C Primer Plus(第6版)第三章编程练习答案
第3章 数据和C(P68-P69)
1 通过试验(即编写带有此类问题的程序)观察系统如何处理整数上溢、浮点数上溢和浮点数下溢的情况。
#include
#include
int main()
{
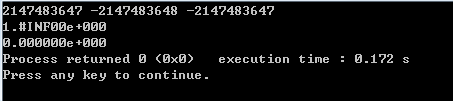
int a = 2147483647;
float b = 3.4E38 * 100.0f;
float c = (3.4E-38) / (100.0E100);
printf("%d %d %d\n", a, a+1, a+2); //整数上溢
printf("%e\n", b); //浮点数上溢
printf("%e", c); //浮点数下溢
return 0;
} 对于整数,小于最小值为下溢,大于最大值为上溢(指代数值)。
对于浮点数,绝对值小于浮点数所能表示的最小值,为下溢,当作 0;绝对值大于浮点数所能表示的最大范围,为上溢,当作 INF(指绝对值)。
2 编写一个程序,要求提示输入一个ASCII码值(如66),然后打印输入的字符。
#include
#include
int main()
{
int i;
printf("请输入一个ASCII值:");
scanf("%d", &i);
printf("ASCII值对应的字符为:%c\n", i);
return 0;
} 4 编写一个程序,读取一个浮点数,先打印成小数点形式,再打印成指数形式。然后,如果系统支持,再打印成p记数法(即十六进制记数法)。按以下格式输出(实际显示的指数位数因系统而异):
Enter a floating-point value: 64.25
fixed-point notation: 64.250000
exponential notation: 6.425000e+01
p notation: 0x1.01p+6
#include
#include
int main()
{
float i;
printf("Enter a floating-point value:");
scanf("%f", &i);
printf("fixed-point notation:%f\n", i); //float默认只保留小数部分6位的精度
printf("exponential notation:%e\n", i);
printf("p notation:%a\n", i);
return 0;
} 5 一年大约有3.156E7秒。编写一个程序,提示用户输入年龄,然后显示该年龄对应的秒数。
#include
#include
int main()
{
int age = 0;
float ageMinutes;
printf("请输入您的年龄:");
scanf("%d", &age);
ageMinutes = age * 3.156E7;
printf("年龄对应的秒数为:%f\n", ageMinutes);
printf("年龄对应的秒数为:%e\n", ageMinutes);
return 0;
}
6 1个水分子的质量约为3.0E-23克。1夸脱水大约是950克。编写一个程序,提示用户输入水的夸脱数,并显示水分子的数量。
#include
#include
int main()
{
float quantity_mol = 3.0E-23;
float quantity_qt = 950;
float quarts;
float molecules;
printf("请输入水的夸脱数:");
scanf("%f", &quarts);
molecules = quantity_qt * quarts / quantity_mol;
printf("水分子的数量为:%e", molecules);
return 0;
} 8 在美国的体积测量系统中,1品脱等于2杯,1杯等于8盎司,1盎司等于2大汤勺,1大汤勺等于3茶勺。编写一个程序,提示用户输入杯数,并以品脱、盎司、汤勺、茶勺为单位显示等价容量。思考对于该程序,为何使用浮点类型比整数类型更合适。
#include
#include
int main()
{
float cups;
printf("请输入杯数:");
scanf("%f", &cups);
float pints = cups / 2;
float ounces = 8 * cups;
float spoons = 8 * cups * 2;
float teaspoons = 8 * cups * 2 * 3;
printf("品脱:%f\t盎司:%f\t汤勺:%f\t茶勺:%f\n", pints, ounces, spoons, teaspoons);
return 0;
} 假如用pints用整数类型的话,若杯数是5.5杯,那么pints就会舍去小数位的数字,从而不会那么精确。
若有错误请指出
转载请注明文章出处