ' +
'file an issue.',
);
const nextProps = workInProgress.pendingProps; // null
const prevState = workInProgress.memoizedState; // null
const prevChildren = prevState !== null ? prevState.element : null;
processUpdateQueue(
workInProgress,
updateQueue,
nextProps,
null,
renderExpirationTime,
);
1.7.3. processUpdateQueue
这个函数主要处理update和updateQueue, 并根据update获取state
function processUpdateQueue<State>(
workInProgress: Fiber, // 镜像FiberNode
queue: UpdateQueue<State>,
props: any, // null
instance: any, // null
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
): void {
hasForceUpdate = false;
// 保证镜像FiberNode和真正FiberNode的UpdateQueue是不同的对象地址, 如果发现相同了, clone一个新的
queue = ensureWorkInProgressQueueIsAClone(workInProgress, queue);
// ...
// These values may change as we process the queue.
let newBaseState = queue.baseState;
let newFirstUpdate = null;
let newExpirationTime = NoWork;
// Iterate through the list of updates to compute the result.
// 在1.3.3.2中的update对象
let update = queue.firstUpdate;
let resultState = newBaseState;
while (update !== null) {
const updateExpirationTime = update.expirationTime;
if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
// This update does not have sufficient priority. Skip it.
// 这个更新没有足够的优先级, 跳过
if (newFirstUpdate === null) {
// This is the first skipped update. It will be the first update in
// the new list.
newFirstUpdate = update;
// Since this is the first update that was skipped, the current result
// is the new base state.
newBaseState = resultState;
}
// Since this update will remain in the list, update the remaining
// expiration time.
if (newExpirationTime < updateExpirationTime) {
newExpirationTime = updateExpirationTime;
}
} else {
// This update does have sufficient priority. Process it and compute
// a new result.
resultState = getStateFromUpdate(
workInProgress,
queue,
update,
resultState,
props,
instance,
); // 返回{element: "hello"}
const callback = update.callback; // 为ReactWork._onCommit
if (callback !== null) {
// 这里的Callback是常量值为0b000000100000, workInProgress.effectTag为0
workInProgress.effectTag |= Callback; // 或操作
// Set this to null, in case it was mutated during an aborted render.
update.nextEffect = null;
if (queue.lastEffect === null) {
queue.firstEffect = queue.lastEffect = update;
} else {
queue.lastEffect.nextEffect = update;
queue.lastEffect = update;
}
}
}
// Continue to the next update.
update = update.next;
}
// Separately, iterate though the list of captured updates.
let newFirstCapturedUpdate = null;
update = queue.firstCapturedUpdate; // null
while (update !== null) {
// ...省略
}
if (newFirstUpdate === null) {
queue.lastUpdate = null;
}
if (newFirstCapturedUpdate === null) {
queue.lastCapturedUpdate = null;
} else {
workInProgress.effectTag |= Callback;
}
if (newFirstUpdate === null && newFirstCapturedUpdate === null) {
// We processed every update, without skipping. That means the new base
// state is the same as the result state.
newBaseState = resultState;
}
queue.baseState = newBaseState; // resultState
queue.firstUpdate = newFirstUpdate; // null
queue.firstCapturedUpdate = newFirstCapturedUpdate; // null
// Set the remaining expiration time to be whatever is remaining in the queue.
// This should be fine because the only two other things that contribute to
// expiration time are props and context. We're already in the middle of the
// begin phase by the time we start processing the queue, so we've already
// dealt with the props. Context in components that specify
// shouldComponentUpdate is tricky; but we'll have to account for
// that regardless.
workInProgress.expirationTime = newExpirationTime;
workInProgress.memoizedState = resultState;
// ...
