Nginx常见问题
1. Nginx多Server优先级
在开始处理一个http请求时,nginx会取出header头中的Host变量,与nginx.conf中的每个server_name进行匹配,以此决定到底由哪一个server来处理这个请求,但nginx如何配置多个相同的server_name,会导致server_name出现优先级访问冲突。
1.1 准备nginx对应的配置文件
[root@web01 conf.d]# cat server1.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost test1.com;
location / {
root /code/test1;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@web01 conf.d]# cat server2.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost test2.com;
location / {
root /code/test2;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@web01 conf.d]# cat server3.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost test3.com;
location / {
root /code/test3;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@web01 conf.d]#1.2 准备站点目录
[root@web01 conf.d]# mkdir /code/test{1..3}
[root@web01 conf.d]# echo test1 > /code/test1/index.html
[root@web01 conf.d]# echo test2 > /code/test2/index.html
[root@web01 conf.d]# echo test3 > /code/test3/index.html1.3 检查语法提示冲突,忽略并重启
[root@web01 conf.d]# nginx -t
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "localhost" on 0.0.0.0:80, ignored
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "localhost" on 0.0.0.0:80, ignored
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@web01 conf.d]# nginx -s reload
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "localhost" on 0.0.0.0:80, ignored
nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "localhost" on 0.0.0.0:80, ignored
[root@web01 conf.d]#1.4 浏览器访问测试
#根据域名访问测试正常#根据ip访问
#1. 用户第一次访问,读取server1.conf配置返回结果
[root@lb01 ~]# curl 10.0.0.5
test1
#2. 此时将server1.conf修改为server4.conf重启nginx
[root@lb01 conf.d]# mv server1.conf server4.conf
[root@lb01 conf.d]# nginx -s reload
#3. 再次访问时,读取server2.conf配置返回结果
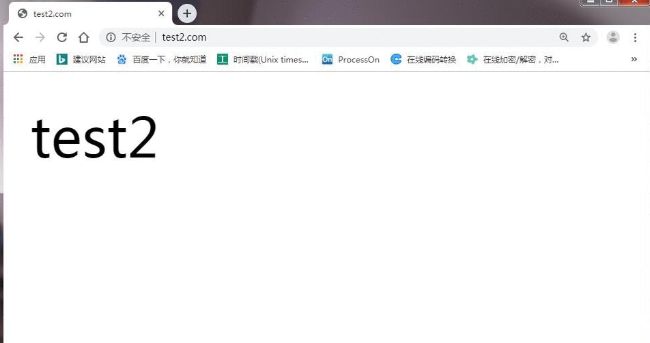
[root@lb01 conf.d]# curl 10.0.0.5
test21.5 多Server_name优先级总结
再开始处理一个HTTP请求时,Nginx会读取header(请求头)中的host,与每个server中的server_name进行匹配,来决定用哪一个server标签来完成处理这个请求,有可能一个Host与多个server中的server_name都匹配,这个时候就会根据匹配优先级来选择实际处理的server。优先级匹配结果如下:
1.首先选择所有的字符串完全匹配的server_name。(完全匹配)
2.选择通配符在前面的server_name,如.haoda.com www.haoda.com3.选择通配符在后面的server_name,如bgx. haoda.com haoda.cn
4.最后选择使用正则表达式匹配的server_name
5.如果全部都没有匹配到,那么将选择在listen配置项后加入[default_server]的server块
6.如果没写,那么就找到匹配listen端口的第一个Server块的配置文件
注意:当出现多个相同的server_name情况下,配置文件排序优先使用则会被调用,所以建议配置相同端口,不同域名,这样不会出现域名访问冲突。
2. Nginx禁止IP直接访问
当用户通过访问IP或者未知域名访问你得网站的时候,你希望禁止显示任何有效内容,可以给他返回500,目前国内很多机房都要求网站关闭空主机头,防止未备案的域名指向过来造成麻烦
2.1 Nginx禁止IP访问
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat server4.conf
server {
listen 80 default_server; #默认优先返回;
server_name _; #空主机头或者IP;
return 500; #直接返回500错误;
}2.2 引流的方式将访问的IP直接跳转主站域名
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat server4.conf
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
return 302 http://test1.com;
}Nginx包含文件Include
一台服务器配置多个网站,如果配置都写在nginx.conf主配置文件中,会导致nginx.conf主配置文件变得非常庞大而且可读性非常的差。那么后期的维护就变得麻烦。 假设现在希望快速的关闭一个站点,该怎么办? 1.如果是写在nginx.conf中,则需要手动注释,比较麻烦 2.如果是include的方式,那么仅需修改配置文件的扩展名,即可完成注释 Include包含的作用是为了简化主配置文件,便于人类可读。
inlcude /etc/nginx/online/*.conf #线上使用的配置
/etc/nginx/offline #保留配置,不启用(下次使用在移动到online中)
Nginx路径root与alias
root与alias路径匹配主要区别在于nginx如何解释location后面的uri,这会使两者分别以不同的方式将请求映射到服务器文件上,alias是一个目录别名的定义,root则是最上层目录的定义。
root的处理结果是:root路径+location路径alias的处理结果是:使用alias定义的路径
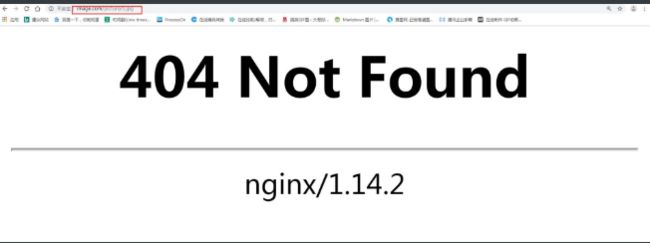
1 使用root时,用户访问http://image.com/picture/1.jpg时,实际上Nginx会到/code/picture/目录下找1.jpg文件
