Hibernate实战——复合主键的成员属性为关联实体
一 配置
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost/hibernate
root
32147
20
1
5000
100
3000
2
true
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
true
true
update
二 PO
1 Product
package org.crazyit.app.domain;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name="product_inf")
public class Product
{
// 定义标识属性
@Id @Column(name="product_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer productId;
private String name;
// 无参数的构造器
public Product(){}
// 初始化全部属性的构造器
public Product(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
// productId的setter和getter方法
public void setProductId(Integer productId)
{
this.productId = productId;
}
public Integer getProductId()
{
return this.productId;
}
// name的setter和getter方法
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return this.name;
}
}2 OrderItem
package org.crazyit.app.domain;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name="order_inf")
public class Order
{
// 定义标识属性
@Id @Column(name="order_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer orderId;
private Date orderDate;
// 关联的的订单项
@OneToMany(targetEntity=OrderItem.class, mappedBy="order")
private Set items
= new HashSet<>();
// 无参数的构造器
public Order(){}
// 初始化全部成员变量的构造器
public Order(Date orderDate)
{
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
// orderId的setter和getter方法
public void setOrderId(Integer orderId)
{
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public Integer getOrderId()
{
return this.orderId;
}
// orderDate的setter和getter方法
public void setOrderDate(Date orderDate)
{
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
public Date getOrderDate()
{
return this.orderDate;
}
// items的setter和getter方法
public void setItems(Set items)
{
this.items = items;
}
public Set getItems()
{
return this.items;
}
} 3 Order
package org.crazyit.app.domain;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
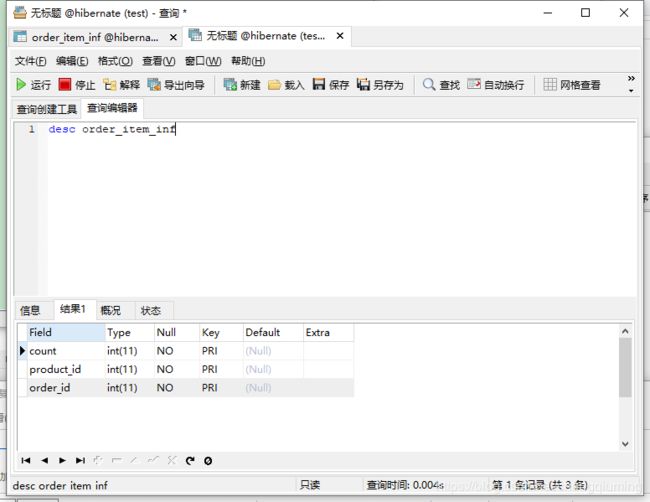
@Table(name="order_item_inf")
public class OrderItem
implements java.io.Serializable
{
// 下面3个属性将作为联合主键
// 定义关联的Order实体
@ManyToOne(targetEntity=Order.class)
// 映射名为order_id的外键列,参照order_inf的order_id主键列
@JoinColumn(name="order_id" , referencedColumnName="order_id")
@Id
private Order order;
// 定义关联的Product实体
@ManyToOne(targetEntity=Product.class)
// 映射名为product_id的外键列,参照product_inf的product_id主键列
@JoinColumn(name="product_id" , referencedColumnName="product_id")
@Id
private Product product;
// 该订单项订购的产品数量
@Id
private int count;
// 无参数的构造器
public OrderItem(){ }
// 初始化全部成员变量的构造器
public OrderItem(Order order , Product product , int count)
{
this.order = order;
this.product = product;
this.count = count;
}
// order的setter和getter方法
public void setOrder(Order order)
{
this.order = order;
}
public Order getOrder()
{
return this.order;
}
// product的setter和getter方法
public void setProduct(Product product)
{
this.product = product;
}
public Product getProduct()
{
return this.product;
}
// count的setter和getter方法
public void setCount(int count)
{
this.count = count;
}
public int getCount()
{
return this.count;
}
// 重写equals()方法,根据product、order、count判断是否相等
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if(this == obj)
{
return true;
}
if(obj != null && obj.getClass() == OrderItem.class)
{
OrderItem target = (OrderItem)obj;
return this.order.equals(target.getOrder())
&& this.product.equals(target.getProduct())
&& this.count == target.getCount();
}
return false;
}
// 重写hashCode()方法,根据product、order、count计算hashCode值
public int hashCode()
{
return (this.product == null ? 0 : this.product.hashCode()) * 31 * 31
+ (this.order == null ? 0 : this.order.hashCode()) * 31
+ this.count;
}
}三 测试
1 工具类
package lee;
import org.hibernate.*;
import org.hibernate.cfg.*;
import org.hibernate.service.*;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.*;
public class HibernateUtil
{
public static final SessionFactory sessionFactory;
static
{
try
{
// 使用默认的hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件创建Configuration实例
Configuration cfg = new Configuration()
.configure();
// 以Configuration实例来创建SessionFactory实例
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.applySettings(cfg.getProperties()).build();
sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
}
catch (Throwable ex)
{
System.err.println("Initial SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
// ThreadLocal可以隔离多个线程的数据共享,因此不再需要对线程同步
public static final ThreadLocal session
= new ThreadLocal();
public static Session currentSession()
throws HibernateException
{
Session s = session.get();
// 如果该线程还没有Session,则创建一个新的Session
if (s == null)
{
s = sessionFactory.openSession();
// 将获得的Session变量存储在ThreadLocal变量session里
session.set(s);
}
return s;
}
public static void closeSession()
throws HibernateException
{
Session s = session.get();
if (s != null)
s.close();
session.set(null);
}
} 2 测试类
package lee;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import java.util.*;
import org.crazyit.app.domain.*;
public class OrderManager
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
OrderManager mgr = new OrderManager();
mgr.createAndStoreOrder();
HibernateUtil.sessionFactory.close();
}
private void createAndStoreOrder()
{
Session sess = HibernateUtil.currentSession();
Transaction tx = sess.beginTransaction();
Order order = new Order(new Date());
Product p1 = new Product("键盘");
Product p2 = new Product("显示器");
OrderItem item1 = new OrderItem(order , p1 , 50);
OrderItem item2 = new OrderItem(order , p2 , 18);
sess.save(order);
sess.save(p1);
sess.save(p2);
sess.save(item1);
sess.save(item2);
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}
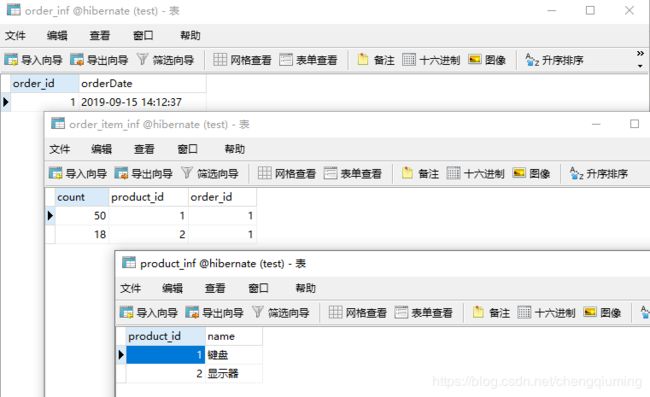
}四 测试
Hibernate:
insert
into
order_inf
(orderDate)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
product_inf
(name)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
product_inf
(name)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
order_item_inf
(product_id, order_id, count)
values
(?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
order_item_inf
(product_id, order_id, count)
values
(?, ?, ?)