}
接下来继续看1.7 updateHostRoot函数
// 续1.7 updateHostRoot函数
processUpdateQueue(
workInProgress,
updateQueue,
nextProps,
null,
renderExpirationTime,
);
const nextState = workInProgress.memoizedState; // 值为{ element: "hello" }
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
const nextChildren = nextState.element; // 'hello'
if (nextChildren === prevChildren) { // prevChildren = null
// If the state is the same as before, that's a bailout because we had
// no work that expires at this time.
resetHydrationState();
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
const root: FiberRoot = workInProgress.stateNode; // 指回FiberRoot
if (
(current === null || current.child === null) &&
root.hydrate &&
enterHydrationState(workInProgress)
) { // current是FiberNode, 此次不为空
workInProgress.effectTag |= Placement;
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
} else {
// Otherwise reset hydration state in case we aborted and resumed another
// root.
reconcileChildren(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
resetHydrationState();
}
return workInProgress.child;
}
1.7.4 reconcileChildren
直接看代码吧:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberBeginWork.js
function reconcileChildren(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber, // 镜像Fiber
nextChildren: any, // "hello"
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, // sync
) {
if (current === null) {
// If this is a fresh new component that hasn't been rendered yet, we
// won't update its child set by applying minimal side-effects. Instead,
// we will add them all to the child before it gets rendered. That means
// we can optimize this reconciliation pass by not tracking side-effects.
// 如果这是一个尚未渲染的新组件,我们会在渲染之前将它们全部添加到子项中
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
} else {
// If the current child is the same as the work in progress, it means that
// we haven't yet started any work on these children. Therefore, we use
// the clone algorithm to create a copy of all the current children.
// If we had any progressed work already, that is invalid at this point so
// let's throw it out.
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
1.7.4.1 reconcileChildFibers
这个函数根据child类型来执行不同的函数, 进而创建各自的FiberNode:
function reconcileChildFibers(
returnFiber: Fiber, // 镜像Fiber
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null, // null
newChild: any, // "hello"
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
): Fiber | null {
// This function is not recursive(递归的).
// If the top level item is an array, we treat it as a set of children,
// not as a fragment. Nested arrays on the other hand will be treated as
// fragment nodes. Recursion happens at the normal flow.
// Handle top level unkeyed fragments as if they were arrays.
// This leads to an ambiguity(歧义) between <>{[...]} and <>....
// We treat the ambiguous cases above the same.
const isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment =
typeof newChild === 'object' &&
newChild !== null &&
newChild.type === REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE &&
newChild.key === null;
if (isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment) {
newChild = newChild.props.children;
}
// Handle object types
const isObject = typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null;
// 根据React类型调用不同函数, 我这边为了看起来简单就是个字符串
if (isObject) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
return ...;
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
return ...;
}
}
if (typeof newChild === 'string' || typeof newChild === 'number') {
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleTextNode(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
'' + newChild,
expirationTime,
),
);
}
// ...后面省略
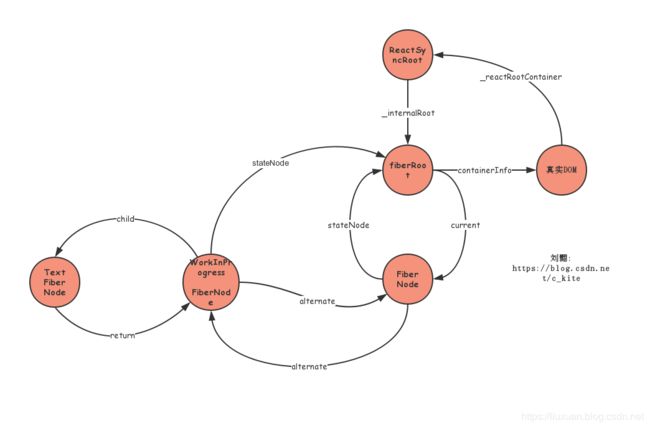
下面来看下reconcileSingleTextNode函数, 该函数主要创建了一个Text类型的Fiber, 代码如下:
function reconcileSingleTextNode(
returnFiber: Fiber, // 镜像Fiber
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null, // null
textContent: string, // 'hello'
expirationTime: ExpirationTime, // Sync
): Fiber {
// There's no need to check for keys on text nodes since we don't have a
// way to define them.
// 我们不需要去检查文本上的节点
if (currentFirstChild !== null && currentFirstChild.tag === HostText) {
// We already have an existing node so let's just update it and delete
// the rest.