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat image.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name image.com;
location /picture {
root /code;
}
}2 使用alias时,用户访问http://image.com/picture/1.jpg时,实际上Nginx会到/code/目录下找1.jpg文件
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat image.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name image.com;
location /picture {
alias /code;
}
}3 线上一般配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name image.oldboy.com;
location / {
root /code;
}
location ~* ^.*\.(png|jpg|gif)$ {
alias /code/images/;
}
}Nginx try_file路径匹配
nginx的try_file路径匹配,Nginx会按顺序检查文件及目录是否存在(根据 root 和 alias 指令设置的参数构造完整的文件路径),并用找到的第一个文件提供服务。在元素名后面添加斜杠 / 表示这个是目录。如果文件和目录都不存在,Nginx会执行内部重定向,跳转到命令的最后一个 uri 参数定义的 URI 中。
1 Nginx try_file配置实例1
#1. 配置nginx
[root@lb01 conf.d]# vim try.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name try.haoda.com;
root /code;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri /404.html;
}
}
#2. 创建实例目录与文件
[root@lb01 conf.d]# echo try11111 > /code/index.html
[root@lb01 conf.d]# echo '404 404 404' > /code/404.html
#3. 尝试访问try.haoda.com
[root@lb01 conf.d]# curl try.haoda.com
404 404 404
#由于访问的是try.haoda.com,而$uri取得是域名后面我们写的内容,它找不到,所以返回后面的内容,即404.html
#4. 尝试访问try.haoda.com/index.html
[root@lb01 conf.d]# curl try.haoda.com/index.html
try11111
#由于访问的是try.haoda.com/index.html,而$uri取到了index.html所以返回/code/index.html的内容
#5. 修改配置为
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /404.html;
}
#6. 再次尝试访问try.haoda.com
[root@lb01 conf.d]# curl try.haoda.com
try11111
#我们访问的是try.haoda.com,而$uri我们没有写任何内容,于是他访问的便是“空/”,即匹配到/code/index.html举例
location /images/ {
try_files $uri $uri/ /404.html;
}用户请求try.haoda.com/images/image1.gif,Nginx 会首先通过用于这个 location,在本地目录中查找这个文件。如果“image1.gif”文件不存在,Nginx 会查找“image1.gif/”目录,即“try.haoda.com/images/image1.gif/”,如果都不存在,会重定向到“/404.html”
2 Nginx try_file配置实例2
#1. 配置nginx
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat try.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name try.haoda.com;
root /code;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ @java; #当$uri和$uri/都匹配不到时,由后端的java来进行处理,名字可自定义,但一定要加@
}
location @java {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.8:8080; #配置后端tomcat
}
}
#2. 配置后端tomcat
[root@web02 ~]# cd /usr/share/tomcat/webapps/ROOT
[root@web02 ROOT]# echo 'i am tomcat' > index.html
[root@web02 ROOT]# systemctl start tomcat
#3. 把文件都挪走
[root@lb01 code]# mv index.html index1.html /tmp/
#4. 测试访问
[root@lb01 code]# curl http://try.haoda.com/index.html
i am tomcatNginx调整上传文件大小
在nginx使用上传文件的过程中,通常需要设置保温大小限制,避免出现413 Request Entity Too Large
nginx上传文件大小限制配置语法
Syntax: client_max_body_size size;
Default: client_max_body_size 1m;
Context: http, server, locationnginx长传文件大小限制配置示例
#也可以放入http层,全局生效
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
client_max_body_size 200m;
}Nginx优雅显示错误页面
error_page错误日志
1 第一种配置情况(跳转网络地址)
#error_page配置的是http这种的网络地址
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat error.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.haoda.com;
root /code;
#error_page 404 http://www.baidu.com;
location / {
index index.html;
error_page 404 http://www.baidu.com;
}
}2 第二种配置情况(跳转本地地址)
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat error.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name error.haoda.com;
root /code;
location / {
index index.html;
}
#error_page 403 404 /404.jpg;
error_page 403 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
root /code;
index index.html;
}
}