机器学习入门:入手sklearn框架+线性回归+案例(基金数据的预测)
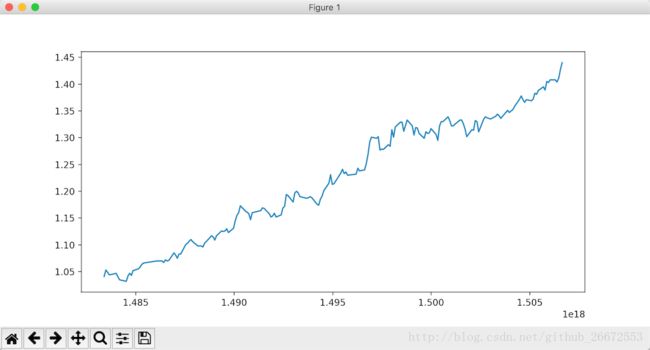
读取基金数据,然后画线
# coding: utf-8
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取csv文件里的基金数据
fund = pd.read_csv("./csv/001112.csv", dtype={"fcode":str})
fund['fdate'] = pd.to_datetime(fund['fdate']) # 把fdate列 转换成pandas里的日期格式
fund = fund.set_index("fdate").sort_index(ascending=False) # 设置fdate列为索引列,然后排序
# 把基金净值增值趋势用matplotlib包画出来
x = fund.loc['2017'].index
y = fund.loc['2017']['NAV']
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()机器学习 ☞ 预测篇
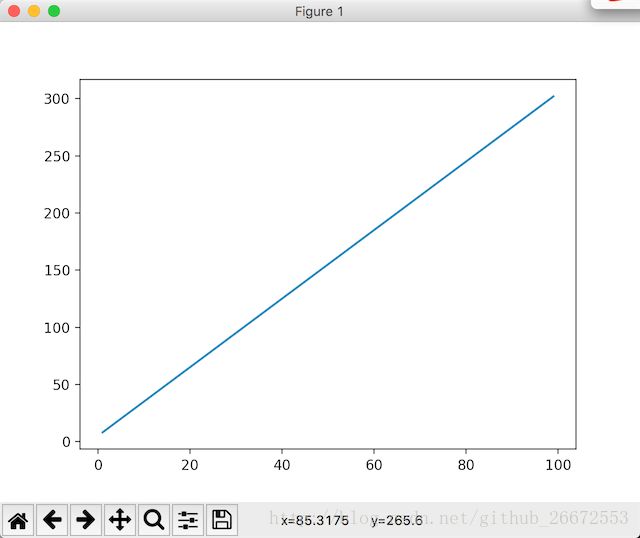
我们先来学习预测算法中最基本的线性回归。
a,b = 3,5 # 随便定义的2个数字
x = np.arange(1,100)
y = a*x + 5
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()可以看出,我们直线的方程是:y = 3x + 5。
在数学中a就是直线的斜率,b就是截距。
超牛的机器学习包:sklearn
官网:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/install.html
这个包,有很多机器学习的算法。如回归、贝叶斯、决策树等。
1、安装
cd到你项目虚拟环境的bin目录下
执行
./python3 -m pip install -U scikit-learn -i http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ --trusted-host mirrors.aliyun.com因为安装这个包比较慢,我们上面使用了阿里云的镜像。
同时还要安装一个包scipy,这是高级科学计算包。
./python3 -m pip install -U scipy2、利用sklearn来完成一元线性回归的测试
API地址:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.linear_model
#引入包
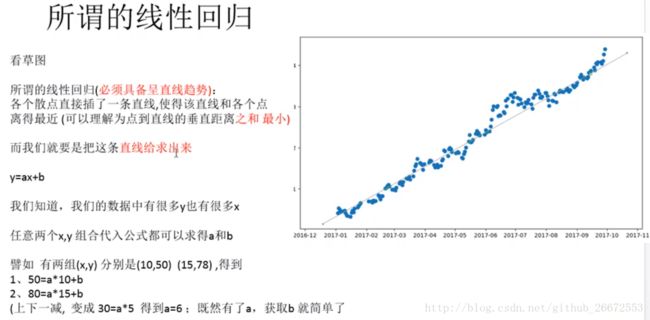
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression“LinearRegression”就是“线性回归”的意思。当我们的数据通过肉眼看 具备了线性条件时,它就能用上了。
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression.html#sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# 读取csv文件里的基金数据
fund = pd.read_csv("./csv/001112.csv", dtype={"fcode":str})
fund['fdate'] = pd.to_datetime(fund['fdate']) # 把fdate列 转换成pandas里的日期格式
fund = fund.set_index("fdate").sort_index(ascending=False) # 设置fdate列为索引列,然后排序
# 把基金净值增值趋势用matplotlib包画出来
x_date = fund.loc['2017'].index
x_int64 = x_date.astype(np.int64) # 把date类型转换成int64类型
y = fund.loc['2017']['NAV']
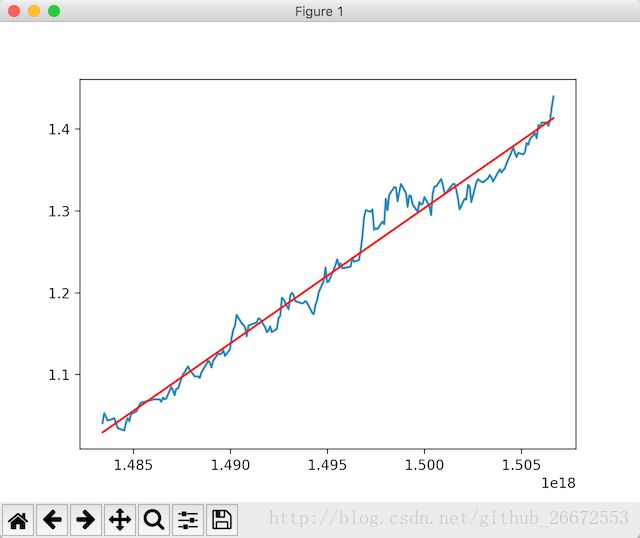
plt.plot(x_date,y) # 画原始数据的线
# 创建线性回归对象
lr = LinearRegression()
x = x_int64.values.reshape(-1,1) # 把日期 变成二维数组的形式
y = y.values.reshape(-1,1) # 同样把Y轴的值 变成二维数组的形式
lr.fit(x,y) # 对x轴和y轴进行修正(训练)
# 把原始的x和y进行fix()后,就可以开始预测
testX = pd.to_datetime(np.array(["2017-09-29","2017-09-30"])).astype(np.int64).values.reshape(-1,1)
newY = lr.predict(testX)
print(newY) # 预测29号 30号的Y轴的值
"""
[[ 1.41340871]
[ 1.41483561]]
"""
# 画出 预测的线
# x轴和原始数据一样
# y轴的值需要经过预测
plt.plot(x_date,lr.predict(x_int64.values.reshape(-1,1)),"red")
# 最后显示出画的线
plt.show()红色的线就是sklearn 预测出来的。
上面代码中的 部分测试代码:
# 把原始的x和y进行fix()后,就可以开始预测
testX = pd.to_datetime(np.array(["2017-09-29","2017-09-30"])).astype(np.int64).values.reshape(-1,1)
newY = lr.predict(testX)
print(newY) # 预测29号 30号的Y轴的值
"""
[[ 1.41340871]
[ 1.41483561]]
"""这部分代码只是为了演示LinearRegression 是预测能力。