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, currentFirstChild.sibling);
const existing = useFiber(currentFirstChild, textContent, expirationTime);
existing.return = returnFiber;
return existing;
}
// The existing first child is not a text node so we need to create one
// and delete the existing ones.
// currentFirstChild为null其实下面这个函数什么都没做
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, currentFirstChild);
const created = createFiberFromText(
textContent, // hello
returnFiber.mode,
expirationTime,
); // 创建一个tag为6, mode为0的FiberNode
created.return = returnFiber;
return created;
}
placeSingleChild函数只是改了Text FiberNode的effectTag就不看了, 到目前为止是这样的, 小节一下:
接下来一路返回到了1.7 updateHostRoot函数, 继续执行
reconcileChildren(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
// 下面这个函数重置了这几个变量:
/*
hydrationParentFiber = null;
nextHydratableInstance = null;
isHydrating = false;
*/
resetHydrationState();
}
return workInProgress.child;
}
返回刚刚的Text FiberNode, 一路回到1.6.2. workLoop函数, 将刚刚返回的Text FiberNode节点代入继续执行performUnitOfWork函数, 流程和上面差不多, 由于例子中ReactDOM.render('hello', document.getElementById('root'));除了text节点没有其他, 则此次beginWork函数返回值为null, 之后便进入了completeUnitOfWork函数, 尝试完成当前work.
1.8 completeUnitOfWork, 续1.6.2. workLoop
代码如下:
function completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress: Fiber): Fiber | null {
// Attempt to complete the current unit of work, then move to the
// next sibling. If there are no more siblings, return to the
// parent fiber.
// 尝试完成当前的工作单元,然后转到下一个兄弟。 如果没有兄弟,返回parent fiber。
while (true) {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate.
// Ideally nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here
// means that we don't need an additional field on the work in
// progress.
// 理想情况下,没有什么可以依赖于current,但在此依赖它意味着我们在正在进行的工作中不需要额外的字段
// 注意此时触发这个函数的Fiber是Text FiberNode, 它没有alternate
const current = workInProgress.alternate; // null
if (__DEV__) {
setCurrentFiber(workInProgress);
}
const returnFiber = workInProgress.return; // parent Fiber, 参考上一小节总结的那个图
const siblingFiber = workInProgress.sibling; // null
// Incomplete是常量值为0b010000000000
// NoEffect是常量值为0b000000000000
if ((workInProgress.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect) {
if (__DEV__ && replayFailedUnitOfWorkWithInvokeGuardedCallback) {
// Don't replay if it fails during completion phase.
mayReplayFailedUnitOfWork = false;
}
// This fiber completed.
// Remember we're completing this unit so we can find a boundary if it fails.
nextUnitOfWork = workInProgress;
// ...省略
nextUnitOfWork = completeWork(
current,
workInProgress,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
// 未完
1.8.1. completeWork
该函数根据传参过来Fiber的tag执行不同的处理, 此时处理的Text:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberCompleteWork.js
function completeWork(
current: Fiber | null, // null
workInProgress: Fiber, // Text Fiber Node
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps; // "hello"
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case HostText: {
let newText = newProps; // "hello"
if (current && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
const oldText = current.memoizedProps;
// If we have an alternate, that means this is an update and we need
// to schedule a side-effect to do the updates.
updateHostText(current, workInProgress, oldText, newText);
} else {
// 检查Root是否正确并返回
const rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer(); // 真实DOM
const currentHostContext = getHostContext();
// hydrate是 React 中提供在初次渲染的时候,去复用原本已经存在的 DOM 节点,减少重新生成节点以及删除原本 DOM 节点的开销,来加速初次渲染的功能
// 这个下次有机会整体看吧, 下面这个函数false
let wasHydrated = popHydrationState(workInProgress); // false
if (wasHydrated) {
if (prepareToHydrateHostTextInstance(workInProgress)) {
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
} else {
workInProgress.stateNode = createTextInstance(
newText,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
workInProgress,
);
}
}
break;
}
// 省略
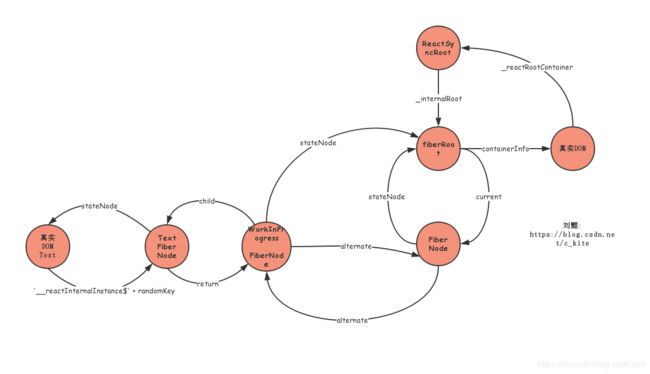
1.8.1.1 createTextInstance
这个函数主要创建一个真实的TextNode节点, 并将它和Fiber关联上, 代码如下:
const randomKey = Math.random()
.toString(36) // 36进制
.slice(2);
const internalInstanceKey = '__reactInternalInstance$' + randomKey;
export function precacheFiberNode(hostInst, node) {
node[internalInstanceKey] = hostInst;
}
// packages\react-dom\src\client\ReactDOMHostConfig.js
function createTextInstance(
text: string, // "hello"
rootContainerInstance: Container, // "真实DOM"
hostContext: HostContext,
internalInstanceHandle: Object, // Text FiberNode
): TextInstance {
if (__DEV__) {
const hostContextDev = ((hostContext: any): HostContextDev);
// 检查当前节点是否可以放在父节点下
validateDOMNesting(null, text, hostContextDev.ancestorInfo);
}
// 下面设个函数获取document, 调用其createTextNode方法创建text节点
// 返回真实Dom Text节点
const textNode: TextInstance = createTextNode(text, rootContainerInstance);
precacheFiberNode(internalInstanceHandle, textNode);
return textNode;
}
又可以小节一下了:
接下来返回到了1.8 completeUnitOfWork函数, 我们继续分析下去, 接下来其实主要是把Root镜像Fiber Node的firstEffect和lastEffect赋值成了Text Fiber Node, 然后把当前的workInProgress变量赋值成Root镜像Fiber Node继续while循环:
nextUnitOfWork = completeWork(
current,
workInProgress,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
}
// 更新当前Fiber的childExpirationTime
resetChildExpirationTime(workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
if (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
// Completing this fiber spawned new work. Work on that next.
return nextUnitOfWork;
}
// returnFiber 为Root的镜像Fiber Node
if (
returnFiber !== null &&
(returnFiber.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect
) {
// Append all the effects of the subtree and this fiber onto the effect
// list of the parent. The completion order of the children affects the
// side-effect order.
if (returnFiber.firstEffect === null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect; // 都为null
}
// workInProgress.lastEffect为null
if (workInProgress.lastEffect !== null) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress.lastEffect;
}
// If this fiber had side-effects, we append it AFTER the children's
// side-effects. We can perform certain side-effects earlier if
// needed, by doing multiple passes over the effect list. We don't want
// to schedule our own side-effect on our own list because if end up
// reusing children we'll schedule this effect onto itself since we're
// at the end.
const effectTag = workInProgress.effectTag;
// Skip both NoWork and PerformedWork tags when creating the effect list.
// PerformedWork effect is read by React DevTools but shouldn't be committed.
if (effectTag > PerformedWork) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress;
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress;
}
}
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
return siblingFiber;
} else if (returnFiber !== null) {
// If there's no more work in this returnFiber. Complete the returnFiber.
// 将当前的workInProgress赋值成了镜像FiberNode继续循环
workInProgress = returnFiber;
continue;
} else {
// We've reached the root.
return null;
}
第二次while循环最后返回null, 退出while循环, 一路回到1.6.2. workLoop函数, 由于此时函数返回的是null, 因此也退出了workloop函数, 之后再返回到了1.5.2 performWorkOnRoot函数, 继续往下执行, 进入commit阶段
2. commit阶段 completeRoot
代码如下:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberScheduler.js
function completeRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber, // Root的镜像Fiber Node
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): void {
// Check if there's a batch that matches this expiration time.
const firstBatch = root.firstBatch;
if (firstBatch !== null && firstBatch._expirationTime >= expirationTime) {
// ...省略
}
// Commit the root.
root.finishedWork = null;
// Check if this is a nested update (a sync update scheduled during the
// commit phase).
// 检查这是否是嵌套更新
if (root === lastCommittedRootDuringThisBatch) {
// If the next root is the same as the previous root, this is a nested
// update. To prevent an infinite loop, increment the nested update count.
nestedUpdateCount++;
} else {
// Reset whenever we switch roots.
// 进到这里
lastCommittedRootDuringThisBatch = root;
nestedUpdateCount = 0;
}
runWithPriority(ImmediatePriority, () => {
commitRoot(root, finishedWork);
});
}
runWithPriority函数是react-schedule里面的unstable_runWithPriority函数, 主要功能是更改了其包内的currentPriorityLevel和currentEventStartTime变量, 然后开始执行回调函数, 即commitRoot函数
2.1. commitRoot
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberPendingPriority.js
function markCommittedPriorityLevels(
root: FiberRoot,
earliestRemainingTime: ExpirationTime,
): void {
root.didError = false;
if (earliestRemainingTime === NoWork) {
// Fast path. There's no remaining work. Clear everything.
root.earliestPendingTime = NoWork;
root.latestPendingTime = NoWork;
root.earliestSuspendedTime = NoWork;
root.latestSuspendedTime = NoWork;
root.latestPingedTime = NoWork;
// 首此渲染将Fiber root的nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn和expirationTime赋值为0
findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn(NoWork, root);
return;
}
// ...后面省略
}
commitRoot函数代码如下:
function commitRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber, // Root的镜像Fiber Node
): void {
isWorking = true;
isCommitting = true;
startCommitTimer(); // 只在dev触发
// pendingCommitExpirationTime该值在renderRoot函数最后设置了
const committedExpirationTime = root.pendingCommitExpirationTime;
root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = NoWork;
// Update the pending priority levels to account for the work that we are
// about to commit. This needs to happen before calling the lifecycles, since
// they may schedule additional updates.
// 更新待处理的优先级
const updateExpirationTimeBeforeCommit = finishedWork.expirationTime; // 0
const childExpirationTimeBeforeCommit = finishedWork.childExpirationTime; // 0
const earliestRemainingTimeBeforeCommit =
childExpirationTimeBeforeCommit > updateExpirationTimeBeforeCommit
? childExpirationTimeBeforeCommit
: updateExpirationTimeBeforeCommit; // 0
// 由于是首次渲染, 重置了Fiber Root内部的一些参数, 参见上面那个函数
markCommittedPriorityLevels(root, earliestRemainingTimeBeforeCommit);
let prevInteractions: Set<Interaction> = (null: any);
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
// Restore any pending interactions at this point,
// So that cascading work triggered during the render phase will be accounted for.
prevInteractions = __interactionsRef.current;
__interactionsRef.current = root.memoizedInteractions;
}
// Reset this to null before calling lifecycles
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
let firstEffect;
if (finishedWork.effectTag > PerformedWork) {
// A fiber's effect list consists only of its children, not itself. So if
// the root has an effect, we need to add it to the end of the list. The
// resulting list is the set that would belong to the root's parent, if
// it had one; that is, all the effects in the tree including the root.
if (finishedWork.lastEffect !== null) {
finishedWork.lastEffect.nextEffect = finishedWork; // Root的镜像Fiber Node
firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect; // Text Fiber Node
} else {
firstEffect = finishedWork;
}
} else {
// There is no effect on the root.
firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
}
// prepareForCommit函数主要是做了下面这些事情
// eventsEnabled = true
// selectionInformation = {
// focusedElem: 真实DOM元素 body,
// selectionRange: null
// };
prepareForCommit(root.containerInfo);
// Invoke instances of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate before mutation.
nextEffect = firstEffect; // Text Fiber Node
startCommitSnapshotEffectsTimer();
while (nextEffect !== null) {
let didError = false;
let error;
if (__DEV__) {
invokeGuardedCallback(null, commitBeforeMutationLifecycles, null);
if (hasCaughtError()) {
didError = true;
error = clearCaughtError();
}
} else {
try {
commitBeforeMutationLifecycles();
} catch (e) {
didError = true;
error = e;
}
}
// ...未完
commitBeforeMutationLifecycles是pre-commit阶段结束的标志(只有更新时有这个阶段, 挂载时没有), 主要内部是判断是否应该触发getSnapshotBeforeUpdate生命周期.
2.1.1. invokeGuardedCallback
可以看到在Dev环境会调用invokeGuardedCallback函数来进行下一步操作, 下面来具体看下这个函数究竟干了写什么:
在Dev环境使用这个函数的目的: 为了在dev环境可以与浏览器的DevTools更好地配合使用, 保留“Pause on exceptions”行为. React在invokeGuardedCallback中包装了所有用户提供的函数, 所有用户异常都被视为捕获的异常(这样就不会触发"Pause on exceptions"),除非开发人员采取额外步骤在捕获的异常上启用暂停,否则DevTools不会暂停
生产环境直接使用try-catch
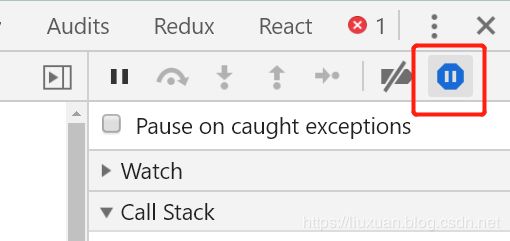
这个"Pause on exceptions"指的是浏览器下图这个行为, 遇到报错直接暂停程序执行了.
代码如下:
function invokeGuardedCallback<A, B, C, D, E, F, Context>(
name: string | null,
func: (a: A, b: B, c: C, d: D, e: E, f: F) => mixed,
context: Context,
a: A,
b: B,
c: C,
d: D,
e: E,
f: F,
): void {
hasError = false;
caughtError = null;
invokeGuardedCallbackImpl.apply(reporter, arguments);
}
实现原理: 同步地将fake event分派给fake DOM node, 在fake event中调用用户提供的函数, 如果回调抛出错误, 则会"捕获", 因为发生在不同的上下文中, 它不会打断正常执行.
下面会涉及到自定义事件, 补充个小知识点:
// 创建事件.
var event = document.createEvent('Event');
// 初始化一个点击事件,可以冒泡,无法被取消
event.initEvent('click', true, false);
// 设置事件监听.
elem.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
}, false);
// 触发事件监听
elem.dispatchEvent(event);
let invokeGuardedCallbackImpl = function<A, B, C, D, E, F, Context>(
name: string | null,
func: (a: A, b: B, c: C, d: D, e: E, f: F) => mixed,
context: Context,
a: A,
b: B,
c: C,
d: D,
e: E,
f: F,
) {
const funcArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 3);
try {
func.apply(context, funcArgs);
} catch (error) {
this.onError(error);
}
};
if (__DEV__) {
// 检查是否支持所用的api
if (
typeof window !== 'undefined' &&
typeof window.dispatchEvent === 'function' &&
typeof document !== 'undefined' &&
typeof document.createEvent === 'function'
) {
const fakeNode = document.createElement('react');
const invokeGuardedCallbackDev = function<A, B, C, D, E, F, Context>(
name: string | null,
func: (a: A, b: B, c: C, d: D, e: E, f: F) => mixed,
context: Context,
a: A,
b: B,
c: C,
d: D,
e: E,
f: F,
) {
const evt = document.createEvent('Event');
// 跟踪用户提供的回调是否引发错误. 在开始时将其设置为true,然后在调用函数后立即将其设置为false, 如果函数错误,`didError`将永远不会设置为false
let didError = true;
// Keeps track of the value of window.event so that we can reset it
// during the callback to let user code access window.event in the
// browsers that support it.
let windowEvent = window.event;
// Keeps track of the descriptor of window.event to restore it after event
// dispatching: https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/13688
// 追踪window.event的描述符, 在event dispathching之后恢复它
const windowEventDescriptor = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(
window,
'event',
);
// 为了fake event创建一个event handler, 使用`dispatchEvent`触发fake event. 在event handler中调用用户提供的回调函数.
const funcArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 3);
function callCallback() {
// We immediately remove the callback from event listeners so that
// nested `invokeGuardedCallback` calls do not clash. Otherwise, a
// nested call would trigger the fake event handlers of any call higher
// in the stack.
fakeNode.removeEventListener(evtType, callCallback, false);
// We check for window.hasOwnProperty('event') to prevent the
// window.event assignment in both IE <= 10 as they throw an error
// "Member not found" in strict mode, and in Firefox which does not
// support window.event.
if (
typeof window.event !== 'undefined' &&
window.hasOwnProperty('event')
) {
window.event = windowEvent;
}
func.apply(context, funcArgs);
didError = false;
}
// 创建一个全局错误event handler, 使用它来捕获抛出的值。 这个错误处理程序可能会多次触发;
let error;
// 使用它来跟踪是否曾调用错误事件.
let didSetError = false;
let isCrossOriginError = false;
function handleWindowError(event) {
error = event.error;
didSetError = true;
if (error === null && event.colno === 0 && event.lineno === 0) {
isCrossOriginError = true;
}
if (event.defaultPrevented) {
// Some other error handler has prevented default.
// Browsers silence the error report if this happens.
// We'll remember this to later decide whether to log it or not.
if (error != null && typeof error === 'object') {
try {
error._suppressLogging = true;
} catch (inner) {
// Ignore.
}
}
}
}
// 创建一个fake event type
const evtType = `react-${name ? name : 'invokeguardedcallback'}`;
// 绑定事件处理程序event handlers
window.addEventListener('error', handleWindowError);
fakeNode.addEventListener(evtType, callCallback, false);
// Synchronously dispatch our fake event. If the user-provided function
// errors, it will trigger our global error handler.
evt.initEvent(evtType, false, false);
fakeNode.dispatchEvent(evt);
if (windowEventDescriptor) {
Object.defineProperty(window, 'event', windowEventDescriptor);
}
if (didError) {
if (!didSetError) {
// The callback errored, but the error event never fired.
error = new Error(
...
);
} else if (isCrossOriginError) {
error = new Error(
....
);
}
this.onError(error);
}
// Remove our event listeners
window.removeEventListener('error', handleWindowError);
};
invokeGuardedCallbackImpl = invokeGuardedCallbackDev;
}
}
继续2.1.1. commitRoot函数:
// 只在dev触发
stopCommitSnapshotEffectsTimer();
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
// Mark the current commit time to be shared by all Profilers in this batch.
// This enables them to be grouped later.
recordCommitTime();
}
// 在树中提交所有side-effects, 将分两次, 第一遍执行所有插入,更新,删除和ref卸载。
nextEffect = firstEffect; // Text Fiber Node
startCommitHostEffectsTimer(); // 记录时间用的, 只在dev触发
while (nextEffect !== null) {
let didError = false;
let error;
if (__DEV__) {
invokeGuardedCallback(null, commitAllHostEffects, null);
if (hasCaughtError()) {
didError = true;
error = clearCaughtError();
}
} else {
try {
commitAllHostEffects();
} catch (e) {
didError = true;
error = e;
}
}
接下来看下commitAllHostEffects函数:
2.1.2. commitAllHostEffects
该函数主要根据fiber node的effectTag执行不同的commit操作, 代码如下:
function commitAllHostEffects() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
if (__DEV__) {
setCurrentFiber(nextEffect);
}
recordEffect();
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag;
if (effectTag & ContentReset) {
// 重置节点文字内容
commitResetTextContent(nextEffect);
}
if (effectTag & Ref) {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
commitDetachRef(current);
}
}
//以下switch语句仅关注placement, updates, and deletions
let primaryEffectTag = effectTag & (Placement | Update | Deletion);
switch (primaryEffectTag) {
case Placement: {
// 例子是就是一个字符串进到这里
commitPlacement(nextEffect);
// Clear the "placement" from effect tag so that we know that this is inserted, before
// any life-cycles like componentDidMount gets called.
// TODO: findDOMNode doesn't rely on this any more but isMounted
// does and isMounted is deprecated anyway so we should be able
// to kill this.
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;
break;
}
case PlacementAndUpdate: {
// Placement
commitPlacement(nextEffect);
// Clear the "placement" from effect tag so that we know that this is inserted, before
// any life-cycles like componentDidMount gets called.
// nextEffect.effectTag目前为2
// Placement常量值为0b000000000010
// 具体位运算可以参考https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Bitwise_Operators
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement; // nextEffect.effectTag = 0
// Update
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
case Update: {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
case Deletion: {
commitDeletion(nextEffect);
break;
}
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
}
if (__DEV__) {
resetCurrentFiber();
}
}
2.1.2.1. commitPlacement
例子进到了这里来看一下, 终于到了实际操作DOM的时候了, 代码如下:
function commitPlacement(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
if (!supportsMutation) {
return;
}
// Recursively insert all host nodes into the parent.
// 返回当前Text Fiber Node的return属性, 也就是镜像fiber node
const parentFiber = getHostParentFiber(finishedWork);
// Note: these two variables *must* always be updated together.
let parent;
let isContainer;
switch (parentFiber.tag) {
case HostComponent:
parent = parentFiber.stateNode;
isContainer = false;
break;
case HostRoot:
parent = parentFiber.stateNode.containerInfo; // 真实DOM节点
isContainer = true;
break;
case HostPortal:
parent = parentFiber.stateNode.containerInfo;
isContainer = true;
break;
default:
invariant(
false,
'Invalid host parent fiber. This error is likely caused by a bug ' +
'in React. Please file an issue.',
);
}
if (parentFiber.effectTag & ContentReset) {
// Reset the text content of the parent before doing any insertions
resetTextContent(parent);
// Clear ContentReset from the effect tag
parentFiber.effectTag &= ~ContentReset;
}
// 此处返回的null
const before = getHostSibling(finishedWork);
// We only have the top Fiber that was inserted but we need to recurse down its
// children to find all the terminal nodes.
let node: Fiber = finishedWork;
while (true) {
if (node.tag === HostComponent || node.tag === HostText) {
if (before) {
if (isContainer) {
insertInContainerBefore(parent, node.stateNode, before);
} else {
insertBefore(parent, node.stateNode, before);
}
} else {
if (isContainer) {
appendChildToContainer(parent, node.stateNode); // 没错, 这里此处直接调用的appendChild
} else {
appendChild(parent, node.stateNode);
}
}
} else if (node.tag === HostPortal) {
// If the insertion itself is a portal, then we don't want to traverse
// down its children. Instead, we'll get insertions from each child in
// the portal directly.
} else if (node.child !== null) {
node.child.return = node;
node = node.child;
continue;
}
if (node === finishedWork) {
return; // 返回
}
while (node.sibling === null) {
if (node.return === null || node.return === finishedWork) {
return;
}
node = node.return;
}
node.sibling.return = node.return;
node = node.sibling;
}
}
后面还有一个commitAllLifeCycles操作, 由于例子比较简单没有进到, 后期分析生命周期的时候再看. 接下来就一路返回退出了. 真长…
3. 初次渲染总结
render阶段有个操作:
- 初始化
Fiber Root和Fiber Node, 将FiberRoot放到Schedule循环链表中 - 执行
renderRoot, 创建镜像Fiber Node - 根据
child类型来执行不同的函数, 进而创建各自的FiberNode - 设置
Fiber Node的side-effects之后进入commit 阶段
commit 阶段有3个主要操作:
- 在更新DOM和ref之前调用
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(pre-commit阶段, 只发生在更新阶段) - 在树中提交所有
side-effects, 将分两次, 第一遍执行所有插入,更新,删除和ref卸载。 - 第二遍提交
side-effects时执行所有生命周期和ref回调